Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits





Francisco Esquembre; Felix J. Garcia Clemente; This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.; Rena F; Zed; ShiXiong (idea)
The central theme across the sources is to deepen students' understanding of the various factors that affect how quickly liquids, specifically water, evaporate. The primary factors highlighted are:
- Surface Area: A larger surface area leads to a faster rate of evaporation.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures result in a quicker evaporation process.
- Humidity: Higher humidity in the surrounding air slows down evaporation.
- Presence of Wind: Wind increases the rate of evaporation.
- Pressure: (Mentioned in the title of one source but not elaborated upon in the provided excerpts).
The sources emphasize the use of an interactive HTML5 applet as a tool for students to explore these relationships through simulation and observation.
Key Ideas and Facts:
- Interactive Simulation: The core of the learning resource is an embedded HTML5 applet that allows secondary school students to visualize and investigate the factors affecting evaporation. The embed code is provided:
- <iframe width="100%" height="100%" src="https://iwant2study.org/lookangejss/03thermalphysics_10temperature/ejss_model_evaporationV2secomdarywithpressure/evaporationV2secomdarywithpressure_Simulation.xhtml " frameborder="0"></iframe>
- Learning Goals: The applet and accompanying materials are designed to help students understand how surface area, temperature, humidity, and wind influence the rate of evaporation. The stated learning goal is to deepen students' understanding of these factors. The resource is also linked to the Pri 5 & 6 SCIENCE (2014) curriculum.
- Impact of Surface Area: The documentation explicitly states the relationship between surface area and evaporation rate:
- "For a small surface area, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time"
- "For a large surface area at the beginning, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time in the blue trail. This implies larger the surface area the shorter the time taken to evaporate"
- Impact of Temperature: The effect of temperature on evaporation is also clearly outlined:
- "For a low temperature, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the red trail"
- "For a high temperature, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the blue trail. This implies higher the surrounding temperature the shorter the time taken to evaporate"
- Impact of Wind: The presence of wind accelerates evaporation:
- "For a low wind condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the red trail"
- "This implies higher the wind the shorter the time taken to evaporate"
- Impact of Humidity: Higher humidity inhibits evaporation:
- "For a low humidity condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the red trail"
- "This implies higher the humidity the longer the time taken to evaporate"
- Experimental Activities: The resource suggests hands-on or virtual experiments using the applet. One example provided involves:
- Changing the temperature in the simulation.
- Observing the graph of water amount over time.
- Recording the time taken for complete evaporation at different temperatures.
- Comparing the graphs to determine which temperature leads to faster evaporation.
- Related Resources: The web page provides links to other relevant materials, including:
- An "Evaporation (Surface Area, Temperature, Humidity, Presence of Wind) for Primary School" resource.
- YouTube videos demonstrating evaporation experiments and the virtual labs. Links provided include:
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JIz7913EQU
- http://weelookang.blogspot.com/2020/06/evaporation-surface-area-temperature.html
- https://weelookang.blogspot.com/2022/02/evaporation-surface-area-temperature.html
- Links to lessons on the Singaporean Ministry of Education's learning platform (VLE).
- Credits and Licensing: The applet is credited to Francisco Esquembre, Felix J. Garcia Clemente, Rena F, Zed, and ShiXiong (idea). It is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License for non-commercial use. Commercial use of the underlying EasyJavaScriptSimulations Library requires contacting This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..
- Target Audience: The primary target audience for this resource is secondary school students, although a related resource is available for primary school levels.
Potential Discussion Points/Further Investigation:
- While pressure is mentioned in the title of the secondary school resource, the provided excerpts do not elaborate on its effect on evaporation. Further investigation into this aspect might be beneficial.
- The resource utilizes graphs to represent the rate of evaporation over time under different conditions. Understanding these graphical representations is crucial for students.
- The links to external resources, particularly the YouTube videos and VLE lessons, could provide additional context and learning activities.
In conclusion, these sources provide a valuable open educational resource for teaching the factors affecting evaporation to secondary school students. The interactive simulation, coupled with clear explanations and suggested activities, offers a practical approach to understanding this scientific phenomenon.
Study Guide: Factors Affecting Evaporation
Quiz
Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
- According to the text, how does the size of the surface area of water affect the time it takes for the water to evaporate?
- What is the relationship between the surrounding temperature and the time required for water to evaporate, as described in the source?
- How does the presence of wind influence the rate of evaporation of water?
- What effect does the level of humidity in the surrounding air have on the evaporation of water?
- Besides surface area, temperature, humidity, and wind, what other factor affecting evaporation is mentioned in the title of one of the sources?
- What happens to the rate of evaporation of water in a container with a small surface area over time?
- Based on the experiment described, what steps are involved in comparing the rate of evaporation at different temperatures?
- For primary school science, what factors of evaporation have virtual labs been developed for, according to the YouTube link descriptions?
- What type of license governs the content of the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore website?
- Who are some of the individuals credited for their contributions to the evaporation simulation and related resources?
Answer Key for Quiz
- The source indicates that the larger the surface area of the water, the shorter the time it takes for the water to completely evaporate. This is implied by the observation that for a large surface area, the rate of evaporation decreases with time in a way that signifies faster overall evaporation compared to smaller surface areas.
- The source states that the higher the surrounding temperature, the shorter the time taken for the water to evaporate. This is supported by the comparison of evaporation rates at low, medium, and high temperatures, where higher temperatures lead to faster evaporation.
- The presence of wind increases the rate of evaporation of water. The source explains that under high wind conditions, water evaporates in a shorter amount of time compared to low or medium wind conditions.
- Higher humidity in the surrounding air leads to a longer time taken for water to evaporate. The source describes that under high humidity conditions, the rate of evaporation decreases in a way that implies slower overall evaporation compared to low humidity conditions.
- Besides surface area, temperature, humidity, and wind, the title of the source "Evaporation (Surface Area, Temperature, Humidity, Presence of Wind, Pressure) for Secondary School" mentions pressure as another factor affecting evaporation.
- For a small surface area, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time. The source does not specify the exact nature of this decrease (linear or otherwise) for small surface areas but notes that it does decrease over time.
- The experiment described involves setting the temperature to a specific value (e.g., 30°C), running the simulation to observe the graph of water remaining over time, saving the graph, and recording the time when the amount of water left is zero. This process is repeated for a different temperature (e.g., 20°C), and the two graphs are then studied to compare the rates of evaporation.
- Virtual labs have been developed for primary school science focusing on the effects of surface area, temperature, and humidity on evaporation, as indicated by the titles of the YouTube link versions provided.
- The content of the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore website is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License.
- Francisco Esquembre, Felix J. Garcia Clemente, Rena F, Zed, and ShiXiong (who provided the idea) are credited for their contributions to the evaporation simulation and related open educational resources.
Essay Format Questions
- Discuss the interplay between surface area and temperature in influencing the rate of evaporation. Using evidence from the provided text, explain how changes in each of these factors independently and potentially together affect how quickly a liquid evaporates.
- Explain the contrasting effects of wind and humidity on the process of evaporation. How does each of these environmental factors either accelerate or impede the transformation of a liquid into a gas, according to the source material?
- Based on the provided information, describe how the concept of evaporation and the factors affecting it are introduced and explored for different educational levels (primary vs. secondary school). What distinctions, if any, are apparent in the approach or the factors emphasized?
- Consider the use of the HTML5 applet and virtual labs as mentioned in the text. How might these interactive tools enhance students' understanding of the factors affecting evaporation compared to traditional teaching methods? What are the potential benefits of using such resources in science education?
- Synthesize the information provided about the various factors influencing evaporation. Imagine you are designing a simple experiment to demonstrate these principles to secondary school students. Outline your experimental setup, the variables you would manipulate, and the expected observations for each factor (surface area, temperature, humidity, and wind).
Glossary of Key Terms
- Evaporation: The process by which a liquid changes into a gas or vapor. This occurs when molecules in the liquid gain enough energy to overcome the intermolecular forces holding them together and escape from the surface.
- Surface Area: The extent of the exposed surface of a liquid. A larger surface area allows more molecules to be at the surface and thus have a greater chance of escaping into the gas phase, increasing the rate of evaporation.
- Temperature: A measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a substance. Higher temperatures mean molecules have more energy, increasing the likelihood that they will have enough energy to evaporate.
- Humidity: The amount of water vapor present in the air. High humidity means the air is already saturated with water vapor, reducing the rate at which more water molecules can evaporate into the air.
- Wind: The movement of air across the surface of a liquid. Wind can carry away water vapor that has just evaporated, preventing it from accumulating above the liquid and increasing the net rate of evaporation.
- Rate of Evaporation: A measure of how quickly a liquid is turning into a gas, often expressed as the amount of liquid evaporated per unit of time.
- HTML5 Applet: A small application that runs within a web browser using the HTML5 standard. In this context, it refers to interactive simulations used to demonstrate the principles of evaporation.
- Virtual Lab: An online simulation of a laboratory experiment, allowing users to manipulate variables and observe the outcomes in a virtual environment.
- Linear Decrease: A decrease at a constant rate over time, represented by a straight line on a graph. The text mentions that under certain conditions (e.g., constant surface area, specific temperature or wind conditions), the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases linearly with time.
\[ \frac{1}{2} \]
Sample Learning Goals
This lesson deepens students' understanding of factors affecting the rate of evaporation.
- Pri 5 & 6 SCIENCE (2014) (2014)
For Teachers
Evaporation (Surface Area, Temperature, Humidity, Presence of Wind) for Primary School
 |
| For a small surface area, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
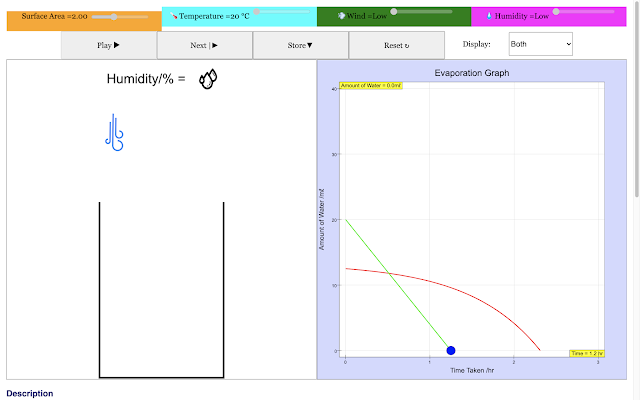 |
| For a middle size surface area, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly as the surface is constant https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a large surface area at the beginning, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time in the blue trail This implies larger the surface area the shorter the time taken to evaporate https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
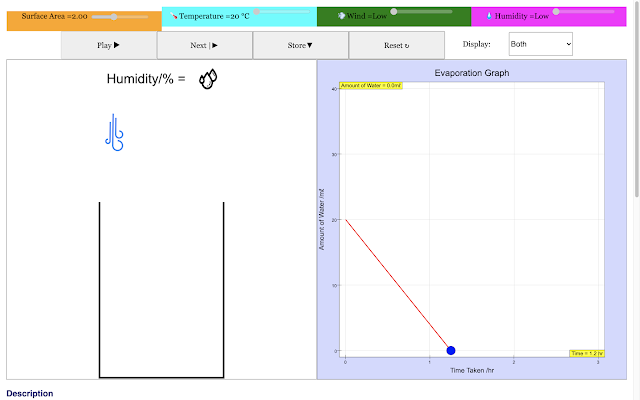 |
| For a low temperature, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the red trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a middle temperature, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the green trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
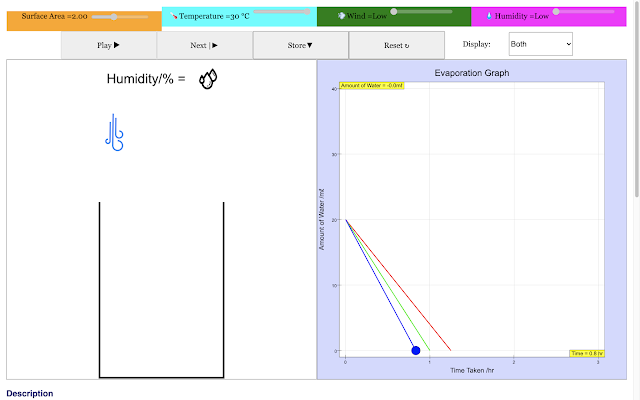 |
| For a high temperature, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the blue trail. This implies higher the surrounding temperature the shorter the time taken to evaporate https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a low wind condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the red trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
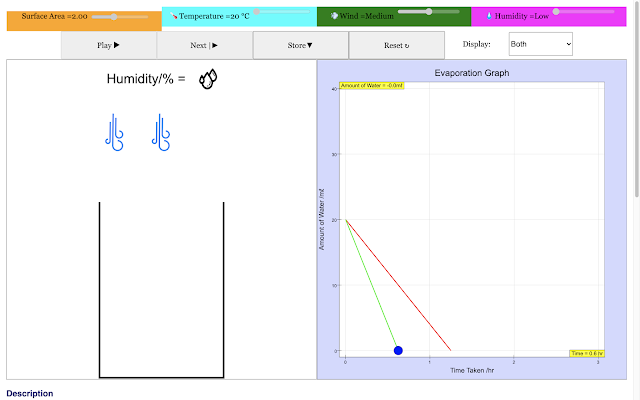 |
| For a medium wind condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the green trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a high wind condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the blue trail This implies higher the wind the shorter the time taken to evaporate https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
Frequently Asked Questions about Evaporation
What is evaporation?
Evaporation is the process by which a liquid, such as water, changes into a gas or vapor. This occurs when molecules within the liquid gain enough kinetic energy to overcome the intermolecular forces holding them together and escape into the surrounding air.
What are the key factors that affect the rate of evaporation?
Several factors influence how quickly evaporation occurs. These include:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures provide more kinetic energy to liquid molecules, increasing the rate at which they can escape and become a gas.
- Surface Area: A larger surface area exposes more liquid molecules to the air, allowing for a greater number of molecules to evaporate at any given time, thus speeding up the overall process.
- Humidity: Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor already present in the air. If the air is already saturated with water vapor (high humidity), the rate of evaporation will be slower because there is less space for more water molecules to enter the gaseous phase. Conversely, dry air (low humidity) allows for a faster rate of evaporation.
- Presence of Wind: Wind or air movement helps to carry away water vapor molecules that have just evaporated from the liquid's surface. This prevents the air directly above the liquid from becoming saturated, allowing more molecules to evaporate and increasing the rate of evaporation.
- Pressure: While not explicitly detailed as prominently as the other factors in the provided text, lower atmospheric pressure generally leads to a faster rate of evaporation. This is because there is less external force pressing down on the liquid surface, making it easier for molecules to escape.
How does temperature affect the time it takes for water to evaporate?
Higher temperatures significantly decrease the time it takes for water to evaporate. The provided information states that at higher surrounding temperatures, the time taken for evaporation is shorter. This is because more water molecules have sufficient energy to break free from the liquid surface and become vapor.
In what way does surface area influence the rate of evaporation?
A larger surface area leads to a faster rate of evaporation and consequently a shorter time for the liquid to completely evaporate. The text explicitly mentions that with a larger surface area at the beginning, the time taken for the water to evaporate is shorter. This is because more molecules are exposed to the air and can escape simultaneously.
How does humidity in the air impact the evaporation process?
Higher humidity in the surrounding air slows down the rate of evaporation, thus increasing the time it takes for a liquid to evaporate completely. The provided text indicates that under high humidity conditions, the time taken for evaporation is longer. This is because the air already contains a significant amount of water vapor, reducing its capacity to hold more.
What role does wind play in the evaporation of a liquid?
The presence of wind or air movement increases the rate of evaporation and reduces the time required for a liquid to evaporate. The text states that with higher wind conditions, the time taken to evaporate is shorter. Wind helps to remove the water vapor that accumulates above the liquid's surface, preventing saturation and allowing more evaporation to occur.
Can you provide examples of how these factors interact in everyday life?
Yes, several everyday scenarios illustrate the interplay of these factors:
- Drying clothes on a clothesline: Clothes dry faster on a warm, sunny, and windy day (high temperature and wind, typically lower humidity) compared to a cool, still, and humid day. Spreading the clothes out (increasing surface area) also speeds up drying.
- Sweating: When we exercise, our body produces sweat to cool down. The evaporation of sweat from our skin is more effective on a dry and windy day because the low humidity and wind allow the sweat to evaporate quickly, taking heat away from our body. On a humid day, sweat evaporates more slowly, making us feel hotter and stickier.
- Water evaporating from a puddle: A shallow puddle (large surface area) will evaporate faster than a deep container with the same volume of water (smaller surface area). The rate will also be higher on a warm, breezy day than on a cool, still day.
What educational resources are available to further understand evaporation?
The provided text mentions several open educational resources, including:
- An interactive HTML5 applet for secondary school that allows exploration of the effects of pressure, surface area, temperature, humidity, and wind on evaporation.
- Links to specific scenarios demonstrating the effects of varying surface area, temperature, and wind conditions.
- A YouTube video demonstrating an experiment on the effect of temperature on the rate of evaporation.
- Links to virtual labs focusing on the impact of surface area, humidity, and wind on evaporation for primary school science.
- Additional resources and lessons available on learning platforms.
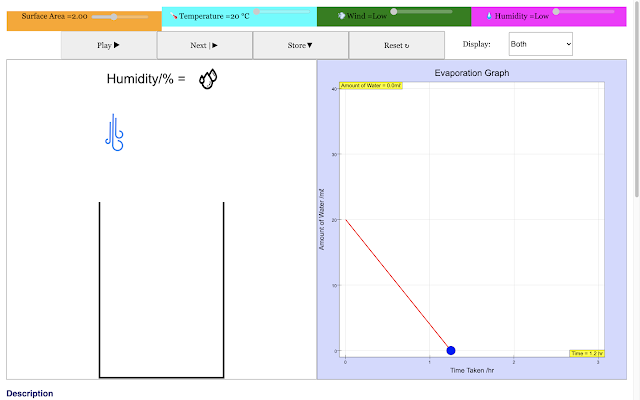 |
| For a low humidity condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the red trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a medium humidity condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the green trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a high humidity condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the blue trail This implies higher the humidity the longer the time taken to evaporate https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
Research
[text]
Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JIz7913EQU
Experiment 1
Change the temperature to 30 ◦c
Click play to see a graph appears
Click store to save the graph at 30 ◦c
Look at the time taken when the amount of water left in the container is zero.
Record the hours the water takes to evaporate.
Change the temperature to 20 ◦c
Record the hours the water takes to evaporate
Study the 2 graphs to compare the rate of evaporation of water.
Which temperature causes the water to evaporate faster?
Version:
- http://weelookang.blogspot.com/2020/06/evaporation-surface-area-temperature.html
- https://weelookang.blogspot.com/2022/02/evaporation-surface-area-temperature.html
Other Resources
https://vle.learning.moe.edu.sg/moe-library/lesson/view/fa3ded3e-8253-418c-b183-5bfd2e316d20?fromCcpm=false
https://vle.learning.moe.edu.sg/moe-library/lesson/view/d2d36336-8fe8-4eb7-bb69-8d813e5a429b?fromCcpm=false
end faq
{accordionfaq faqid=accordion4 faqclass="lightnessfaq defaulticon headerbackground headerborder contentbackground contentborder round5"}
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 12 Temperature & Ideal Gases
- Category: 03 Temperature
- Hits: 6536


.png
)





