
About
Tracker Standing Broad Jump
For Teachers
Credits
Author: lookang, video given to me by nelson
Contact: weelookang@gmail.com
Main Themes:
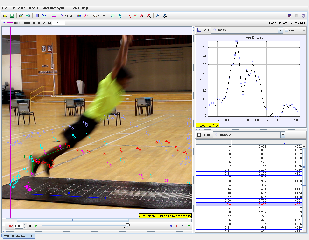
The primary focus of the "Tracker Standing Broad Jump" resource is the application of physics concepts to analyze a common athletic movement: the standing broad jump. It utilizes Tracker, a video analysis and modeling tool, to facilitate this analysis.
Key Concepts and Facts:
- Target Audience: The resource is intended for Junior College students.
- Subject Areas: The resource integrates concepts from Kinematics, Dynamics, and Physical Education.
- Software: Tracker software is used, making it compatible with Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems.
- Educational Value: The resource provides a practical, hands-on approach to learning physics by applying it to a real-world scenario. Students can use Tracker to analyze video recordings of standing broad jumps, allowing them to collect data on displacement, velocity, and acceleration. This approach can enhance understanding of theoretical concepts and develop data analysis skills.
Noteworthy Points:
- The website features numerous other interactive resources, covering a wide array of physics topics.
- The "Tracker Standing Broad Jump" is developed by Nelson Chong.
Quotes:
While the source doesn't provide textual content for direct quotes, the website structure and labels offer insights. The categorization under "Kinematics" and "Dynamics" clearly indicates:
- Kinematics: The resource likely deals with the motion of the jumper without considering the forces causing the motion. This might involve analyzing the trajectory of the jump, measuring jump distance, and calculating the jumper's velocity and acceleration at different points.
- Dynamics: The resource might also delve into the forces involved in the jump, such as the force exerted by the legs, the force of gravity, and air resistance. This could involve calculations of impulse, momentum, and work done during the jump.
Conclusion:
The "Tracker Standing Broad Jump" resource offers a valuable tool for physics education by bridging the gap between theoretical concepts and real-world applications. By utilizing video analysis, students can engage in active learning and develop a deeper understanding of physics principles.
Standing Broad Jump Physics Review
Short Answer Quiz
Instructions: Answer each of the following questions in 2-3 sentences.
- What is kinematics and how does it relate to the standing broad jump?
- Define velocity and acceleration. How do they differ?
- Describe the role of force in a standing broad jump.
- What is the impulse-momentum theorem and how can it be applied to the analysis of a standing broad jump?
- Explain how the law of conservation of energy applies to the standing broad jump.
- What factors can influence the distance of a standing broad jump?
- How does the angle of takeoff affect the jump distance?
- What is the significance of air resistance in the context of a standing broad jump?
- How can video analysis software like Tracker be used to study a standing broad jump?
- What are some real-world applications of the physics principles involved in a standing broad jump?
Short Answer Key
- Kinematics is the study of motion without considering the forces that cause it. In the standing broad jump, kinematics helps us analyze the jumper's position, velocity, and acceleration during the jump.
- Velocity is the rate of change of displacement, having both magnitude and direction. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. They differ in that velocity describes how quickly an object changes position, while acceleration describes how quickly velocity changes.
- Force is crucial in a standing broad jump as it is needed to propel the jumper off the ground. The jumper exerts a force on the ground, and the ground exerts an equal and opposite force back, launching the jumper into the air.
- The impulse-momentum theorem states that the change in momentum of an object is equal to the impulse applied to it. In a standing broad jump, the impulse from the ground on the jumper changes their momentum, leading to their takeoff velocity.
- The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. In the standing broad jump, the jumper's potential energy is converted into kinetic energy during the jump, and back into potential energy as they land.
- Factors influencing jump distance include the jumper's leg strength and power, technique (takeoff angle and body position), body mass, air resistance, and the surface they are jumping from.
- The angle of takeoff significantly impacts jump distance. The optimal angle for maximum distance is typically around 45 degrees.
- Air resistance opposes the motion of the jumper, reducing their horizontal velocity and limiting jump distance. While its effect may be small for a standing broad jump, it's still a factor to consider.
- Tracker allows researchers to track the jumper's motion frame by frame, measuring position, velocity, and acceleration over time. This data helps analyze the jump technique and identify areas for improvement.
- The physics principles involved in a standing broad jump have applications in sports, biomechanics, engineering (designing jumping robots), and understanding human movement.
Essay Questions
- Discuss in detail the role of energy transformations in a standing broad jump, explaining how potential and kinetic energy change throughout the jump.
- Analyze the forces acting on a jumper during a standing broad jump. Include a free-body diagram and explain how Newton's laws of motion apply to the different phases of the jump.
- How does the principle of projectile motion apply to the trajectory of a jumper in a standing broad jump? Explain how factors like takeoff angle and initial velocity affect the jump distance and height.
- Critically evaluate the impact of various biomechanical factors on the performance of a standing broad jump, such as leg power, body mass, and jumping technique.
- Discuss how technology, such as video analysis software and motion capture systems, has advanced our understanding and analysis of the standing broad jump.
Glossary of Key Terms
TermDefinitionKinematicsThe study of motion without considering the forces that cause it. It focuses on describing the position, velocity, and acceleration of objects.DynamicsThe study of motion and the forces that cause it.VelocityThe rate of change of displacement. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.AccelerationThe rate of change of velocity. It is also a vector quantity.ForceA push or pull on an object that can cause a change in its motion.ImpulseThe product of force and the time interval over which the force acts.MomentumThe product of an object's mass and velocity.Impulse-Momentum TheoremStates that the change in momentum of an object is equal to the impulse applied to it.EnergyThe ability to do work.Kinetic EnergyThe energy of motion.Potential EnergyStored energy due to an object's position or configuration.Law of Conservation of EnergyStates that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.Projectile MotionThe motion of an object projected into the air and subject only to the force of gravity.TrajectoryThe path followed by a projectile.Angle of TakeoffThe angle at which a projectile is launched with respect to the horizontal.Air ResistanceA force that opposes the motion of objects through the air.BiomechanicsThe study of the mechanical principles of living organisms, including human movement.TrackerVideo analysis software used to track the motion of objects in videos.
Tracker Standing Broad Jump FAQ
What is the Tracker Standing Broad Jump model?
The Tracker Standing Broad Jump model is an interactive resource that utilizes the Tracker software to analyze the physics behind a standing broad jump. This model allows users to upload a video of a standing broad jump and then use Tracker's tools to track the jumper's movement.
What physics concepts can be explored using this model?
The model can be used to explore several physics concepts within the realm of kinematics and dynamics. These include:
- Projectile motion: Analyze the parabolic trajectory of the jumper's center of mass.
- Velocity and acceleration: Determine the jumper's initial velocity and acceleration during takeoff.
- Force and impulse: Calculate the force exerted by the jumper and the impulse generated during takeoff.
- Energy transformations: Study the transformation of energy from potential to kinetic energy during the jump.
What educational levels is this model appropriate for?
The model is suitable for Junior College level students. It can be incorporated into physics or physical education classes.
What software is required to use the model?
The model utilizes the Tracker video analysis software. This software is freely available for Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems.
How do I use the Tracker Standing Broad Jump model?
- Record a video: Film a standing broad jump. Ensure the camera is stationary and perpendicular to the jumping plane for optimal analysis.
- Import into Tracker: Open the video file within the Tracker software.
- Track the motion: Use Tracker's tools to mark the jumper's center of mass in each frame of the video.
- Analyze the data: Tracker will generate graphs and data tables based on the tracked motion, allowing you to explore the various physics concepts mentioned earlier.
What are the benefits of using Tracker for video analysis?
Tracker offers several advantages for analyzing physics experiments, including:
- Visualization: Visualize the motion of objects in a clear and concise manner.
- Quantitative analysis: Obtain accurate measurements of position, velocity, acceleration, and other physical quantities.
- Open-source and free: Accessible to everyone without any licensing costs.
Are there other Tracker models available for exploring different physics concepts?
Yes, Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore provides a vast collection of Tracker models covering various physics topics, including:
- Simple harmonic motion
- Gravity
- Projectile motion
- Collisions
- Waves
- Electricity and Magnetism
Where can I find more information about Tracker and other available models?
You can find a comprehensive list of models and resources on the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore website.
- Details
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 01 Kinematics
- Hits: 5475
