
About
For Teachers
- elastic different mass 2.mp4
- Conservation of momentum_ws_video_student.docx
Credits
Author: Leong Tze Kwang, Lim Beng Choo
Document Brief: Title: "Tracker 1/5 Elastic Collision with Different Masses by Leongster"
This document analyzes a 1/5 elastic collision scenario where two objects of different masses interact. The focus is on the principles of momentum conservation, energy transfer, and the characteristics of partially elastic collisions.
Study Guide:
Objective: Investigate the dynamics of a 1/5 elastic collision involving objects of unequal masses, examining momentum conservation and the coefficient of restitution.
Key Concepts:
-
Elastic Collisions:
-
Collisions where some kinetic energy is conserved, characterized by the coefficient of restitution . For a 1/5 elastic collision, .
-
-
Conservation of Momentum:
-
The total momentum before and after the collision remains constant: .
-
-
Energy Transfer:
-
A portion of the kinetic energy is converted to other forms, such as heat or deformation.
-
-
Coefficient of Restitution (e):
-
Defined as , where represents velocity, and subscripts and denote initial and final states, respectively.
-
Experiment Overview:
-
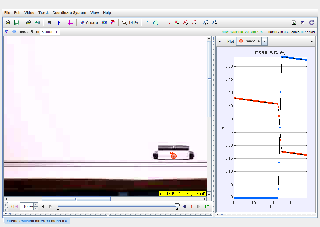
Setup: Two objects of differing masses are allowed to collide on a frictionless surface. The motion is tracked using video analysis tools like Tracker.
-
Procedure:
-
Record initial and final velocities of both objects.
-
Calculate momentum before and after collision to verify conservation.
-
Compute the coefficient of restitution and analyze the energy loss.
-
-
Observation Points:
-
Change in velocity of each mass.
-
Percentage of kinetic energy conserved.
-
Questions to Consider:
-
What determines the post-collision velocities of the two objects?
-
Answer: The relative masses, initial velocities, and the coefficient of restitution .
-
-
How is momentum conservation verified?
-
Answer: By showing that the sum of momenta before the collision equals the sum after the collision.
-
-
What factors influence the amount of energy lost?
-
Answer: The coefficient of restitution and material properties of the colliding objects.
-
Applications:
-
Understanding real-world collisions, such as vehicle impacts.
-
Designing materials and systems to manage energy dissipation.
-
Teaching momentum and energy principles in physics.
FAQ:
-
What is a 1/5 elastic collision? A collision where the coefficient of restitution is 0.2, indicating partial elasticity and significant energy loss.
-
Why use objects of different masses? This setup highlights the effect of mass disparity on velocity changes and energy transfer.
-
How is energy loss calculated? By comparing the total kinetic energy before and after the collision: .
-
What does the coefficient of restitution signify? It measures the elasticity of the collision, with 1 being perfectly elastic and 0 being perfectly inelastic.
-
Can this model be applied to real-world scenarios? Yes, it helps in understanding collisions in sports, vehicle safety, and material testing.
- Details
- Written by leongster
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 02 Dynamics
- Hits: 4055
