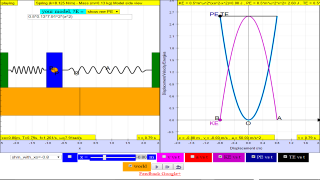
About
1.4.3 Example
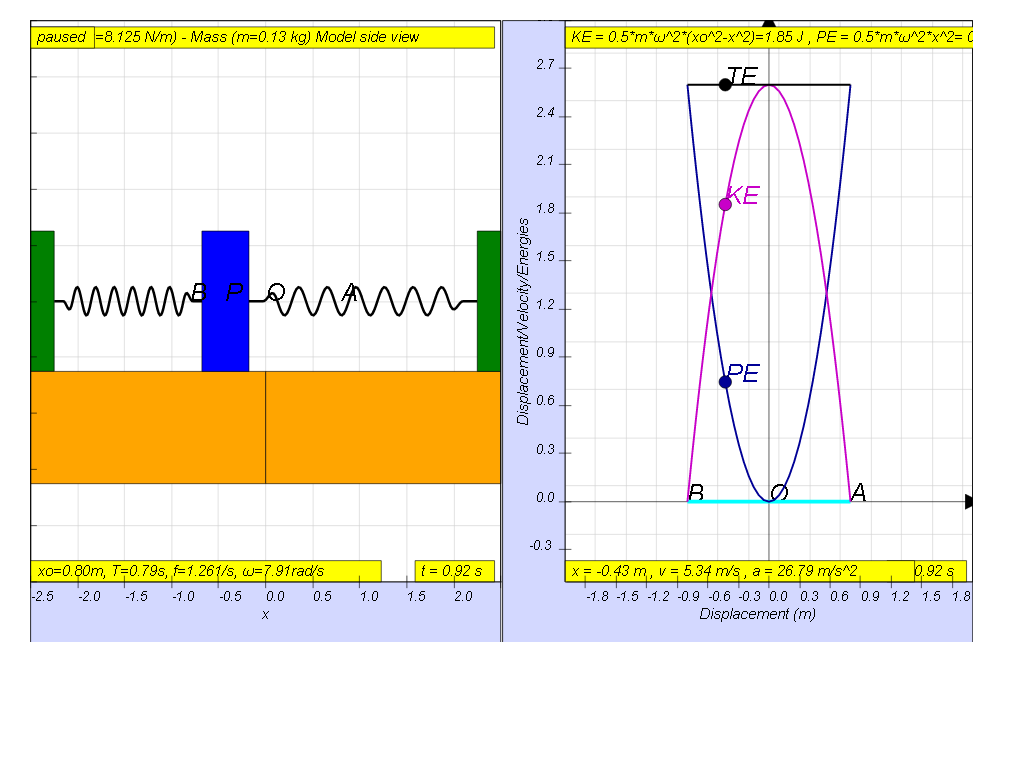
The mass is displaced to the left from its equilibrium position through a
small distance d and is released. The mass undergoes simple harmonic
motion.
The graph shows the variation with displacement x from the equilibrium
position of the kinetic energy of the mass.
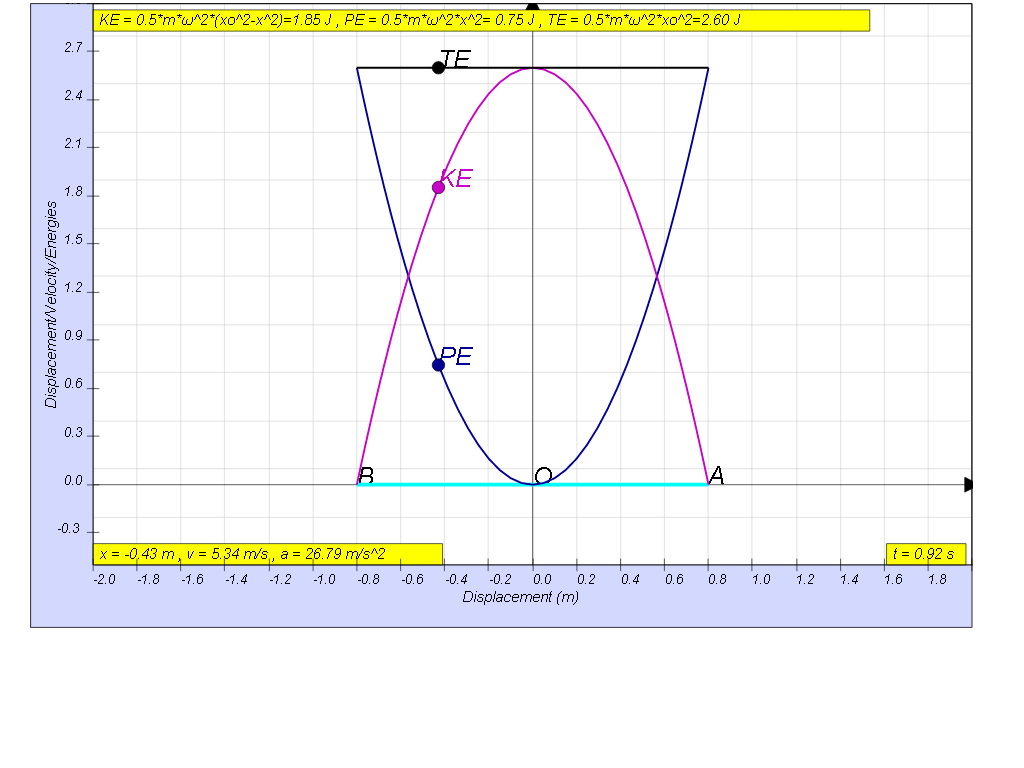
Use the graph to
(a) determine the distance d and the greatest acceleration through
which the mass was displaced initially,
(b) determine the period, frequency and angular frequency.
(c) determine the corresponding equations of displacement, velocity and acceleration.
(d) determine the corresponding equations of elastic potential energy and the total mechanical energy and sketch them on the graph above.
(e) determine the corresponding equations of kinetic energy, potential energy and total energy
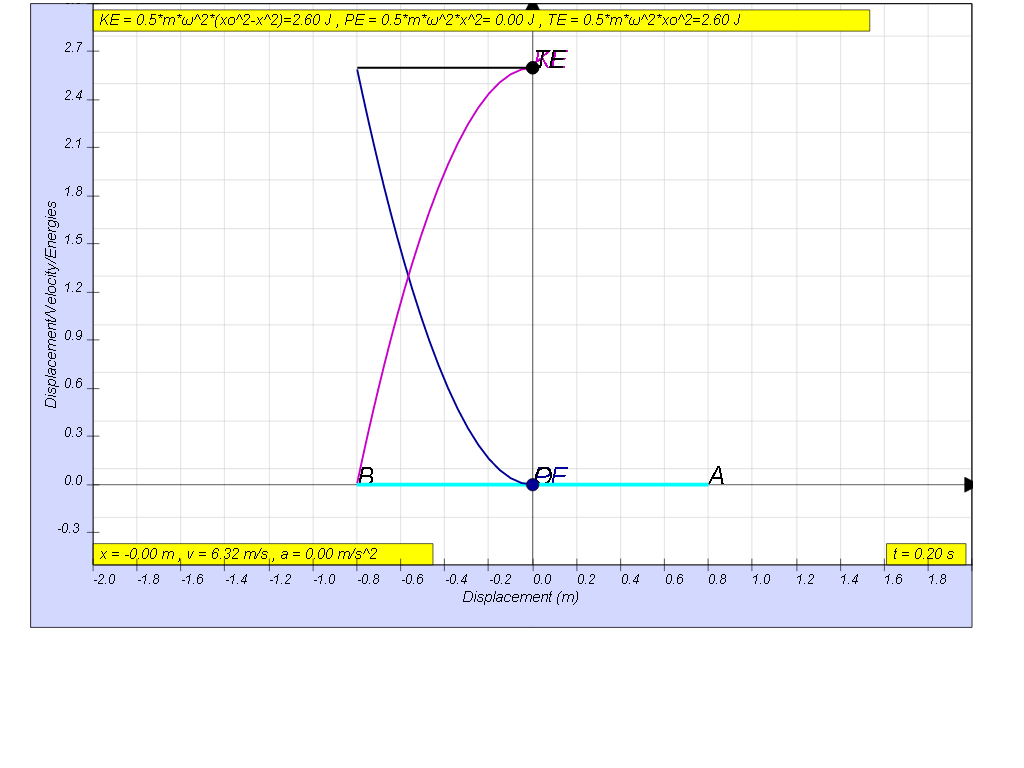
[0.8m, 0.79 s, 1.26 Hz, 7.91 rad/s]
[ x= - 0.8 cos(7.91t), v= 6.32 sin(7.91t), a= 50 cos(7.91t)]
[KE = 2.6 sin 7.912t, PE = 2.6 cos 7.912t, TE =2.6 J]
[KE = 4.06 (0.82-x2), PE = 4.06 x2, TE = 2.6 J]
Using the model, this graph can be shown
the velocity maximum value can be found in the model as well
1.4.3.1 Model:
Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits
 This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Briefing Document: ⚛️Analysis of "10.4.3 Example JavaScript HTML5 Applet Simulation Model - Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore"
1. Overview:
This document analyzes a webpage from the "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore" website. The specific focus is on a page showcasing a JavaScript HTML5 applet simulation model (SHM19) related to simple harmonic motion. The page also serves as a portal to a vast collection of interactive physics simulations and educational resources.
2. Key Themes and Concepts:
- Interactive Physics Simulations: The core theme is the use of interactive simulations built with JavaScript and HTML5 as educational tools. The showcased applet, "SHM19", demonstrates a mass undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM).
- "10.4.3 Example JavaScript HTML5 Applet Simulation Model"
- "Embed this model in a webpage: " This code snippet shows how the simulation can be embedded on a webpage
- Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM): The specific example focuses on SHM, a fundamental concept in physics involving oscillatory motion. The simulation allows users to explore the relationships between displacement, velocity, acceleration, kinetic energy, potential energy, and total mechanical energy in SHM.
- "The mass is displaced to the left from its equilibrium position through a small distance d and is released. The mass undergoes simple harmonic motion."
- Open Educational Resources (OER): The website is dedicated to providing OER, making these simulations freely accessible to educators and learners. The site is clearly dedicated to sharing learning materials.
- "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore"
- Accessibility and Cross-Platform Compatibility: The simulations are designed to work on various devices and operating systems, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones, demonstrating their accessibility.
- "Android/iOS including handphones/Tablets/iPads"
- "Windows/MacOSX/Linux including Laptops/Desktops"
- "ChromeBook Laptops"
- Mathematical and Physical Relationships: The page includes calculations and equations related to SHM, providing users with quantitative analysis alongside the visual simulation.
- "[0.8m, 0.79 s, 1.26 Hz, 7.91 rad/s]",
- "[ x= - 0.8 cos(7.91t), v= 6.32 sin(7.91t), a= 50 cos(7.91t)]",
- "[KE = 2.6 sin 7.912t, PE = 2.6 cos 7.912t, TE =2.6 J]"
- "[KE = 4.06 (0.82-x2), PE = 4.06 x2, TE = 2.6 J]"
- Easy JavaScript Simulation (EJS): EJS is the platform or tool that is often used to create these simulations. The wide array of listed tools and projects are built on EJS.
- "EasyJavaScriptSimulation"
3. Important Ideas and Facts:
- SHM Simulation (SHM19): The applet simulates a mass-spring system where the mass undergoes SHM. It allows for analyzing the displacement, velocity, and acceleration of the mass, as well as the kinetic and potential energies involved.
- Quantitative Analysis: The page provides numerical solutions for a specific scenario, such as the distance "d" (0.8 m), period (0.79 s), frequency (1.26 Hz) and angular frequency (7.91 rad/s). It also gives derived equations for displacement, velocity and acceleration and KE, PE and TE.
- Educational Applications: The page emphasizes the use of simulations to determine important values and equations.
- "Use the graph to (a) determine the distance d and the greatest acceleration through which the mass was displaced initially, (b) determine the period, frequency and angular frequency. (c) determine the corresponding equations of displacement, velocity and acceleration. (d) determine the corresponding equations of elastic potential energy and the total mechanical energy and sketch them on the graph above. (e) determine the corresponding equations of kinetic energy, potential energy and total energy"
- Vast Repository of Resources: The "Related" items at the end of the page demonstrate a wide array of additional simulations and learning resources, covering topics beyond simple harmonic motion. This includes mechanics, electromagnetism, waves, optics, and even some mathematics and other subject matter areas, suggesting that the resource hub is extremely comprehensive.
- Examples: Horizontal Spring Mass Model, Pendulum Model, Earth and Satellite, Newton Cradle, Collision Carts, Electrolysis Model, Double Slit Diffraction Model and many more.
- Focus on Singaporean Curriculum: There are clear indications that many of the resources on this website are designed to support the Singaporean curriculum, as evidenced by several entries including Building the Singapore Young Physicists' Tournament (SYPT) Team Assignment Web App.
- Community and Collaboration: The page lists authors and collaborators, suggesting that the simulations are developed through a community effort. There are also several references to workshops and projects involving teachers and students, showing that the resources are constantly being improved.
- Ongoing Development: References to dates and specific project names suggest that this resource is not static and that work is continuously being done to improve and expand the collection.
4. Quotes that Emphasize Key Points:
- On Interactive Learning: "Embed this model in a webpage: " This highlights how the simulations are integrated into a learning environment.
- On the Focus of the Simulation: "The mass is displaced to the left from its equilibrium position through a small distance d and is released. The mass undergoes simple harmonic motion." This explains the core concept being explored.
- On the Goals of the Resource: "Use the graph to (a) determine the distance d and the greatest acceleration through which the mass was displaced initially, (b) determine the period, frequency and angular frequency. (c) determine the corresponding equations of displacement, velocity and acceleration. (d) determine the corresponding equations of elastic potential energy and the total mechanical energy and sketch them on the graph above. (e) determine the corresponding equations of kinetic energy, potential energy and total energy" This states the specific learning objectives linked to the simulation.
5. Conclusion
The provided webpage is an access point to a rich collection of interactive physics simulations. The specific "SHM19" model is an example of how these simulations can be used to explore and understand complex physical phenomena like simple harmonic motion. The overall collection showcases an accessible, open-source approach to education using interactive simulations that run across a range of platforms. The sheer volume and variety of resources point to a dedicated and collaborative effort to create valuable and comprehensive educational tools that appear to be geared to the Singapore education system.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Study Guide
Quiz
Instructions: Answer each question in 2-3 sentences.
- What is simple harmonic motion?
- In the context of the provided material, what physical system is used to demonstrate simple harmonic motion?
- What is the significance of "d" in the description of the simulation?
- What type of energy is at its maximum when the displacement in SHM is zero?
- What is the relationship between period and frequency?
- How can the model be used to determine the maximum velocity of the oscillating mass?
- What are the three equations derived for displacement, velocity, and acceleration?
- What is the total mechanical energy in the provided example, and how is it related to kinetic and potential energy?
- According to the provided equations, how does potential energy relate to displacement (x) in this SHM model?
- What kind of digital tool is used to create the model used in this source?
Quiz Answer Key
- Simple harmonic motion (SHM) is a type of periodic motion where the restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium and acts in the opposite direction. It results in oscillations back and forth around a central point.
- The physical system is a mass attached to a spring undergoing horizontal oscillations, a common example used to demonstrate simple harmonic motion.
- "d" represents the initial displacement of the mass from its equilibrium position, which initiates the simple harmonic motion when the mass is released.
- When displacement is zero, the kinetic energy of the mass is at its maximum, as all the potential energy has been converted into motion.
- Period and frequency are inversely related. The period is the time for one complete oscillation, while frequency is the number of oscillations per unit time, specifically one second.
- The model allows for direct observation of the velocity, and the maximum velocity can be found either by visual inspection or via data analysis provided by the model.
- The equations are: displacement x = -0.8 cos(7.91t); velocity v = 6.32 sin(7.91t); acceleration a = 50 cos(7.91t).
- The total mechanical energy is 2.6 J and it is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy, which constantly converts from one form to the other.
- The elastic potential energy (PE) is proportional to the square of the displacement (x), as represented in the equation PE = 4.06x².
- The model is created using Easy JavaScript Simulation (EJS), which allows for interactive physics simulations in a web-based environment.
Essay Questions
Instructions: Answer the following essay questions using the information provided in the sources and your own understanding of the concepts.
- Explain how energy conservation is demonstrated in the SHM model, including how kinetic and potential energy change over time. Discuss how this model simplifies the real world example and how that simplification may be useful.
- Discuss the significance of the mathematical equations derived from the model, and how these equations describe the position, velocity, and acceleration of the mass during its motion.
- Describe how the interactive simulation can be used as a tool for exploring and understanding simple harmonic motion compared to a static description of SHM in textbook form.
- Analyze the role of Easy JavaScript Simulation (EJS) in creating interactive learning resources, referencing examples in the provided text beyond the specific SHM model.
- Compare and contrast the potential and limitations of using simulations as an educational tool in learning complex physics concepts like simple harmonic motion.
Glossary of Key Terms
- Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM): A type of periodic motion where the restoring force is proportional to the displacement and acts in the opposite direction, resulting in oscillation around an equilibrium point.
- Displacement (x): The distance of an object from its equilibrium position.
- Equilibrium Position: The position where the net force acting on an object is zero.
- Amplitude: The maximum displacement from the equilibrium position during SHM.
- Period (T): The time taken for one complete cycle of oscillation.
- Frequency (f): The number of complete cycles of oscillation per unit time, typically measured in Hertz (Hz).
- Angular Frequency (ω): A measure of frequency in radians per second, calculated as ω = 2πf.
- Kinetic Energy (KE): The energy an object possesses due to its motion.
- Potential Energy (PE): Stored energy that an object possesses due to its position or condition.
- Total Mechanical Energy (TE): The sum of the kinetic and potential energy of a system, assuming no other forms of energy transfer.
- Restoring Force: A force that acts to bring a displaced object back to its equilibrium position.
- Easy JavaScript Simulation (EJS): A software tool for creating interactive simulations, especially in the fields of physics and mathematics.
FAQ on Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore
- What is Easy JavaScript Simulation (EJS) and how is it used in the provided resources? EJS is a software tool that allows the creation of interactive simulations using JavaScript. The resources use EJS to build models of various physics concepts, making it possible for students to explore and understand these principles interactively. The simulations are typically embedded in web pages and are accessible across a range of devices including computers, tablets, and smartphones. They cover diverse topics from mechanics and oscillations to electromagnetism and optics. The focus is on creating resources that are both educational and engaging, and adaptable for different learning environments.
- What kind of physics concepts are covered by the provided simulations? The simulations cover a wide array of physics topics, including Newtonian mechanics (like simple harmonic motion and collisions), oscillations, energy work and power, gravitational fields and potential, wave phenomena (such as superposition and diffraction), electromagnetism, optics, and relativity. There are also resources focusing on primary science concepts like light and shadow, friction, and basic mechanics, as well as mathematics and geography-based simulations. The simulations are designed for different educational levels, ranging from primary to junior college and beyond.
- Can you provide an example of how a simulation is used in the context of Simple Harmonic Motion? One of the simulations, "SHM19," focuses on Simple Harmonic Motion. In this model, a mass is displaced from its equilibrium position and then released. Users can observe the motion, and the simulation provides graphical representations of displacement, velocity, and acceleration, as well as kinetic and potential energy. The example also shows how to derive equations for displacement, velocity, acceleration, potential energy, and total mechanical energy using given data from the simulation. The simulation provides the period, frequency, and angular frequency and is designed to give users a thorough and quantitative understanding of SHM.
- How are these simulation resources accessed and used? The simulations are typically embedded within webpages using an iframe, making them accessible directly in a browser. They are designed to run on various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices. The resources are available online through a platform called iwant2study.org/ospsg, which serves as a repository for various EJS simulations. There are many topics and levels available and accessible through this platform. Users can find the simulations and supporting information through navigation menus that categorize them by subject and educational level.
- Are these resources limited to only physics? No, while there is a significant emphasis on physics simulations, the resources also include simulations for mathematics, chemistry, geography, and even language learning. There are interactive games and other tools that span different disciplines. Some simulations are intended to enhance general learning skills or cross-curricular topics such as computer programming, interactive games, and design. It is evident the platform aims to create a holistic and comprehensive collection of resources for a variety of educational subjects.
- What kind of interactive tools are available, besides simulations, on the site? Besides the simulations, the site also offers interactive tools such as typing games, matching games, card games, virtual labs for science experiments, math coordinate tools, graphing tools, and even tools for geometry and design (such as nets of pyramids and other 3D shapes). There are also tools to support data analytics and literacy enhancement. This shows that the platform aims to offer not only simulations but a comprehensive suite of interactive resources to suit different learning styles and subject requirements.
- Who are the creators and contributors to these open educational resources? The resources are primarily developed by educators and researchers associated with the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore initiative. Several names are mentioned throughout the provided content such as "lookang" as well as references to workshops by specific individuals and projects by teachers. These contributions seem to come from a variety of sources indicating a collaborative, community-based approach to resource creation. There is also collaboration with international experts, with some projects being supported by entities like MOE CPDD1, and references to workshops with international researchers.
- Are these resources free to use and what about commercial applications? The educational materials are available under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License, meaning they can be freely used and shared for educational purposes as long as they are properly attributed, with adaptations being available if those works are also licensed using the same license. However, commercial use of the EasyJavaScriptSimulations Library requires contacting This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. and adhering to their specific license. This dual licensing approach supports the open sharing of educational material while still maintaining the rights of the developers for commercial applications.
- Details
- Parent Category: 02 Newtonian Mechanics
- Category: 09 Oscillations
- Hits: 7768