Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits




 This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.; Francisco Esquembre; Felix J. Garcia Clemente; Rena F; Zed
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.; Francisco Esquembre; Felix J. Garcia Clemente; Rena F; Zed
2. Source Overview:
- Source 1: "Changes of a Electromagnet's Polarity"
- This excerpt appears to be the title page or introductory information for a resource, likely a simulation or interactive tool.
- It lists the authors: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it., Francisco Esquembre, Felix J. Garcia Clemente, Rena F, Zed.
- It indicates a copyright year of 2020 and compilation using EJS 6.1 BETA (200414).
- It mentions release under a license (the specific license is not detailed in this excerpt).
- Source 2: "Changes of an Electromagnet's Polarity simulation Primary School HTML5 Applet Javascript - Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore | Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore"
- This excerpt is from the "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore" website.
- It explicitly identifies the resource as a "simulation Primary School HTML5 Applet Javascript."
- It is categorized under "Primary," "Physics," "Electricity and Magnetism," and "Electromagnetism," suggesting its target audience and subject matter.
- It credits Siti and Coco, implying their involvement in the development or context of the simulation.
- It provides an embed code for integrating the simulation into a webpage: <iframe width="100%" height="100%" src="https://iwant2study.org/lookangejss/05electricitynmagnetism_21electromagnetism/ejss_model_Magnets/_Magnets_Simulation.xhtml " frameborder="0"></iframe>.
- It lists credits including the email address This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it., Francisco Esquembre, Felix J. Garcia Clemente, Rena F, and Zed, aligning with the authorship of Source 1.
- It provides "Sample Learning Goals" and "For Teachers" sections with direct links to initial setup, switching the magnet side and object, and demonstrations of "Like poles repel" and the magnet remaining stationary when too far. This suggests specific interactive elements and learning objectives of the simulation. For example, under "For Teachers," it states:
- "Switch magnet side https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970Direct link"
- "Like poles repel https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970Direct link"
- It includes a link to a YouTube video titled "Changes of an Electromagnet polarity Virtual Lab for Primary School Science."
- It is part of a larger collection of Open Educational Resources, as indicated by the website name and the extensive list of other simulations and resources available on the platform. This list covers a wide range of science and mathematics topics, suggesting a comprehensive initiative for interactive learning tools.
- The platform operates under a "Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License" for its content, while commercial use of the "EasyJavaScriptSimulations Library" requires a separate license.
3. Main Themes and Important Ideas/Facts:
- Focus on Primary School Physics: The simulation is explicitly designed for primary school students, focusing on the fundamental concepts of electromagnetism, specifically the change of an electromagnet's polarity.
- Interactive Learning through Simulation: The core of the resource is an HTML5 applet built with Javascript, offering an interactive and visual way for students to explore how an electromagnet's polarity can be changed. The availability of an embed code highlights its usability in online learning environments.
- Open Educational Resource: The simulation is part of the "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore" initiative, emphasizing its free accessibility and potential for adaptation and sharing under the Creative Commons license.
- Clear Learning Goals and Teacher Support: The inclusion of "Sample Learning Goals" (though the specific text is "[texthttps://iwant2study.org/lookangejss/05electricitynmagnetism_21electromagnetism/ejss_model_Magnets/_Magnets_Simulation.xhtml " frameborder="0"></iframe> - This is the direct code for embedding the simulation, highlighting its practical implementation.
- Source 2 (under Sample Learning Goals): "[texthttps://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970Direct link", "Like poles repel https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970Direct link" - These links suggest key interactive features and learning outcomes related to electromagnet polarity and magnetic interactions.
- Source 2: "Contents are licensed Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License" - This clarifies the open licensing terms for the educational content.
5. Implications and Potential Use:
- This simulation provides a valuable tool for primary school educators to teach the concept of electromagnet polarity changes in an engaging and interactive manner.
- The HTML5 format ensures accessibility across various devices without the need for specific plugins.
- The availability of learning goals and teacher resources facilitates the integration of the simulation into lesson plans.
- The open-source nature allows for potential adaptation and customization by educators or developers.
- The connection to a broader platform of OER and related video resources enriches the learning experience and provides opportunities for exploring related scientific concepts.
6. Further Information Needed:
- The specific content and functionality of the simulation itself. Accessing the embed link would provide a clearer understanding of the interactive elements and how polarity changes are demonstrated.
- The detailed "Sample Learning Goals" for the simulation.
- The content provided through the "For Teachers" direct links.
- The specific license under which "Changes of a Electromagnet's Polarity" (Source 1) is released.
This briefing document provides a foundational understanding of the resources related to the "Changes of an Electromagnet's Polarity" simulation. Further exploration of the provided links and the simulation itself would offer a more comprehensive view of its educational value.
Study Guide: Understanding Electromagnet Polarity
Key Concepts
- Electromagnetism: The interaction between electric currents and magnetic fields. An electric current creates a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field can induce an electric current.
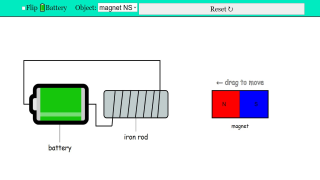
- Electromagnet: A type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. It typically consists of a coil of wire wound around a ferromagnetic core (like iron). The magnetic field exists only when the current is flowing.
- Magnetic Poles: Regions at the ends of a magnet where the magnetic field is strongest. Magnets have a north-seeking pole (North pole) and a south-seeking pole (South pole).
- Polarity of a Magnet: Refers to which end of the magnet is the North pole and which end is the South pole.
- Factors Affecting Electromagnet Polarity:Direction of Current: The direction in which the electric current flows through the coil of wire determines the polarity of the electromagnet. Reversing the direction of the current reverses the magnetic poles.
- Winding Direction of the Coil: The way the wire is wound around the core (clockwise or counterclockwise) also influences the electromagnet's polarity for a given current direction.
- Right-Hand Rule (for Solenoids): A helpful mnemonic for determining the polarity of an electromagnet. If you curl the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the current flow in the coil, your thumb will point in the direction of the North pole of the electromagnet.
- Simulation: A computer-based model that allows users to interact with and observe a system or phenomenon, such as how changing current affects an electromagnet's polarity.
- Open Educational Resources (OER): Teaching, learning, and research materials that are freely available for use, adaptation, and sharing.
Quiz
Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
- What is the fundamental principle behind electromagnetism, and how does it relate to the creation of an electromagnet?
- Describe the basic construction of an electromagnet. What are its key components?
- What does the polarity of an electromagnet refer to? Why is understanding its polarity important?
- Identify the two primary factors that determine the polarity of an electromagnet.
- Explain how reversing the direction of the electric current in an electromagnet's coil affects its magnetic poles.
- How does the winding direction of the wire coil influence the polarity of an electromagnet, assuming the current direction remains the same?
- Describe the Right-Hand Rule for solenoids. How can it be used to determine the North pole of an electromagnet?
- According to the provided sources, what type of educational resource is the "Changes of an Electromagnet's Polarity simulation"? What does this imply about its accessibility and use?
- Based on the breadcrumbs provided, in which subject area and topic would you typically find the study of electromagnet polarity?
- Briefly describe one potential learning goal that a teacher might have when using a simulation focused on changes in electromagnet polarity with primary school students.
Answer Key
- Electromagnetism is the interaction between electric currents and magnetic fields. In an electromagnet, an electric current flowing through a coil of wire creates a magnetic field, effectively turning the coil into a magnet.
- An electromagnet typically consists of a coil of insulated wire (often called a solenoid) wound around a ferromagnetic core, such as iron. When an electric current passes through the wire, the core becomes magnetized, enhancing the magnetic field.
- The polarity of an electromagnet refers to which end of the magnet acts as the North-seeking pole and which end acts as the South-seeking pole. Understanding the polarity is crucial for predicting how the electromagnet will interact with other magnetic materials or magnetic fields (attraction or repulsion).
- The two primary factors that determine the polarity of an electromagnet are the direction of the electric current flowing through the coil and the winding direction (clockwise or counterclockwise) of the coil around the core.
- Reversing the direction of the electric current flowing through the coil of an electromagnet causes its magnetic poles to reverse. The end that was previously the North pole will become the South pole, and vice versa.
- If the winding direction of the wire coil around the core is changed (e.g., from clockwise to counterclockwise) while the direction of the current remains the same, the polarity of the resulting electromagnet will be reversed.
- The Right-Hand Rule for solenoids states that if you curl the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the current flow through the loops of the coil, your extended thumb will point in the direction of the North magnetic pole of the electromagnet.
- The "Changes of an Electromagnet's Polarity simulation" is identified as an Open Educational Resource (OER). This means it is freely available for educators and students to use, and potentially adapt and share, for learning about electromagnetism.
- Based on the breadcrumbs "Primary > Physics > Electricity and Magnetism > Electromagnetism," the study of electromagnet polarity would typically be found within the subject area of Physics, under the broader topic of Electricity and Magnetism, and more specifically within Electromagnetism.
- A potential learning goal for primary school students using this simulation could be to understand that changing the way electricity flows through a wire wrapped around a nail can make the nail's ends attract or push away other magnets, demonstrating the relationship between electricity and magnetism.
Essay Format Questions
- Discuss the relationship between electric current and magnetic fields. Explain how this relationship is utilized in the creation and manipulation of an electromagnet's polarity.
- Describe the factors that influence the strength and polarity of an electromagnet. Focus specifically on how the direction of current and the winding of the coil contribute to these properties.
- Explain the practical applications of electromagnets in everyday life and in various technologies. How does the ability to control their polarity make them useful in these applications?
- Consider the use of simulations, such as the one mentioned in the source, as a tool for teaching scientific concepts like electromagnet polarity. What are the potential benefits and limitations of using such resources in a primary school setting?
- Based on the provided information, discuss the role of open educational resources in science education. How does the availability of resources like the electromagnet polarity simulation contribute to learning and teaching?
Glossary of Key Terms
- Ampere (A): The SI unit of electric current, measuring the rate of flow of electric charge.
- Ferromagnetic Material: A material, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, that can be strongly magnetized by an external magnetic field and can retain some magnetism after the field is removed.
- Magnetic Field: A region around a magnet or a current-carrying wire where a magnetic force can be detected. Magnetic field lines are used to represent the direction and strength of the field.
- Solenoid: A coil of wire wound into a tightly packed helix. When an electric current flows through it, it creates a magnetic field similar to that of a bar magnet.
- Volt (V): The SI unit of electric potential difference or voltage, representing the electric potential energy per unit charge.
- Ohm (Ω): The SI unit of electrical resistance, measuring the opposition to the flow of electric current.
- Direct Current (DC): An electric current that flows in one direction only.
- Alternating Current (AC): An electric current that periodically reverses direction. While not explicitly mentioned in the context of polarity change, it's a fundamental concept in electricity.
- Permeability: A measure of a material's ability to support the formation of magnetic fields within it. Ferromagnetic materials have high permeability.
- Induced Current: An electric current created in a conductor by a changing magnetic field (related to Faraday's law of induction, a broader concept related to electromagnetism).
Sample Learning Goals
[text]
For Teachers
Initial setup https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970 Direct link |
Switch magnet sidehttps://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970 Direct link |
Switch objecthttps://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970 Direct link |
Like poles repelhttps://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970 Direct link |
Magnet remains stationary when it is too farhttps://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970 Direct link |
Research
[text]
Video
Version:
Other Resources
[text]
Frequently Asked Questions: Changes of an Electromagnet's Polarity
1. What is the purpose of the "Changes of an Electromagnet's Polarity" simulation?
The primary purpose of this simulation is to provide a visual and interactive tool for primary school students (and potentially others) to understand how the polarity of an electromagnet can be changed. It allows users to explore the relationship between the direction of electric current and the resulting magnetic poles of an electromagnet.
2. Who created this simulation and what is its licensing?
This simulation was compiled with EJS 6.1 BETA and is credited to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it., Francisco Esquembre, Felix J. Garcia Clemente, Rena F, and Zed. It is released under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License for non-commercial use. For commercial use of the underlying EasyJavaScriptSimulations Library, specific terms apply as outlined on the EjsWiki and require direct contact with This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..
3. For what educational level is this simulation primarily designed?
The description explicitly states that this is a "Primary School HTML5 Applet," indicating that it is intended for students at the primary school level. The inclusion under "Primary" and "Electricity and Magnetism" within the breadcrumbs further supports this.
4. How can this simulation be accessed and embedded?
The simulation can be accessed and run via the provided iframe embed code: <iframe width="100%" height="100%" src="https://iwant2study.org/lookangejss/05electricitynmagnetism_21electromagnetism/ejss_model_Magnets/_Magnets_Simulation.xhtml " frameborder="0"></iframe>. This code allows the simulation to be directly embedded into webpages. Direct links for initial setup and specific functionalities are also provided.
5. What are some example learning goals associated with this simulation?
While the exact text of the learning goals isn't provided in the excerpts, the "For Teachers" section gives hints. The provided direct links suggest learning about switching the magnet side and object, and understanding the principle that "like poles repel." Another link suggests exploring when a magnet remains stationary due to distance.
6. Are there any additional resources, such as videos, related to this simulation?
Yes, a YouTube link version of a "Changes of an Electromagnet polarity Virtual Lab for Primary School Science" is provided: https://weelookang.blogspot.com/2020/06/changes-of-electromagnets-polarity.html. This suggests a video demonstration or explanation accompanies the simulation.
7. What other types of educational resources are developed and shared by "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore"?
The extensive list of items following the "end faq" marker demonstrates a wide range of interactive simulations and resources covering various subjects beyond electromagnetism, including physics, mathematics, chemistry, and even language-based games. These resources utilize HTML5 Applet Javascript and often focus on primary and secondary school levels. The platform is involved in various initiatives like the SLS Hackathon, promoting the use of open-source tools in education.
8. Where can teachers find initial setup instructions and direct links for specific functionalities within the simulation?
A "For Teachers" section provides direct links for initial setup (https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970Direct link), switching the magnet side (https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970Direct link), switching the object (https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970Direct link), understanding "like poles repel" (https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970Direct link), and observing when a magnet remains stationary due to distance (https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/970Direct link).
- Details
- Written by Coco Lee
- Parent Category: 02 Static Electricity
- Category: 01 Electromagnetism
- Hits: 8720