Breadcrumbs
06 Modern Physics
Modern Physics. This final section interrogates the structure of atoms – peering past their vast electronic shells into their central cores, the incredibly dense nuclear regions. In that secret heart of atoms, the electrical repulsion of like charges is overwhelmed by mysterious nuclear forces, which act as an invisible hand causing random and spontaneous disintegration for radioactive substances. Conservation laws also guide the analysis of nuclear reactions such as fusion and fission, which humanity has exploited in times of peace but also in times of war. In H2 Physics, learners catch glimpses into a paradigm shift that famously rocked the foundations of physics – the quantum revolution. Waves are particle-like particles are wave-like; nature at its smallest scales does not behave in accordance with a deterministic classical clockwork conception, requiring a new framework to harmonise both particle-like and wave-like properties into a coherent theory expressed in terms of probability, complex numbers, and linear algebra. In H3 Physics, learners are challenged with yet another paradigm shift – the theory of relativity that questioned accepted wisdom about the absolute nature of space and time. Space and time do not exist independently of each other, and the relative motion of observers distorts their assignments of space and time coordinates. Simultaneity is not as obvious as we naïvely expect because of the universal limiting speed of light.
1. Symmetry 2.Integrability 3. Duality 4. Enormous advances in physics and some of these advances have brought into question, or have directly contradicted, certain theories that call for new knowledge to be created
- QUVIS: https://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/physics/quvis/
- PhET: http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/category/physics/quantum-phenomena
- Physlet Quantum Physics: http://www.compadre.org/pqp/
- Quantum Lab: http://www.didaktik.physik.uni-erlangen.de/quantumlab/english/index.html .
- Spins Physics: http://www.physics.orst.edu/~mcintyre/ph425/spins/index_SPINS_OSP.html, http://www.compadre.org/osp/items/detail.cfm?ID=7329
- Falstad Quantum: http://www.falstad.com/mathphysics.html .
- Quantum Mechanics: http://www.embd.be/quantummechanics/default.html
- Excited States and Photons: http://concord.org/stem-resources/excited-states-and-photons
- “Quantum Made Simple”, http://toutestquantique.fr/en/
- Open Source Physics Quantum Magnetism simulation, http://www.compadre.org/osp/items/detail.cfm?ID=12308.
- https://www.hbarra.es/ Jose Ignacio Fernández Palo
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 1054
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 1221
- Details
- Written by Fremont
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 7287
Read more: Bound Eigenstate Superposition JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Fremont
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 9726
Read more: ⏳Light Cone Simulator JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Wei Chiong
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 7630
Read more: Free Particle Wavepacket JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Fremont
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 9472
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 6553
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 6084
- Details
- Written by Wei Chiong
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 57236
Read more: Millikan Oil Drop Experiment JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Wei Chiong
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 2988
- Details
- Written by Wei Chiong
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 60413
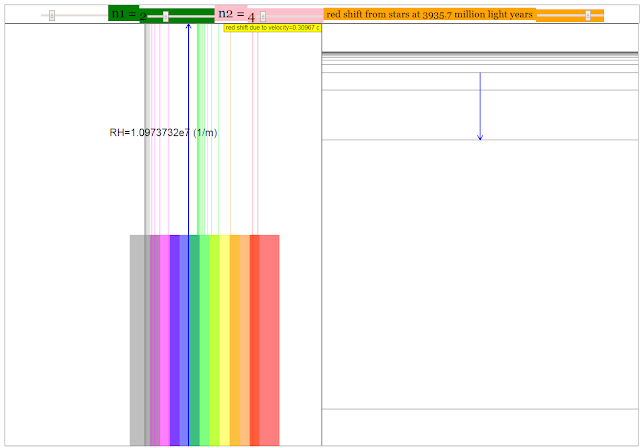
Read more: Atomic Spectra of Hydrogen and Redshift JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Fremont
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 13920
Read more: Michelson Interferometer JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Fremont
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 6015
Read more: ⚛️SLS Bohr's Theory of the Hydrogen Atom JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Fremont
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 20276
Read more: ⚛️Bohr's Theory of the Hydrogen Atom JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 7232
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 20297
Read more: Wave Particle Duality JavaScript HTML5 Applet Simulation Model
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 8859
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 11363
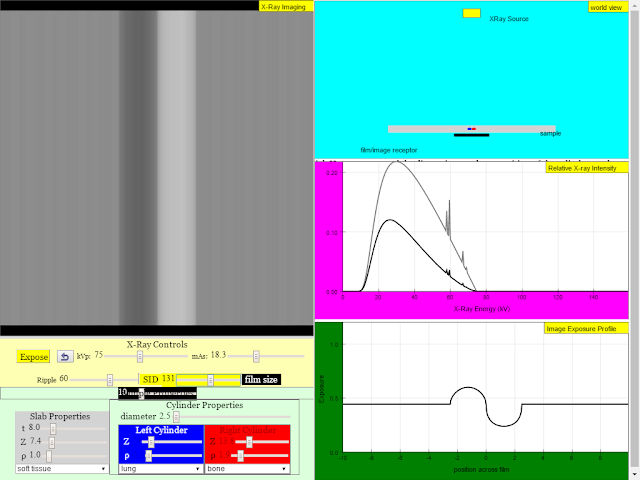
Read more: X-Ray Imaging Physics JavaScript HTML5 Applet Simulation Model by Michael R. Gallis
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 16453
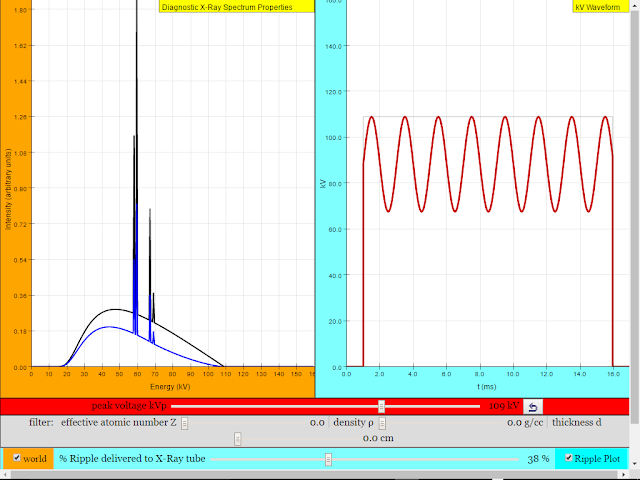
Read more: X-Ray Spectrum JavaScript HTML5 Applet Simulation Model by Michael R. Gallis
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Physics
- Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Hits: 47929
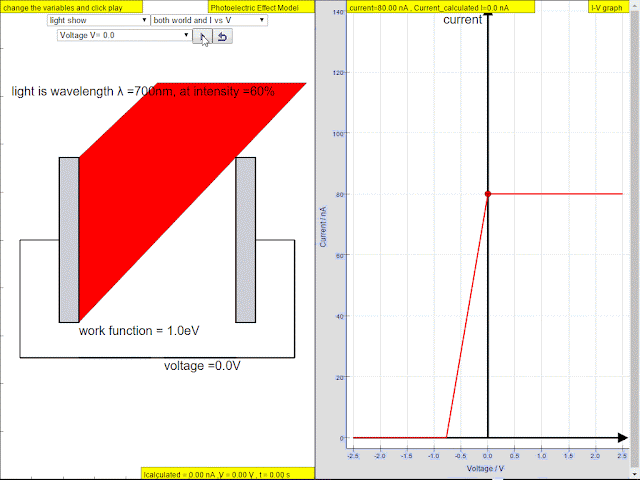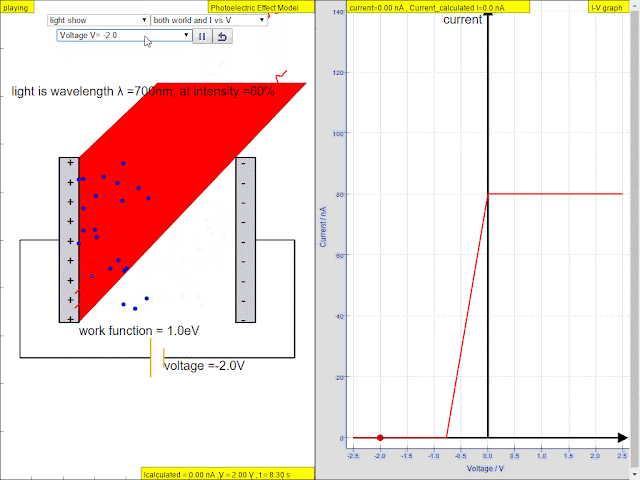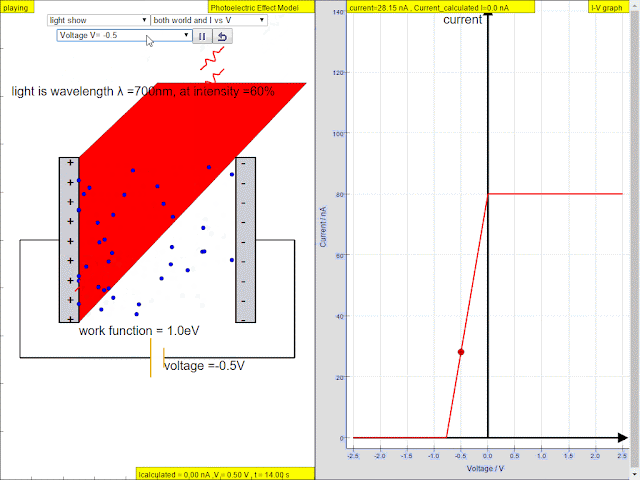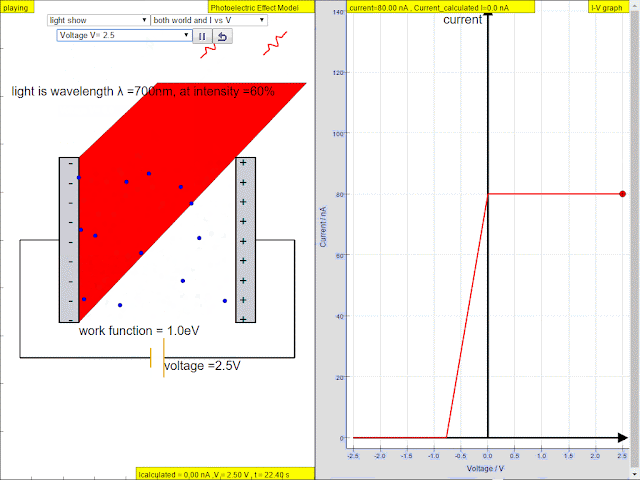
Read more: ⚛️Photoelectric Effect JavaScript HTML5 Applet Simulation Model
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 01 Quantum Physics
- Hits: 3612
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 11173
- Details
- Written by Fremont
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 17557
Read more: Bragg's Law Simulator (for n=1) JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Fremont
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 6973
Read more: ⚛️Nuclear Binary System Simulator JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 7424
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 22222
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 11267
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 15340
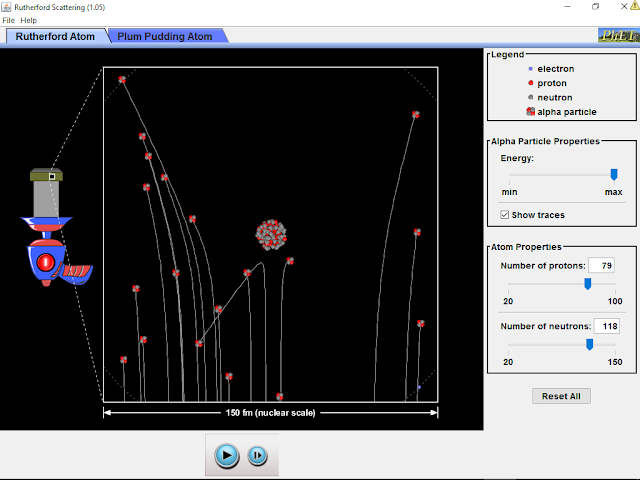
Read more: ⚛️Three State Radioactive Decay JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5 by Fu-Kwun Hwang
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 8477
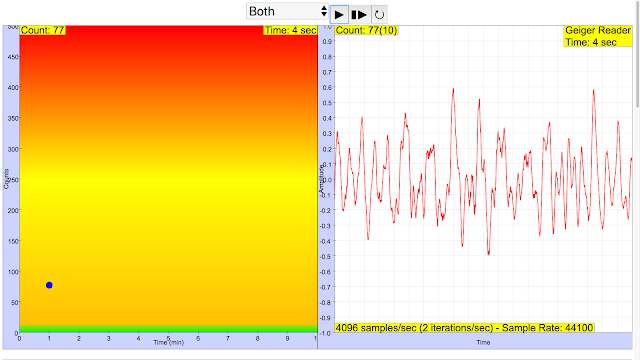
Read more: ☢️Geiger Reader App JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 16197
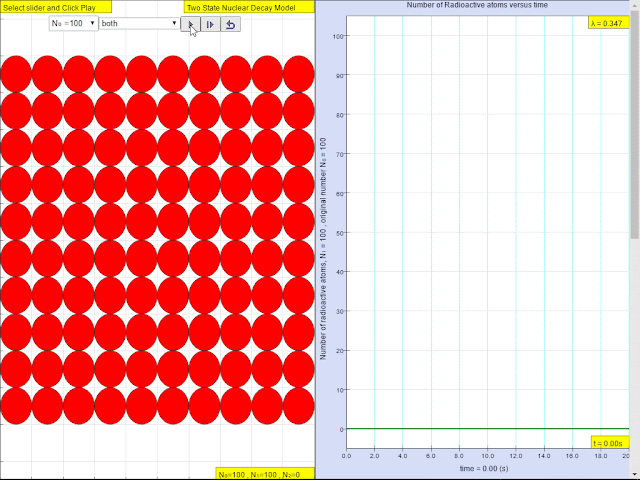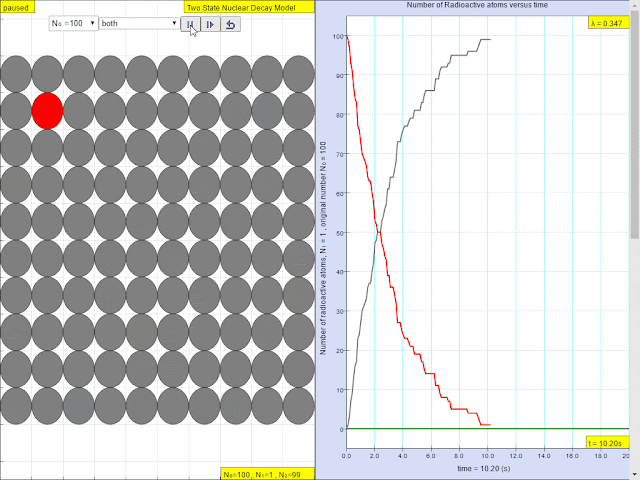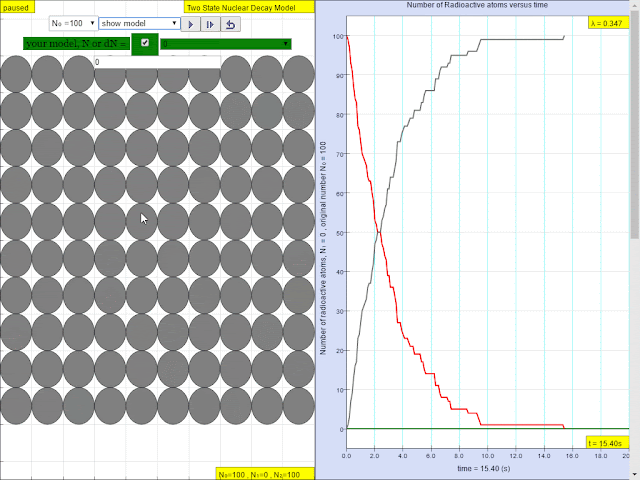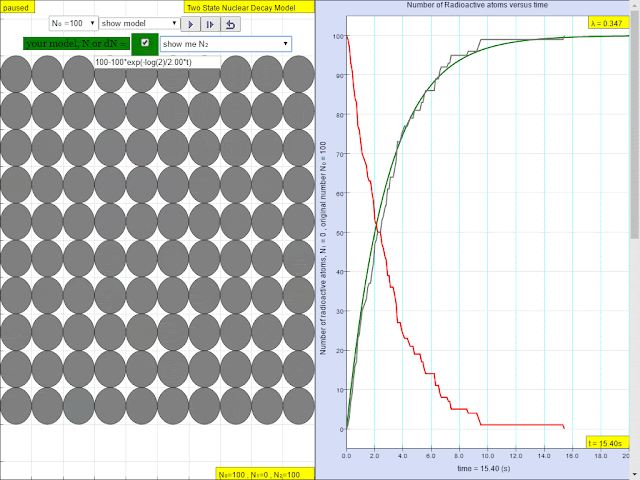
Read more: ⚛️Two State Radioactive Decay JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5 by Fu-Kwun Hwang
- Details
- Written by leongster
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 10239
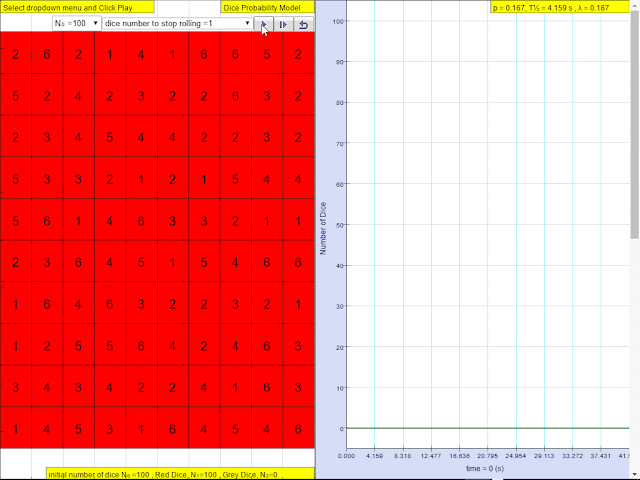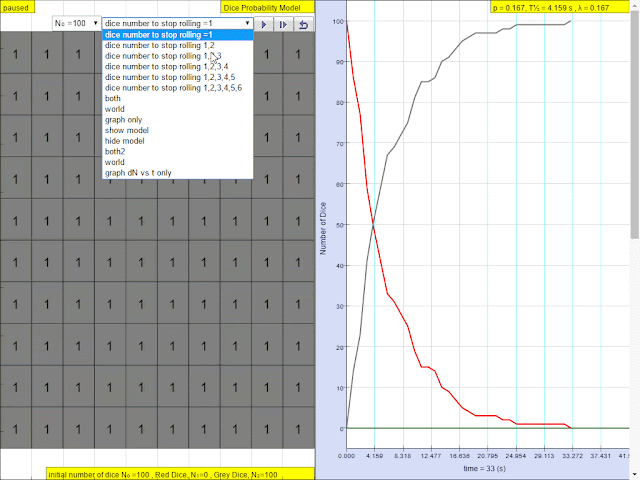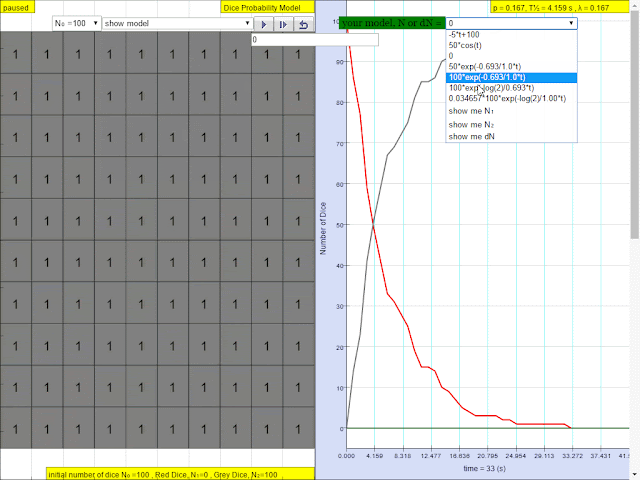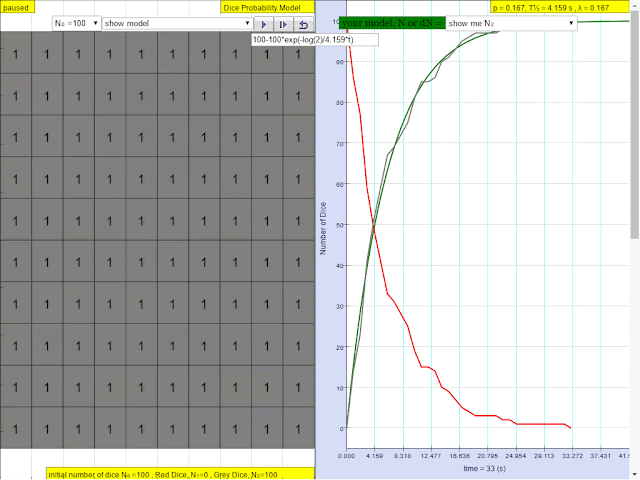
Read more: Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5 by Fu-Kwun Hwang & Leong Tze Kwang
- Details
- Written by leongster
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 4894
Read more: SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 12018
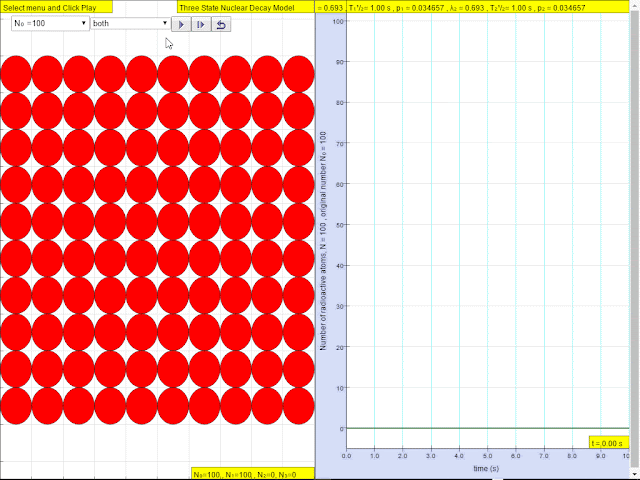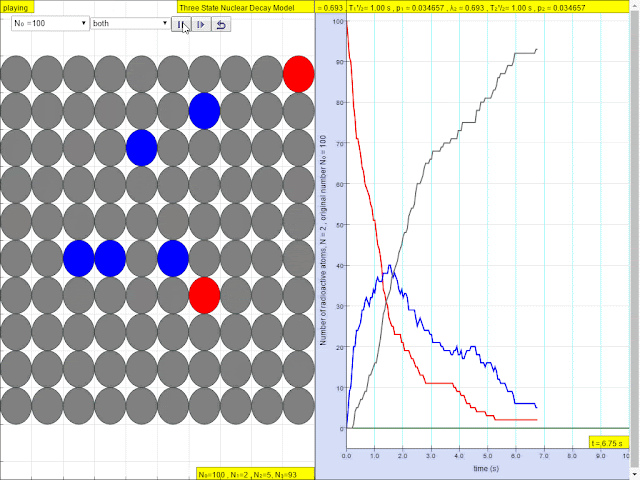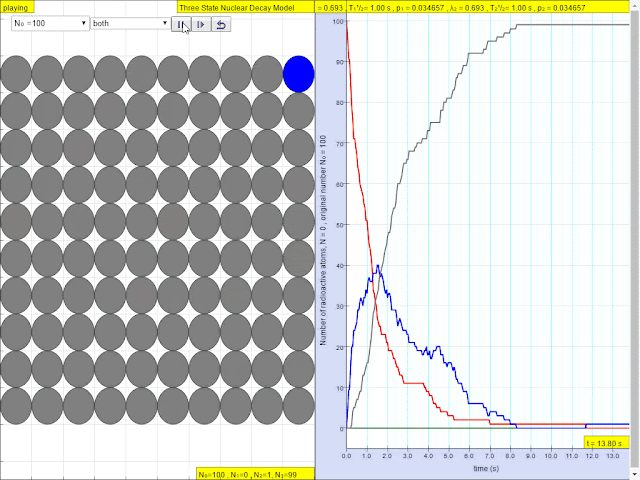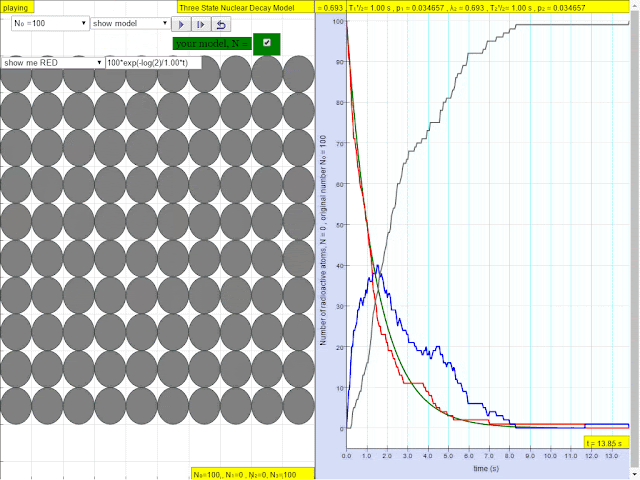
Read more: ⚛️Three State Nuclear Decay JavaScript Model by Wolfgang Christian
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 03 Special Relativity
- Hits: 9654
Read more: Exploring Hydrogen Atom Probability Densities in 3D with JavaScript and EJSS
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 03 Special Relativity
- Hits: 6595
- Details
- Written by Wei Chiong
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 04 Laser and Semi-conductors
- Hits: 18935
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 04 Laser and Semi-conductors
- Hits: 9494
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 04 Laser and Semi-conductors
- Hits: 9057
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 04 Laser and Semi-conductors
- Hits: 9293
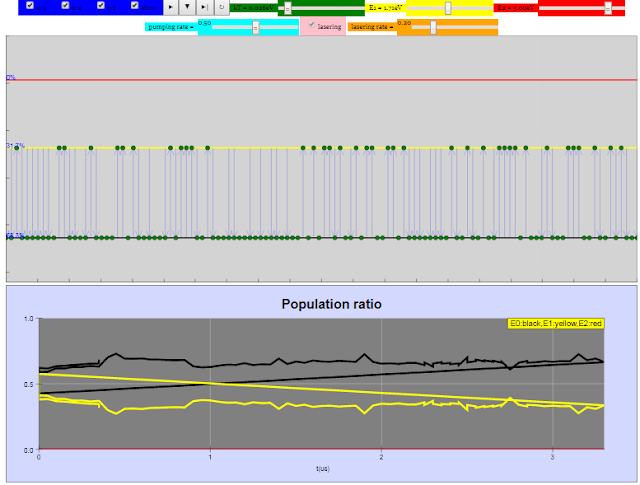
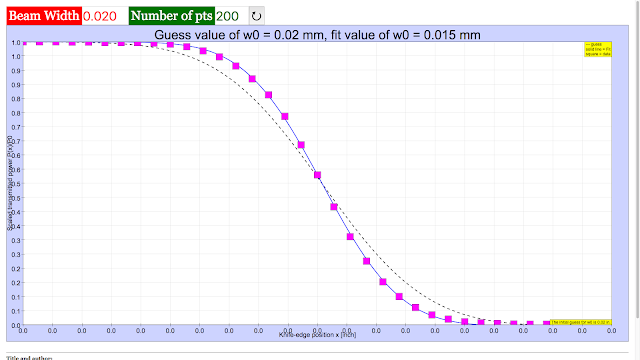
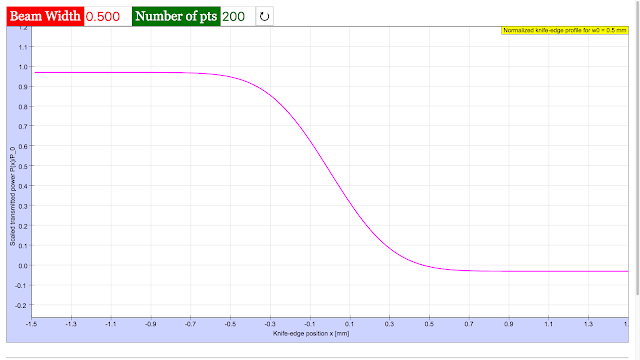
Read more: PICUP Laser Beam Profile EXERCISE 3: THE KNIFE-EDGE PROFILE
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 04 Laser and Semi-conductors
- Hits: 9446
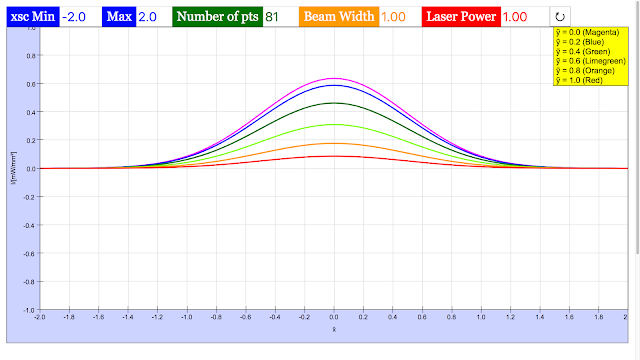
Read more: 🔦PICUP Laser Beam Profile EXERCISE 2: THE TEM00 MODE: A CONTOUR PLOT