About
Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits


 Fu-Kwun Hwang - Dept. of Physics, National Taiwan Normal Univ.; lookang; leongster
Fu-Kwun Hwang - Dept. of Physics, National Taiwan Normal Univ.; lookang; leongster
Core Concept: Dice Rolling as a Model for Random Processes
The underlying theme connecting these sources is the use of a simple dice rolling process as a model to illustrate more complex random phenomena. While the first source ("Dice Rolling Model") is brief and lacks specific details, its title suggests a focus on the probabilistic nature of dice rolls and potentially its applications in modeling.
2. "SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5": A Concrete Example
The second, more extensive source details a specific JavaScript simulation applet titled "SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5." This resource leverages the familiar concept of dice throwing to model a particular random process: radioactive decay.
2.1. Authorship and Licensing:
- The applet is designed by Fu-Kwun Hwang (Dept. of Physics, National Taiwan Normal Univ.).
- Additional contributors include lookang and leongster.
- It is released under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License, indicating it is open educational resource that can be shared and adapted with attribution.
2.2. Purpose and Functionality:
- The primary purpose of this simulation is to visualize and understand the process of radioactive decay.
- It achieves this by drawing an analogy between individual radioactive nuclei decaying and individual "boxes" (representing nuclei) changing color (to RED) as they "decay."
- The user can set the probability for a nucleus to decay and observe how the number of decayed nuclei increases over time. This directly links the probability of a single event (a die roll resulting in a "decay" outcome) to the macroscopic behavior of a system (the overall decay rate).
2.3. Theoretical Basis:
The "Theory" section explicitly connects the dice rolling analogy to the mathematical model of radioactive decay:
- It assumes that each radioactive nucleus has an independent probability p of decaying within a given time.
- This leads to the differential equation: dN(t)/dt = -p*N(t), where N(t) is the number of undecayed nuclei at time t. This equation describes the rate of change of undecayed nuclei being proportional to the number of undecayed nuclei present.
- The solution to this differential equation is given as: N(t) = N0 e^(-pt) = N0 e^(-(ln2/T0.5)t), where N0 is the initial number of nuclei and T0.5 is the half-life. This equation describes the exponential decay of radioactive material.
Quote: "Each nucleus has the same probability p (p<1) decayed into daughter product. It means that dN(t)/dt= -p*N(t) , where dN(t) is the number of nucleus decayed into daughter product at time t."
Quote: "The solution is N(t)=N0 e -pt = N 0 e -(ln2/T0.5)) t where N(0) is total number of nucleus at time t."
2.4. Technical Implementation:
- The applet is developed using EasyJavaScriptSimulation (EJS) and is in HTML5 format.
- This makes it accessible across various platforms, including desktops, laptops, Chromebooks, and mobile devices (Android/iOS).
- The source code is available ("Code" link), promoting transparency and allowing for modifications and further development.
- The applet can be embedded into webpages using an <iframe> tag, making it easily integratable into online learning resources.
2.5. Connections to Other Resources:
The source provides links to related resources, including:
- The developer's blog post about the JavaScript version.
- The original Java version of the model.
- A similar Java version by Wolfgang Christian on the Open Source Physics platform.
These links indicate a history and community around this type of simulation, suggesting its value in physics education.
2.6. Broader Context and Related Simulations:
The extensive list of other simulation applets available on the platform highlights a broader effort to create interactive, web-based tools for teaching various science and mathematics concepts. The topics range from nuclear physics and electromagnetism to mechanics, waves, and even mathematical concepts like calculus and fractals. The inclusion of "Games" suggests an element of gamification in some of these learning tools.
3. Key Takeaways and Potential Applications:
- Analogical Learning: The dice rolling analogy provides an intuitive way for students to grasp the probabilistic nature of random processes like radioactive decay.
- Visualisation of Abstract Concepts: The simulation visually demonstrates how individual random events at the microscopic level lead to a predictable macroscopic behavior (exponential decay).
- Interactive Learning: The ability to set the decay probability and observe the simulation in real-time promotes active engagement and experimentation.
- Accessibility and Flexibility: Being HTML5-based, the applet is widely accessible and can be easily integrated into online learning platforms.
- Open Educational Resource: The Creative Commons license encourages the use, adaptation, and sharing of this resource within the educational community.
4. Further Considerations:
- The "Dice Rolling Model" excerpt itself is too brief to provide significant information. Understanding its specific focus would require further context.
- While the radioactive decay model is well-explained, the direct mapping between a die roll outcome and a nucleus decaying might need careful explanation to avoid misconceptions about the continuous nature of time in radioactive decay.
In conclusion, the "SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5" is a valuable open educational resource that effectively utilizes the familiar concept of chance (represented by dice) to model the probabilistic nature of radioactive decay. Its interactive and visual nature, combined with its accessibility and open licensing, makes it a potentially powerful tool for physics education.
Dice Rolling Model and Radioactive Decay Simulation Study Guide
Key Concepts
- Dice Rolling Model: This model uses the familiar process of rolling dice to illustrate probabilistic events. Each face of a die represents a possible outcome with an equal probability (for a fair die). Multiple dice rolls can be used to simulate more complex probability distributions.
- Radioactive Decay: A process where unstable atomic nuclei spontaneously lose energy by emitting radiation (particles or electromagnetic waves). This decay results in the transformation of one nuclide into another, often of a different element.
- Probability (p): The likelihood of a specific event occurring. In the context of radioactive decay, 'p' represents the probability of a single nucleus decaying within a given time interval. It is always a value between 0 and 1.
- Number of Radioactive Nuclei (N(t)): The quantity of undecayed radioactive atoms present at a specific time 't'.
- Decay Rate (dN(t)/dt): The rate at which radioactive nuclei decay over time. It is proportional to the number of radioactive nuclei present and the probability of decay, expressed as dN(t)/dt = -p*N(t). The negative sign indicates a decrease in the number of undecayed nuclei.
- Exponential Decay: The mathematical relationship describing the decrease in the number of radioactive nuclei over time. The equation is N(t) = N₀ * e^(-pt), where N₀ is the initial number of nuclei at time t=0, 'e' is the base of the natural logarithm, 'p' is the decay probability, and 't' is time.
- Half-life (T₀.₅): The time required for half of the radioactive nuclei in a sample to decay. It is related to the decay probability 'p' by the equation T₀.₅ = ln(2) / p, which can be rearranged to p = ln(2) / T₀.₅. The exponential decay equation can also be expressed in terms of half-life: N(t) = N₀ * e^(-(ln2/T₀.₅)t).
- Simulation Applet: An interactive computer program, in this case built with JavaScript (EasyJavaScriptSimulation), that models a real-world process (like dice rolling or radioactive decay). Users can often manipulate parameters within the applet to observe the effects on the simulation.
- Open Educational Resources (OER): Teaching, learning, and research materials that are freely available for use, adaptation, and sharing. The SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5 is identified as an OER.
- Open Source Physics (OSP): An initiative focused on creating and disseminating computational tools and resources for physics education, often involving simulations like the one described.
Quiz
- Explain the connection between the dice rolling model and the concept of probability in radioactive decay. Provide an example of how a die roll could represent a decay event.
- What does the term "dN(t)/dt" represent in the context of radioactive decay, and what does the negative sign in the equation dN(t)/dt = -p*N(t) signify?
- Describe the meaning of 'N₀' and 'N(t)' in the exponential decay equation N(t) = N₀ * e^(-pt). How does the number of undecayed nuclei change over time according to this equation?
- Define the half-life (T₀.₅) of a radioactive substance. Explain its relationship to the decay probability 'p' and why it is a useful concept for characterizing radioactive decay.
- How does the provided simulation applet visualize the process of radioactive decay? What do the boxes and the color change to red represent in the simulation?
- According to the "Theory" section, what key assumption is made about the probability of decay for each radioactive nucleus? Why is this assumption important for the given mathematical model?
- Explain why the SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5 is considered an Open Educational Resource (OER). What are the potential benefits of using OER in education?
- Identify Fu-Kwun Hwang as mentioned in the provided sources. What is his role in the development of the described models and simulations?
- What are some of the advantages of using a JavaScript-based simulation applet for teaching and learning about radioactive decay compared to purely theoretical explanations?
- Briefly describe one other simulation applet listed in the "SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5" source that appears to explore a different scientific or mathematical concept.
Quiz Answer Key
- The dice rolling model illustrates probability by showing that each face of a fair die has an equal chance of appearing. In radioactive decay, 'p' represents the probability of a single nucleus decaying, similar to the probability of rolling a specific number on a die. For example, if the probability of decay in a certain time interval is 1/6, this could be analogous to rolling a specific number on a six-sided die, where that outcome signifies a decay event.
- "dN(t)/dt" represents the instantaneous rate of change in the number of undecayed radioactive nuclei (N) with respect to time (t), which is essentially the decay rate. The negative sign indicates that the number of undecayed nuclei is decreasing over time as they decay into daughter products.
- 'N₀' represents the initial number of radioactive nuclei present in a sample at the starting time (t=0). 'N(t)' represents the number of radioactive nuclei that remain undecayed at some later time 't'. The exponential decay equation shows that the number of undecayed nuclei decreases exponentially over time, meaning the rate of decrease is proportional to the amount present.
- Half-life (T₀.₅) is the time it takes for exactly half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay. It is inversely related to the decay probability 'p'; a higher probability of decay leads to a shorter half-life (T₀.₅ = ln(2) / p). Half-life is useful because it provides a characteristic timescale for the decay of a particular radioactive isotope, making it easier to predict how much of the substance will remain after a certain period.
- The simulation applet represents each radioactive nucleus as a box. As time progresses in the simulation, each box has a probability of changing color to red, indicating that the nucleus has decayed. The increase in the number of red boxes over time visually demonstrates the process of radioactive decay and the decrease in the number of undecayed nuclei.
- The key assumption is that each radioactive nucleus has the same probability 'p' of decaying into a daughter product, and this probability is constant over time and independent of other nuclei. This assumption is crucial for the mathematical model because it allows for a straightforward probabilistic treatment of the decay process and leads to the exponential decay law.
- The applet is considered an Open Educational Resource (OER) because it is released under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License, as indicated at the end of the webpage. This license typically allows for free use, adaptation, and sharing of the resource, provided that attribution is given and any derivative works are shared under a similar license. The benefits of using OER include increased accessibility to educational materials, cost savings, and the potential for customization and improvement by the wider educational community.
- Fu-Kwun Hwang is identified as a professor in the Department of Physics at National Taiwan Normal University and is credited as the designer of both the JavaScript and the original Java versions of the radioactive decay model and related simulations. He is a key figure in the development of these Open Source Physics educational tools.
- Using a JavaScript-based simulation applet offers several advantages, such as providing a visual and interactive representation of an abstract concept like radioactive decay, allowing students to explore the effects of changing parameters (like decay probability), and making the learning process more engaging and intuitive compared to solely relying on mathematical formulas and textual explanations. The accessibility through web browsers also makes it easy to distribute and use across various devices.
- One other simulation applet listed is "PICUP Projectile Motion: Experiment and Computational Model Ex 1 n 3 JavaScript HTML5 Applet Simulation Model." This applet appears to explore the physics of projectile motion by allowing users to interact with a computational model, potentially comparing it with experimental data.
Essay Format Questions
- Discuss the strengths and limitations of using a dice rolling model as an analogy to explain the probabilistic nature of radioactive decay. In what ways does the model effectively illustrate the concept, and where does the analogy break down?
- Explain the derivation and significance of the exponential decay law (N(t) = N₀ * e^(-pt)) in the context of radioactive decay. How are the concepts of decay probability and half-life incorporated into this model, and what are the implications of this mathematical relationship?
- Analyze the role of interactive simulations, such as the SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet, in enhancing student understanding of abstract scientific concepts like radioactive decay. What pedagogical benefits do these types of resources offer compared to traditional teaching methods?
- Explore the impact of Open Educational Resources (OER) and initiatives like Open Source Physics (OSP) on science education. Discuss the advantages and challenges associated with the development and use of freely available educational materials like the simulation applet described in the sources.
- Considering the various simulation applets listed in the "SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5" source, discuss the breadth of scientific and mathematical concepts that can be explored through interactive computational models. Provide specific examples and reflect on the potential of such tools for interdisciplinary learning.
Glossary of Key Terms
- Applet: A small application, often written in Java or JavaScript, that runs within another application, typically a web browser.
- Decay Constant (λ): An alternative way to express the probability of decay per unit time for a radioactive nucleus. It is related to 'p' in the provided text (often p is used for probability within a specific time step in simulations, while λ is the continuous decay constant). λ = p if the time interval is very small, and T₀.₅ = ln(2) / λ.
- Daughter Product: The stable or radioactive nuclide that results from the radioactive decay of a parent nuclide.
- Exponential Function: A mathematical function where the independent variable appears in the exponent, leading to rapid growth or decay (e.g., e^x or e^(-kt)).
- HTML5: The latest evolution of the standard defining HTML (HyperText Markup Language), used for structuring and presenting content on the World Wide Web. It supports multimedia and is often used for interactive web applications.
- Isotope: Variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, and consequently in nucleon number. Radioactive isotopes are unstable and undergo radioactive decay.
- Nucleus (plural: Nuclei): The small, dense region at the center of an atom, consisting of protons and neutrons.
- Probability Distribution: A mathematical function that describes the likelihood of different outcomes in a random experiment.
- Radioactive: Exhibiting or relating to the emission of ionizing radiation or particles caused by the spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei.
- Simulation: The imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time using a model.
- Spontaneous Process: A process that occurs naturally under certain conditions without any external force or influence.
Theory
Assume the number of radioactive nucleus is N(t) --- not yet decayed into daughter product.
Each nucleus has the same probability p (p<1) decayed into daughter product.
It means that dN(t)/dt= -p*N(t) , where dN(t) is the number of nucleus decayed into daughter product at time t.
The solution is N(t)=N0 e -pt = N0 e -(ln2/T0.5)) t where N(0) is total number of nucleus at time t.
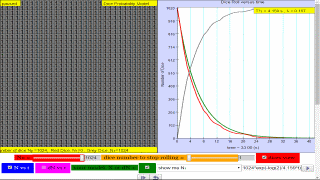
Each box represents a nucleus.
This applet lets you set the probability for a nucleus to decay and watch how the number of decayed nuclei (color changed to RED) increased with time t.
YouTube
Other Resources
- http://weelookang.blogspot.sg/2015/12/ejss-radioactive-decay-model.html lookang's blogpost about this JavaScript version
- http://www.phy.ntnu.edu.tw/ntnujava/index.php?topic=194.0 by Fu-Kwun Hwang original Java version
- http://www.opensourcephysics.org/items/detail.cfm?ID=10576 by Wolfgang Christian similar Java version
Frequently Asked Questions about the Dice Rolling Model and Simulations
1. What is the purpose of the Dice Rolling Model as described in these sources?
The Dice Rolling Model, as presented by Fu-Kwun Hwang and colleagues, serves as an analogy and a simulation tool to understand probabilistic processes, particularly radioactive decay. By simulating the rolling of dice, where each die has a certain probability of landing on a specific face (representing decay), the model visually demonstrates how a large number of independent probabilistic events unfold over time. This makes abstract concepts like exponential decay more intuitive and accessible, especially in educational settings.
2. How does the Dice Rolling Model relate to radioactive decay?
The model directly parallels radioactive decay by treating each die as a radioactive nucleus. The act of a die landing on a specific "decay" face represents a nucleus decaying into its daughter product. The probability of a die "decaying" (landing on the chosen face) in each roll corresponds to the decay probability of a radioactive nucleus within a given time interval. By observing a collection of dice being rolled repeatedly, users can see the overall decrease in the number of "undecayed" dice, which mirrors the exponential decay law of radioactive materials.
3. What are the key features of the "SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5"?
This online simulation applet allows users to interactively explore the Dice Rolling Model. Key features include the ability to set the probability of decay (the chance of a die landing on its "decay" face), visualize each "nucleus" (represented by a box), and observe how the number of "decayed" nuclei (colored red) increases over time. The applet is designed to be accessible on various devices, including computers, tablets, and smartphones, as it is built using HTML5 and EasyJavaScriptSimulation.
4. Who developed these resources, and under what licensing terms are they available?
The Dice Rolling Model and the associated JavaScript simulation applet were primarily designed by Fu-Kwun Hwang from the Department of Physics at National Taiwan Normal University, with contributions from lookang and leongster. These resources are released under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License. This license allows for the sharing and adaptation of the materials, provided that appropriate credit is given to the original authors and any derivative works are shared under the same license. Commercial use of the EasyJavaScriptSimulations Library, however, requires a separate license obtained by contacting This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..
5. Where can I access and use the "SLS Dice Throw JavaScript Model Simulation Applet HTML5"?
The simulation applet can be directly accessed and embedded in webpages using the provided iframe code, which links to the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore website: https://iwant2study.org/lookangejss/06QuantumPhysics_20nuclear/ejss_model_decaychangeNweediceSLS/decaychangeNweediceSLS_Simulation.xhtml. This allows educators and students to easily integrate the interactive model into their learning platforms.
6. What is the theoretical basis behind the Dice Rolling Model's application to radioactive decay?
The theoretical foundation lies in the probabilistic nature of radioactive decay. Each radioactive nucleus has an independent probability (p) of decaying within a given time period. For a large number of nuclei (N(t)), the rate of decay (dN(t)/dt) is proportional to the number of undecayed nuclei, expressed as dN(t)/dt = -p*N(t). The solution to this differential equation yields the exponential decay law: N(t) = N₀ * e^(-pt), where N₀ is the initial number of nuclei and t is time. This equation can also be expressed in terms of the half-life (T₀.₅): N(t) = N₀ * e^(-(ln2/T₀.₅)t). The Dice Rolling Model visually and practically demonstrates this probabilistic and exponential behavior.
7. Are there other similar physics simulations available from the same developers or platform?
Yes, the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore platform hosts a wide variety of interactive physics simulations covering various topics, including nuclear physics, mechanics, waves, electromagnetism, and thermal physics. These simulations, often created using EasyJavaScriptSimulation, are designed for educational purposes and are accessible online. The provided text lists numerous examples of such simulations, ranging from radioactive decay and nuclear systems to mechanics, optics, and even games related to mathematical and physics concepts.
8. How can educators utilize the Dice Rolling Model simulation in their teaching?
Educators can use the Dice Rolling Model simulation as an engaging and visual tool to introduce the concept of probability and its application to natural phenomena like radioactive decay. By allowing students to manipulate the decay probability and observe the simulation, they can develop a more intuitive understanding of exponential decay, half-life, and the statistical nature of these processes. The accessibility of the HTML5 applet across different devices makes it suitable for both in-class activities and remote learning. Furthermore, it can serve as a basis for discussions on the limitations of macroscopic analogies when applied to quantum phenomena.
- Details
- Written by leongster
- Parent Category: 06 Modern Physics
- Category: 02 Nuclear
- Hits: 4895