About
Fourier coefficients
The Fourier series of a periodic function f(x) with period x = 2π is of the form
f(x) = a0 /2 + Σ (ancos(nx) + bnsin(nx)); n=1,2,3....∞
To calculate the coefficients of the series, one starts with the following assumed identities:
∫f(x)cos(mx)dx = ∫cos(mx) Σ(a0/2 + Σ ancos(nx) + bnsin(nx))dx
∫f(x)sin(mx)dx = ∫sin(mx) Σ(a0/2 + Σ ancos(nx) + bnsin(nx))dx
where one integrates over one base period (m = 1).
Suppressing constants, the following types of integral are to be evaluated, summed over index n:
With m = 1,2,3...∞ and n = 1,2,3...∞: order of the harmonic (fundamental m, n = 1)
cos (mx)
sin (mx)
cos (mx) * (a*cos (nx) + b*sin (nx))
sin (mx) * (a*cos (nx) + b*sin(nx))
All integrals are zero except of those few where the indices are identical: m = n and the function types are the same (sine or cosine). Therefore every sum for a specific index n has only one member and the coefficients can easily be derived from the reduced equations as:
a0 = 2/T∫f(t) dt
an= 2/T∫cos(nx) f(t) dt
bn = 2/T∫sin(nx) f(t) dt
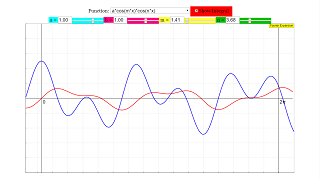
This simulation demonstrates the different types of functions and their integral.
Operation of the simulation
A ComboBox holds a list of all function combinations described on the Fourier Coefficients page. When one is selected it is displayed in red. The antiderivative is calculated for the fundamental period and drawn as a blue curve. Its end value at x = 2pi is the definite integral over one fundamental period, which is needed for the calculation of the coefficients. The integration process is slowed down to visualize more clearly the consequence of changes in parameters or indices.
Some of the selectable functions contain parameters a and b which can be changed continuously by sliders a/ b . Two other sliders m/n select the critical indices m and n as real numbers between 1 and 10.
Parameters and indices are maintained when functions are changed. Integration is started automatically at any change as long as the selection Integral remains active.
By means of sliders a and b scaling of the ordinate can be adjusted to the specific function. They also allow phase shifting of functions.
E1: Choose cosx in the comboBox. It will be calculated and displayed in red. Activate the Integral check box. The integration process will begin with the initial value of the function at x = 0 and will progress in red to the end of the fundamental period x = 2 π. Reflect why the end value and hence the definite integral over the interval [0, 2pi] is zero for integer n.
E2: Change index n with the slider and watch the integral curve. Reflect again why the definite integral is always zero for integer n.
E3: Choose sinx and verify the experiments for it.
E4: Choose asinx + bcosnx and assure yourself by varying a, b, n that the superposition is always a simple, phase shifted periodical, whose definite integral is zero for integer n.
E5: Choose cosx * sinx and assure yourself that the definite integral is always zero for integer n.
E6: Choose the remaining "mixed" functions and assure yourself that the definite integral is non zero only when both terms are of the same type and have identical indices.
E7: Integrate some of the functions analytically and verify the experimental findings.
E8: Conclude in general which characteristics of the functions sine and cosine are the base of your results.
This file was created by Dieter Roess November 2008
This simulation is part of
“Learning and Teaching Mathematics using Simulations
– Plus 2000 Examples from Physics”
ISBN 978-3-11-025005-3, Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG
Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits
 Dieter Roess - WEH- Foundation; Tan Wei Chiong; Loo Kang Wee
Dieter Roess - WEH- Foundation; Tan Wei Chiong; Loo Kang Wee
Sample Learning Goals
[text]
For Teachers
The Fourier Series is a series that decomposes any periodic curves into a sum of sines and cosines.
In this simulation, you are instead given several functions with multiple parameters a, b, m, n to select from and you can adjust them with either the sliders or the fields provided. The appearance of the periodic wave will change accordingly.
There is also a red checkbox labeled "Show Integral" that when checked, does exactly what it says.
The integral is shown in red, and the value of the integral curve at a point denotes the net area under the curve from 0 to that point. Do play around with the parameters and see how it affects the curve.
Research
[text]
Video
[text]
Version:
- http://weelookang.blogspot.sg/2016/02/vector-addition-b-c-model-with.html improved version with joseph chua's inputs
- http://weelookang.blogspot.sg/2014/10/vector-addition-model.html original simulation by lookang
Other Resources
[text]
What is a Fourier Series and what is its purpose?
A Fourier Series is a mathematical way to represent any periodic function as a sum of simple sine and cosine waves. Its purpose is to decompose complex periodic signals into their fundamental frequency components and their harmonics, making them easier to analyze and understand.
What is the fundamental period in the context of Fourier Series?
The fundamental period (denoted as T or 2π in the provided text) is the smallest repeating interval of a periodic function. The Fourier analysis focuses on this base period to determine the constituent sine and cosine waves that make up the function.
What are Fourier coefficients and how are they calculated?
Fourier coefficients (a₀, a<0xE2><0x82><0x99>, b<0xE2><0x82><0x99>) are the amplitudes of the constant term, cosine terms, and sine terms, respectively, in the Fourier Series representation of a function. They are calculated using definite integrals of the function multiplied by cosine or sine functions over one fundamental period. The formulas provided are: a₀ = 2/T ∫f(t) dt a<0xE2><0x82><0x99>= 2/T ∫ cos(nx) f(t) dt b<0xE2><0x82><0x99> = 2/T ∫ sin(nx) f(t) dt
What is the significance of the indices 'm' and 'n' in the context of Fourier Series integrals?
The indices 'm' and 'n' represent the order of the harmonics (integer multiples of the fundamental frequency) in the cosine and sine terms. When evaluating the integrals for the Fourier coefficients, only terms where the indices of the integrating function and the component of the Fourier series are identical (m = n) and the trigonometric functions are the same (both sine or both cosine) result in non-zero values. This orthogonality property is crucial for isolating each coefficient.
What does the provided JavaScript simulation allow users to do?
The JavaScript simulation allows users to explore different function combinations (sines, cosines, and their products or sums) and visualize their integration over one fundamental period. Users can adjust parameters (a, b) and indices (m, n) using sliders and observe how these changes affect the function and its integral. The simulation helps understand which functions yield non-zero definite integrals over a period.
What is the relationship between the definite integral of sine and cosine functions (and their linear combinations or products) over a fundamental period and their Fourier coefficients?
The definite integral of sine and cosine functions (or their specific combinations) over a fundamental period is directly related to the Fourier coefficients. As highlighted in the "Experiments" section, the definite integral of simple sine and cosine functions with integer indices over the interval [0, 2π] is typically zero. Non-zero integrals occur for "mixed" functions only when the sine or cosine terms have the same type and identical indices, which allows for the determination of the non-zero Fourier coefficients for those specific frequencies present in the function.
According to the experiments described, under what conditions is the definite integral of combinations of sine and cosine functions non-zero over a fundamental period?
The experiments demonstrate that the definite integral of combinations of sine and cosine functions over a fundamental period [0, 2π] is generally zero, except when integrating the square of a sine or cosine term (implicitly suggested when "both terms are of the same type and have identical indices"). For example, integrating cos(nx) * cos(nx) or sin(nx) * sin(nx) will yield a non-zero result, which is fundamental to extracting the a<0xE2><0x82><0x99> and b<0xE2><0x82><0x99> coefficients.
What fundamental characteristics of sine and cosine functions are key to the results observed in the Fourier analysis?
The key characteristics of sine and cosine functions that underlie the results are their periodicity and their orthogonality over a fundamental period. Orthogonality means that the integral of the product of two different sine or cosine functions (or a sine and a cosine function) with integer multiples of the fundamental frequency over one period is zero. This property allows the Fourier Series to uniquely decompose a periodic function into its constituent sinusoidal components, as each coefficient can be independently determined through integration due to this orthogonality.
- Details
- Written by Wei Chiong
- Parent Category: 2 Sequences and series
- Category: 2.1 Sequences and series
- Hits: 10410