Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits





Francisco Esquembre; Felix J. Garcia Clemente; This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.; Rena F; Zed; ShiXiong (idea)
1. Introduction:
This briefing document summarizes the key themes and important ideas presented in two provided sources related to the topic of evaporation for primary school students. The materials appear to be designed to deepen students' understanding of the factors that influence the rate of evaporation through interactive simulations and potentially accompanying lesson plans.
2. Main Themes and Important Ideas:
The primary focus of these resources is to educate primary school students (specifically mentioned for Pri 5 & 6 SCIENCE (2014)) on the four main factors affecting the rate of evaporation: surface area, temperature, humidity, and the presence of wind. The materials utilize an HTML5 applet, suggesting an interactive and visual learning approach.
Key Ideas and Facts from the Sources:
- Target Audience: The resources are specifically designed for primary school students, particularly those in Primary 5 and 6 Science based on the Singaporean curriculum ("Pri 5 & 6 SCIENCE (2014) (2014)").
- Learning Goal: The core learning goal is to enhance students' understanding of the factors that affect how quickly liquids evaporate. The description explicitly states: "This lesson deepens students' understanding of factors affecting the rate of evaporation."
- Interactive Simulation: The presence of an "HTML5 Applet JavaScript" indicates a strong emphasis on interactive learning. An embed link for an iframe is provided, suggesting that teachers can easily integrate this simulation into their online learning platforms.
- Visual Representation: The description of the applet mentions "trails" (red, green, blue) to visually represent the rate of evaporation under different conditions. This visual approach is crucial for engaging primary school students and making abstract concepts more concrete.
- Impact of Surface Area: The resource clearly states the relationship between surface area and the rate of evaporation:
- "This implies larger the surface area the shorter the time taken to evaporate" (referring to the observation that evaporation decreases faster with a larger surface area initially).
- Impact of Temperature: The resource highlights the effect of temperature on evaporation:
- "This implies higher the surrounding temperature the shorter the time taken to evaporate" (showing that higher temperatures lead to faster evaporation).
- Impact of Wind: The influence of wind is also addressed:
- "This implies higher the wind the shorter the time taken to evaporate" (indicating that more wind speeds up the evaporation process).
- Impact of Humidity: The role of humidity is explained:
- "This implies higher the humidity the longer the time taken to evaporate" (demonstrating that higher humidity slows down evaporation).
- Experimentation and Observation: The resource includes a description of a simple virtual experiment where students can:
- Change the temperature.
- Observe a graph appearing over time.
- Store graphs for comparison.
- Record the time taken for all the water to evaporate under different temperatures.
- Compare the rate of evaporation at different temperatures to answer the question: "Which temperature causes the water to evaporate faster?"
- Supplementary Resources: The document provides links to other potentially related resources on the Singaporean Ministry of Education's learning platform (VLE). It also includes a YouTube link to a video demonstrating "Evaporation due to surface area, humidity and wind virtual labs for primary school science."
- Credits and Licensing: The resources are credited to Francisco Esquembre, Felix J. Garcia Clemente, This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it., Rena F, Zed, and ShiXiong (idea). They are released under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License, promoting open educational resources.
3. Analysis and Implications for Teaching:
These resources offer a valuable tool for teaching the concept of evaporation and the factors affecting it to primary school students. The interactive HTML5 applet provides a hands-on (albeit virtual) experience that can help students visualize and understand these abstract scientific principles. The inclusion of a guided virtual experiment further encourages inquiry-based learning.
The explicit linking to the Singaporean science curriculum suggests that this resource is aligned with specific educational standards. Teachers can utilize the embed link to integrate the simulation directly into their online lessons or learning management systems. The supplementary resources and video link provide additional avenues for exploration and reinforcement.
4. Further Considerations:
- The first source mentioned in the title is not provided, so it's unclear what additional information or context it might offer. It could potentially include lesson plans, worksheets, or further explanations of the concepts.
- The "For Teachers" section within the second source provides direct statements about the relationship between each factor and evaporation rate, likely serving as guiding information for educators using the simulation.
- The extensive list of other Open Educational Resources suggests a broader ecosystem of science and mathematics learning tools developed by the same team or community.
5. Conclusion:
The provided excerpts highlight a well-structured and interactive resource designed to teach primary school students about the factors influencing evaporation. The use of a visual simulation, guided experimentation, and clear statements of the scientific principles makes this a potentially effective tool for engaging young learners and deepening their understanding of this fundamental scientific concept. The open licensing encourages wider adoption and adaptation within educational settings.
Evaporation Study Guide
Key Concepts
- Evaporation: The process by which a liquid changes into a gas or vapor.
- Rate of Evaporation: How quickly a liquid turns into a gas.
- Surface Area: The total area of the liquid exposed to the air.
- Temperature: The degree or intensity of heat present in a substance or object.
- Humidity: The amount of water vapor in the air.
- Wind: The movement of air.
Quiz
Instructions: Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
- What is evaporation, and what determines its rate?
- Explain how increasing the surface area of a liquid affects its rate of evaporation.
- Describe the relationship between temperature and the rate at which a liquid evaporates.
- How does the level of humidity in the air influence the rate of evaporation?
- Explain why wind can increase the speed at which a liquid evaporates.
- According to the provided text, how does the rate of evaporation change over time for different surface areas?
- Based on the text, what happens to the time it takes for water to evaporate when the surrounding temperature is higher?
- How does a low wind condition compare to a high wind condition in terms of the rate of water evaporation, as stated in the text?
- According to the text, how does high humidity affect the time taken for water to evaporate compared to low humidity?
- What were the learning goals mentioned in the text for the lesson on evaporation?
Quiz Answer Key
- Evaporation is the process where a liquid changes into a gas or vapor. The rate of evaporation, or how fast this happens, is influenced by factors like surface area, temperature, humidity, and the presence of wind.
- Increasing the surface area of a liquid exposes more of its molecules to the air. This allows more molecules to gain enough energy to escape the liquid phase and become a gas, thus increasing the rate of evaporation.
- Higher temperatures provide liquid molecules with more kinetic energy. With increased energy, more molecules can overcome the intermolecular forces holding them together in the liquid state and escape as gas, leading to a faster rate of evaporation.
- High humidity means there is already a large amount of water vapor in the air. This reduces the air's capacity to hold more water vapor, thus slowing down the rate at which more liquid water can evaporate into the air.
- Wind helps to remove the water vapor that has just evaporated from the surface of the liquid. This prevents the air above the liquid from becoming saturated with water vapor, allowing more liquid molecules to evaporate more quickly.
- The text indicates that for all surface areas (small, medium, large), the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time. For a large surface area, the time taken to evaporate is shorter.
- The text states that a higher surrounding temperature leads to a shorter time taken for water to evaporate. This is because more molecules have enough energy to change into a gaseous state at higher temperatures.
- The text describes that under a low wind condition, the rate of evaporation decreases with time, and this occurs more slowly compared to a high wind condition. Higher wind speeds lead to a shorter time for evaporation.
- According to the text, higher humidity results in a longer time taken for water to evaporate. This is because the air is already saturated with more water vapor, reducing the rate at which more water can turn into gas.
- The learning goals mentioned in the text state that the lesson aims to deepen students' understanding of the factors affecting the rate of evaporation for Primary 5 & 6 Science (2014) curriculum.
Essay Format Questions
- Discuss the interconnectedness of surface area and temperature in influencing the rate of evaporation. Provide examples to illustrate your points.
- Explain the opposing roles of humidity and wind in the process of evaporation. How do these two factors interact to affect how quickly a liquid evaporates?
- Based on the provided materials, design a simple experiment that primary school students could conduct to investigate the effect of one of the factors (surface area, temperature, humidity, or wind) on the rate of evaporation. Describe the materials needed, the procedure, and the expected results.
- Critically analyze how the provided HTML5 applet could be used as a learning tool to enhance primary school students' understanding of the factors affecting evaporation. What are its strengths and potential limitations?
- Imagine you are a teacher explaining the concept of evaporation to primary school students. Describe how you would use the concepts of surface area, temperature, humidity, and wind, along with relatable real-world examples, to help them understand this process.
Glossary of Key Terms
- Evaporation: The transformation of a liquid into a gas or vapor, typically occurring at the surface of the liquid.
- Surface Area: The total extent of the exposed outer layer of a substance, in this context, the liquid exposed to the air.
- Temperature: A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance; a higher temperature indicates greater molecular motion.
- Humidity: The concentration of water vapor present in the air, usually expressed as relative humidity (the amount of water vapor relative to the maximum amount the air can hold at a given temperature).
- Wind: The natural movement of air, especially in the form of a current of air blowing from a definite direction. It can carry away evaporated molecules.
- Rate: A measure of how quickly something happens or changes over time; in this context, how much liquid turns into a gas in a given amount of time.
- Linear: Progressing in a straight line or sequence; in the text, it describes how the rate of evaporation decreases over time under certain conditions.
- Saturated: When air holds the maximum amount of water vapor it can at a particular temperature; at this point, the rate of evaporation significantly decreases.
- Kinetic Energy: The energy possessed by an object due to its motion. Higher temperature means higher kinetic energy of liquid molecules.
- Intermolecular Forces: The attractive forces that exist between molecules in a liquid; molecules need enough energy to overcome these forces to evaporate.
Sample Learning Goals
This lesson deepens students' understanding of factors affecting the rate of evaporation.
- Pri 5 & 6 SCIENCE (2014) (2014)
For Teachers
Evaporation (Surface Area, Temperature, Humidity, Presence of Wind) for Primary School
 |
| For a small surface area, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
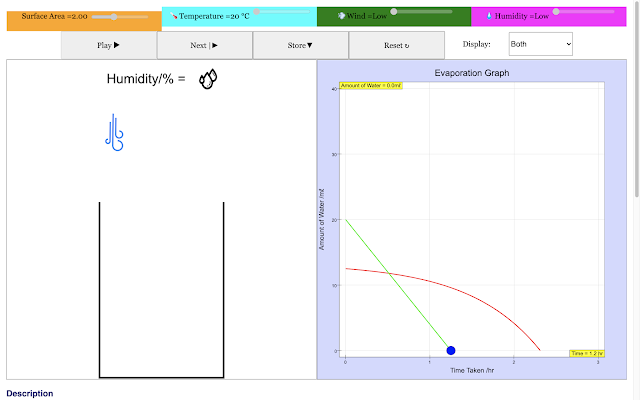 |
| For a middle size surface area, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly as the surface is constant https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a large surface area at the beginning, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time in the blue trail This implies larger the surface area the shorter the time taken to evaporate https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
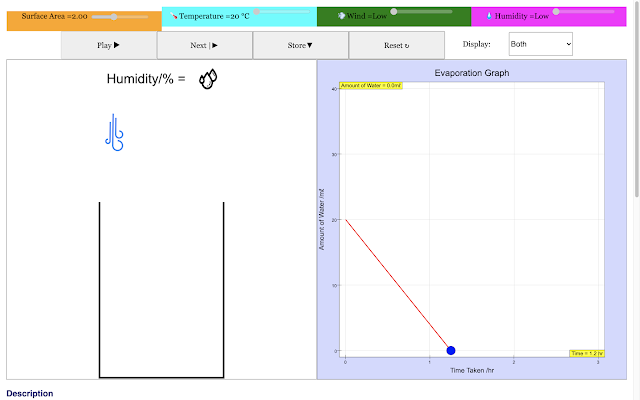 |
| For a low temperature, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the red trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a middle temperature, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the green trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
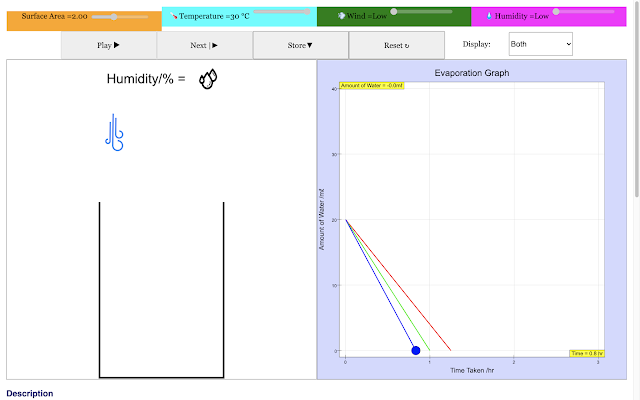 |
| For a high temperature, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the blue trail. This implies higher the surrounding temperature the shorter the time taken to evaporate https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a low wind condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the red trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
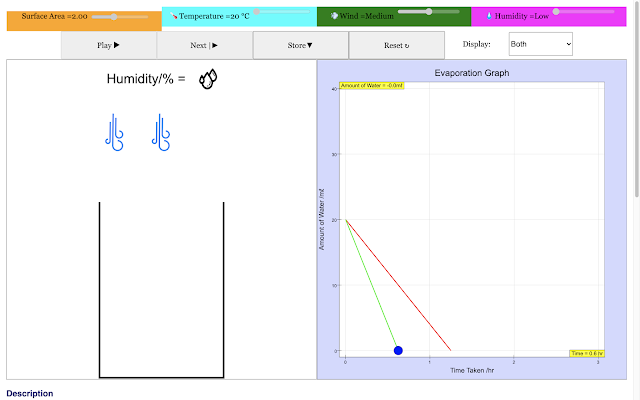 |
| For a medium wind condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the green trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a high wind condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the blue trail This implies higher the wind the shorter the time taken to evaporate https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
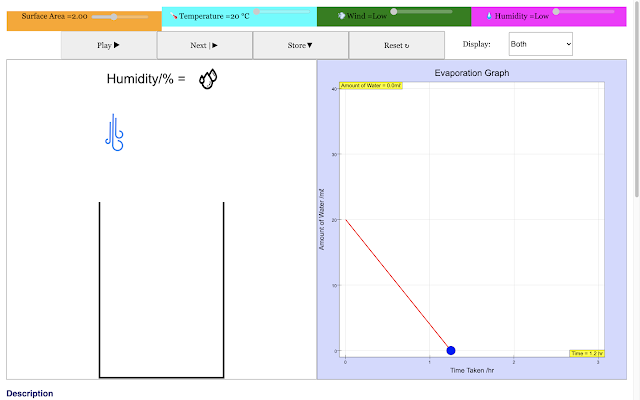 |
| For a low humidity condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the red trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a medium humidity condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the green trail https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
 |
| For a high humidity condition, the rate of evaporation of water in the container decreases with time linearly in the blue trail This implies higher the humidity the longer the time taken to evaporate https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/968 Direct Link |
Research
[text]
Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JIz7913EQU
Experiment 1
Change the temperature to 30 ◦c
Click play to see a graph appears
Click store to save the graph at 30 ◦c
Look at the time taken when the amount of water left in the container is zero.
Record the hours the water takes to evaporate.
Change the temperature to 20 ◦c
Record the hours the water takes to evaporate
Study the 2 graphs to compare the rate of evaporation of water.
Which temperature causes the water to evaporate faster?
Version:
Other Resources
https://vle.learning.moe.edu.sg/moe-library/lesson/view/fa3ded3e-8253-418c-b183-5bfd2e316d20?fromCcpm=false
https://vle.learning.moe.edu.sg/moe-library/lesson/view/d2d36336-8fe8-4eb7-bb69-8d813e5a429b?fromCcpm=false
Frequently Asked Questions about Evaporation
1. What is evaporation?
Evaporation is the process by which a liquid, such as water, changes into a gas or vapor. This happens when some of the liquid molecules gain enough energy to overcome the forces holding them together and escape into the air.
2. What are the main factors that affect how quickly water evaporates?
The main factors that influence the rate of evaporation are surface area, temperature, humidity, and the presence of wind.
3. How does surface area impact the rate of evaporation?
A larger surface area allows more liquid molecules to be exposed to the air. This increased exposure means more molecules have the opportunity to gain enough energy to evaporate, thus speeding up the process. The sources indicate that a larger surface area leads to a shorter time for the water to evaporate completely.
4. How does temperature affect the rate of evaporation?
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules. Higher temperatures mean that more molecules have sufficient energy to break free from the liquid and become a gas. Therefore, a higher surrounding temperature results in a faster rate of evaporation and a shorter time for the liquid to disappear.
5. What role does humidity play in the rate of evaporation?
Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air. When the humidity is low, the air can hold more water vapor, allowing more water to evaporate. Conversely, high humidity means the air is already saturated with water vapor, making it harder for more liquid water to turn into gas, thus slowing down evaporation. Higher humidity leads to a longer time for evaporation.
6. How does wind influence the rate of evaporation?
Wind helps to carry away the water vapor that has just evaporated from the surface of the liquid. This prevents the air directly above the liquid from becoming saturated, which would slow down further evaporation. Therefore, a higher wind condition leads to a faster rate of evaporation and a shorter time for the liquid to evaporate.
7. Are there any tools or simulations available to learn more about evaporation?
Yes, there are interactive simulations and applets designed for primary school students to explore the factors affecting evaporation. These tools allow users to change variables like temperature, surface area, humidity, and wind to observe their effects on the rate of evaporation in real-time through graphs and visual representations.
8. For what educational levels are these resources on evaporation intended?
These resources are specifically designed for primary school students, particularly those in Pri 5 & 6 Science (based on the Singaporean curriculum mentioned in the sources). The materials aim to deepen their understanding of the factors influencing the rate of evaporation through engaging and interactive methods.
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: 12 Temperature & Ideal Gases
- Category: 03 Temperature
- Hits: 17329