Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits





This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.; Francisco Esquembre; Felix J. Garcia Clemente; ShiXiong (idea); Rena F; Zed
1. Introduction:
This briefing document reviews two sources detailing an interactive simulation titled "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface for Primary School Science." This Easy JavaScript Simulation (EJS) tool, developed by a team including This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it., Francisco Esquembre, Felix J. Garcia Clemente, and others, is designed to help primary school students understand fundamental concepts of magnetism through hands-on virtual experimentation. The resources provide context, learning objectives, features, and pedagogical suggestions for using the simulation.
2. Main Themes and Important Ideas:
The primary theme across both sources is the development and application of an interactive simulation to facilitate primary school students' learning about magnetism, specifically the interactions between two bar magnets. Key ideas and facts include:
- Focus on Fundamental Magnetic Concepts: The simulation targets core principles of magnetism relevant to primary science, primarily the concepts of magnetic poles (north and south), attraction of unlike poles, and repulsion of like poles. The "Success Criteria" explicitly state: "I can identify the characteristics of magnets that like poles of magnets repel, unlike poles of magnets attract. I can use the words like poles, like poles, attract and repel to explain my observation of how poles of magnets interact."
- Interactive and Hands-On Learning: The simulation emphasizes active learning through manipulation. Students can "manipulate the magnets by moving and rotating them, observing how they interact with each other in real time." This hands-on approach encourages exploration and discovery.
- Visualisation of Abstract Concepts: A significant feature is the ability to visualize magnetic field lines. The sources highlight that "The simulation visually demonstrates the invisible magnetic field lines around each magnet. This helps students comprehend the concept of magnetic fields and how they influence the movement and behavior of other magnets." The ability to toggle this feature on and off is considered a "powerful feature."
- Real-Time Feedback: The simulation provides "Real-Time Feedback" as students interact with the magnets, instantly showing the effects of their actions. This immediacy helps students connect cause and effect in magnetic interactions.
- User-Friendly Design: The interface is specifically designed to be "intuitive for young learners," utilizing simple "drag-and-drop mechanics."
- Versatile Classroom Application: The resources suggest various ways teachers can integrate the simulation into their lessons, including:
- Introduction to magnetism
- Interactive demonstrations
- Hands-on group activities for prediction and testing
- Assessment tool to check understanding
- Benefits for Student Learning: The simulation is expected to enhance:
- Engagement: "The interactive nature of the simulation keeps students engaged in their learning, making science more fun and exciting."
- Visualization: It makes "abstract concepts easier to grasp" by visualizing invisible magnetic fields and forces.
- Accessibility: Being web-based, it is "accessible on any device with an internet connection."
- Alignment with Learning Goals: The "Sample Learning Goals" provide a clear framework for what students should be able to do after engaging with the simulation, such as "distinguish between the north and south poles of a bar magnet" and "explain how like poles (north-north or south-south) repel each other, while unlike poles (north-south) attract each other."
- Credits and Licensing: The simulation is attributed to several individuals and released under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License for non-commercial use. Commercial use of the underlying EasyJavaScriptSimulations Library requires a separate license.
- Availability and Embedding: The simulation can be directly run from provided links and can also be embedded in other webpages using an iframe code snippet.
- Related Resources: The "Other Resources" section provides links to various other magnetism-related simulations and interactive tools, suggesting a broader ecosystem of learning materials from the same developers and the Open Source Physics community.
3. Key Quotes:
- On the simulation's purpose: "This simulation provides a hands-on experience with two bar magnets, helping students visualize and understand the fundamental concepts of magnetism, such as attraction and repulsion."
- On the learning objectives: "Students can learn about the north and south poles of magnets and how like poles repel each other while opposite poles attract."
- On the visualization feature: "One of the most powerful features of the simulation is the ability to toggle magnetic field lines on and off. This visualization makes an abstract concept, like magnetic fields, more concrete for young learners."
- On the user interface: "The simulation has been designed to be intuitive for young learners. Simple drag-and-drop mechanics allow students to easily move and rotate the bar magnets to see the effects of their actions."
- On the educational value: "By providing an interactive and visual learning experience, it helps to make the invisible world of magnetic fields and forces accessible to young learners. Teachers can use this tool to create more engaging, hands-on science lessons that encourage curiosity and exploration."
4. Conclusion:
The "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" simulation appears to be a valuable educational resource for primary school science teachers looking to engage students in learning about magnetism. Its interactive nature, visual aids (magnetic field lines), and clear learning objectives align well with pedagogical best practices for teaching fundamental scientific concepts. The provision of embedding code and links to related resources further enhances its utility for educators. The explicit success criteria and sample learning goals provide a clear roadmap for integrating the simulation into lesson plans and assessing student understanding.
Study Guide: Interacting Bar Magnets
Quiz
Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
- What are the two types of poles found on a bar magnet?
- Describe what happens when the north pole of one bar magnet is brought close to the south pole of another bar magnet. Use the term "attract" in your answer.
- Explain what occurs when the south pole of one bar magnet is brought close to the south pole of another bar magnet. Use the term "repel" in your answer.
- According to the "Success Criteria," what are two key things you should be able to identify regarding magnets?
- How does the simulation allow students to explore the strength of magnetic forces?
- What is meant by "magnetic field lines," and how does the simulation help students understand this concept?
- Describe one way teachers can use the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" simulation as part of a lesson on magnetism.
- What does the "Hands-On Learning" aspect of the simulation encourage students to do?
- Name two real-world examples of magnets mentioned in the "Sample Learning Goals."
- What is one benefit of using the web-based simulation for learning about magnetism?
Quiz Answer Key
- The two types of poles found on a bar magnet are the north pole and the south pole. These poles are located at opposite ends of the magnet and are where the magnetic force is strongest.
- When the north pole of one bar magnet is brought close to the south pole of another bar magnet, they attract each other. This means they will move towards each other due to the magnetic force between the unlike poles.
- When the south pole of one bar magnet is brought close to the south pole of another bar magnet, they repel each other. This means they will move away from each other due to the magnetic force between the like poles.
- According to the "Success Criteria," students should be able to identify the characteristics of magnets where like poles repel and unlike poles attract. Additionally, they should be able to use the words "like poles," "unlike poles," "attract," and "repel" to explain their observations of magnetic interactions.
- The simulation allows students to explore the strength of magnetic forces by observing how the magnets interact at different distances. Students can move the magnets closer or further apart and see the resulting increase or decrease in the force of attraction or repulsion.
- Magnetic field lines are invisible lines of force that surround a magnet and represent the area of magnetic influence. The simulation helps students understand this concept by offering an option to visually display these field lines around the bar magnets.
- Teachers can use the simulation as an interactive demonstration tool during class by moving and rotating the magnets on a projected screen. This allows students to visually see the interactions between the poles and the patterns of the magnetic field lines in real time.
- The "Hands-On Learning" aspect of the simulation encourages students to actively experiment with the virtual magnets, make predictions about their behavior in different orientations, and then observe the outcomes to test their hypotheses.
- Two real-world examples of magnets mentioned in the "Sample Learning Goals" are fridge magnets and compasses. These examples help students connect the abstract concepts of magnetism to familiar objects.
- One benefit of using the web-based simulation is its accessibility, as it can be accessed on any device with an internet connection. This allows students to explore magnetism both in the classroom and at home, promoting flexible learning opportunities.
Essay Format Questions
- Discuss the importance of hands-on experimentation in primary school science education, using the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" simulation as a specific example of how interactive tools can facilitate this type of learning about magnetism.
- Explain the fundamental principles of magnetic attraction and repulsion between the poles of bar magnets. Describe how the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" simulation effectively demonstrates these principles to primary school students.
- Analyze the features of the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" simulation that make it a user-friendly and effective tool for primary school students learning about magnetism. Consider aspects such as the interface, feedback mechanisms, and visualization options.
- Describe several ways a primary school teacher could integrate the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" simulation into a lesson plan about magnetism. Explain how each method could contribute to students' understanding of the topic.
- Evaluate the benefits of using virtual simulations, like the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" model, as a supplement to traditional teaching methods for introducing abstract scientific concepts such as magnetic fields and forces to young learners.
Glossary of Key Terms
- Magnet: An object that produces a magnetic field and has the ability to attract or repel certain materials, such as iron and nickel.
- Bar Magnet: A rectangular-shaped magnet with a north pole at one end and a south pole at the other.
- North Pole: One of the two poles of a magnet. It is the end that points towards the Earth's geographic north pole when the magnet is allowed to rotate freely.
- South Pole: The other of the two poles of a magnet. It is the end that points towards the Earth's geographic south pole when the magnet is allowed to rotate freely.
- Like Poles: The same magnetic poles (north-north or south-south). Like poles repel each other.
- Unlike Poles: Opposite magnetic poles (north-south). Unlike poles attract each other.
- Attract: To pull towards each other. Magnetic attraction occurs between unlike poles.
- Repel: To push away from each other. Magnetic repulsion occurs between like poles.
- Magnetic Field: The area around a magnet where its magnetic force can be detected. Magnetic field lines are used to represent this invisible field.
- Simulation: A computer-based model that imitates a real-world system or process, allowing users to interact with and observe its behavior.
- Interactive: Allowing users to actively participate and influence the outcome or behavior of a system or tool.
- Visualization: The use of visual aids, such as diagrams or animations, to represent abstract concepts or data in a more understandable way.
Success Criteria:
I can identify the characteristics of magnets that like poles of magnets repel, unlike poles of magnets attract.
I can use the words like poles, like poles, attract and repel to explain my observation of how poles of magnets interact.
Sample Learning Goals for "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" Simulation
-
Identify Magnetic Poles:
- Students will be able to distinguish between the north and south poles of a bar magnet.
-
Describe the Behavior of Like and Unlike Poles:
- Students will explain how like poles (north-north or south-south) repel each other, while unlike poles (north-south) attract each other.
-
Explore the Strength of Magnetic Forces:
- Students will observe how the distance between two magnets affects the strength of the attractive or repulsive forces.
-
Predict and Test Magnetic Interactions:
- Students will make predictions about how two magnets will behave when brought close together, and use the simulation to test their hypotheses.
-
Apply Concepts to Real-World Examples:
- Students will relate their understanding of magnetic forces to real-life examples of magnets, such as fridge magnets, compasses, and magnetic toys.
-
Engage in Hands-On Experimentation:
- Students will experiment with rotating and moving the magnets in different orientations to explore the full range of magnetic interactions.
For Teachers Exploring Magnetism with the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" EJS Simulation
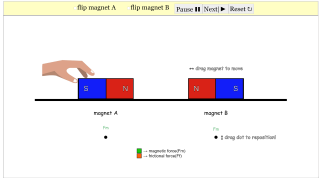
In primary school science, understanding the principles of magnetism can be both fascinating and challenging for young learners. To aid this process, we have developed an interactive Easy JavaScript Simulation (EJS) called "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" designed specifically for primary school students. This simulation provides a hands-on experience with two bar magnets, helping students visualize and understand the fundamental concepts of magnetism, such as attraction and repulsion.
Overview of the Simulation
The 2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface simulation allows students to experiment with two virtual bar magnets placed on a flat surface. Students can manipulate the magnets by moving and rotating them, observing how they interact with each other in real time. The simulation models the magnetic forces at play and provides an engaging way for students to explore the behavior of magnets.
Key Learning Objectives
-
Understanding Magnetic Poles: Students can learn about the north and south poles of magnets and how like poles repel each other while opposite poles attract.
-
Exploring Magnetic Fields: The simulation visually demonstrates the invisible magnetic field lines around each magnet. This helps students comprehend the concept of magnetic fields and how they influence the movement and behavior of other magnets.
-
Observing Attraction and Repulsion: Students can move the magnets closer together or further apart, witnessing how the distance between them affects the strength of the attractive or repulsive force.
-
Hands-On Learning: This interactive approach encourages students to experiment, make predictions, and observe outcomes, all of which promote a deeper understanding of magnetism.
Features of the Simulation
-
User-Friendly Interface: The simulation has been designed to be intuitive for young learners. Simple drag-and-drop mechanics allow students to easily move and rotate the bar magnets to see the effects of their actions.
-
Real-Time Feedback: As students move the magnets, the simulation instantly updates to show how the magnets interact with each other. This real-time feedback helps students draw connections between cause and effect.
-
Magnetic Field Visualization: One of the most powerful features of the simulation is the ability to toggle magnetic field lines on and off. This visualization makes an abstract concept, like magnetic fields, more concrete for young learners.
How to Use the Simulation in the Classroom
Teachers can integrate the 2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface simulation into their lessons on magnetism. Here are a few ways to use the simulation effectively:
-
Introduction to Magnetism: Begin by explaining the basic properties of magnets, such as the existence of magnetic poles and the behavior of magnetic fields. Then, use the simulation to allow students to explore these concepts at their own pace.
-
Interactive Demonstrations: Teachers can use the simulation as a live demonstration tool during class. By moving and rotating the magnets in front of the class, students can visually see the interactions and magnetic field patterns.
-
Hands-On Group Activities: Students can work in small groups to explore different configurations of the magnets. They can be tasked with predicting what will happen when two like poles are brought together, then using the simulation to test their hypotheses.
-
Assessment Tool: After learning about magnetism, teachers can assess students’ understanding by asking them to recreate specific magnetic interactions using the simulation or explain the behavior of the magnets based on what they observe.
Benefits of the Simulation
-
Engagement: The interactive nature of the simulation keeps students engaged in their learning, making science more fun and exciting.
-
Visualization: The simulation provides a way to visualize magnetic fields and forces that are otherwise invisible, making abstract concepts easier to grasp.
-
Accessible: Because the simulation is web-based, it can be accessed on any device with an internet connection, allowing students to explore magnetism at home or in the classroom.
Conclusion
The 2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface simulation is a powerful educational tool designed to enhance primary school students' understanding of magnetism. By providing an interactive and visual learning experience, it helps to make the invisible world of magnetic fields and forces accessible to young learners. Teachers can use this tool to create more engaging, hands-on science lessons that encourage curiosity and exploration.
Be sure to try out the simulation in your next lesson on magnetism to help your students grasp these fundamental scientific concepts in a fun and interactive way!
| Initial Setup https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/972 Direct Link |
| Like-poles facing each other https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/972 Direct Link |
| Unlike-poles facing each other https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/972 Direct Link |
| Magnets are too far from each other https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/972 Direct Link |
Research
Video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cbn5X_i1h88&t=4s
Version:
Other Resources
- https://www.physicsclassroom.com/Physics-Interactives/Electromagnetism/Bar-Magnets/Interactive
- Need a Bar Magnet and Earth?
- Need a Bar Magnet Field Line?
- Need 2 Bars Magnet?
- Need a 3D visualization of a Bar Magnet Field Line?
- Need 2 Bar Magnets on a level surface for Primary School Science?
- Need Riveting and Rotating Paperclip and Magnet to demonstrate magnetism passes through non-magnetic materials
- Need Suspended Magnet with effects of Heating?
- Need Stacking Ring Magnets?
- Need More Simulations? Check this out!
FAQ: Exploring Magnetism with Bar Magnets
Q1: What are the fundamental properties of magnets that this resource focuses on for primary school science?
This resource primarily focuses on two key characteristics of magnets: the existence of magnetic poles (north and south) and the interactions between them. Specifically, it highlights that like poles (north-north or south-south) repel each other, while unlike poles (north-south) attract each other.
Q2: What is the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" simulation, and how does it help students learn about magnetism?
The "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" simulation is an interactive digital tool designed for primary school students to explore magnetism. It provides a virtual space where students can manipulate two bar magnets by moving and rotating them on a flat surface. By observing the real-time interactions between the magnets, students can visualize the forces of attraction and repulsion, and develop a hands-on understanding of these fundamental magnetic concepts.
Q3: What are some specific learning goals that students can achieve by using this simulation?
Through the simulation, students can:
- Identify and distinguish between the north and south poles of a bar magnet.
- Describe and explain the behavior of like and unlike magnetic poles, using the terms "attract" and "repel."
- Observe how the distance between two magnets affects the strength of the magnetic forces acting between them.
- Make predictions about how magnets will interact and then test these predictions using the simulation.
- Connect their understanding of magnetic interactions to real-world examples of magnets and their applications.
- Engage in active experimentation by changing the magnets' positions and orientations.
Q4: How can teachers effectively use the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" simulation in their primary science lessons?
Teachers can integrate the simulation in various ways:
- As an introduction to the topic of magnetism, allowing students to freely explore the basic behaviors of magnets.
- For interactive demonstrations during class, visually showing the principles of attraction, repulsion, and magnetic fields.
- As a tool for hands-on group activities, where students can test hypotheses and discuss their observations.
- As an assessment method, asking students to demonstrate specific magnetic interactions or explain the behavior they observe.
Q5: What are the key features of the simulation that make it user-friendly and effective for young learners?
The simulation boasts several features designed for ease of use and learning:
- An intuitive interface with simple drag-and-drop controls for moving and rotating the magnets.
- Real-time feedback, instantly showing how the magnets respond to student actions.
- The ability to visualize the magnetic field lines around each magnet, making this abstract concept more tangible.
Q6: Besides the simulation itself, what other resources are mentioned in the provided text that could be helpful for teaching and learning about magnetism?
The text mentions several other resources, including:
- Links to direct setups within the simulation, such as "Like-poles facing each other" and "Unlike-poles facing each other."
- A video demonstrating the "2 Bar Magnets on a Levelled Surface" virtual lab.
- Links to other interactive physics resources, such as simulations on bar magnets and magnetic field lines from The Physics Classroom.
- Mentions of other simulations covering a wide range of science and math topics, highlighting the broader context of interactive educational tools.
Q7: What is the educational philosophy or approach behind the development of this simulation?
The development of the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" simulation is rooted in the principles of interactive and hands-on learning. By providing a virtual environment where students can actively manipulate variables and observe the outcomes in real time, it aims to enhance engagement, foster deeper understanding of abstract concepts through visualization, and encourage a more exploratory and inquiry-based approach to learning about magnetism.
Q8: Who are the creators and contributors to the "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" resource, and under what licensing terms is it released?
The "2 Bar Magnets on a Level Surface" resource was compiled with EJS 6.0 and is credited to This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it., Francisco Esquembre, Felix J. Garcia Clemente, with the initial idea by ShiXiong and contributions from Rena F and Zed. The simulation and associated materials are released under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License, which encourages sharing and adaptation with appropriate attribution and similar licensing terms. The EasyJavaScriptSimulations library used in its compilation has its own commercial use license, as detailed in the provided links.
- Details
- Written by Coco Lee
- Parent Category: 05 Electricity and Magnetism
- Category: 07 Magnetism
- Hits: 14018