http://weelookang.blogspot.sg/2011/07/blended-learning-workshop-njc-2011-july.html
Briefing Document: Blended Learning and Open Educational Resources in Singapore (2011)
I. Introduction:
This document summarizes the key concepts and ideas discussed at a blended learning workshop held at National Junior College (NJC) in Singapore on July 7, 2011. The workshop focused on the implementation of blended learning approaches, leveraging technology and open educational resources (OER), particularly in the context of physics education in Singapore. It explores the challenges, benefits, models, and tools related to blended learning. The workshop was intended to facilitate a discussion and understanding of "the use of online platforms / tools for e-learning" and "the implementation of blended approaches - challenges and benefits".
II. Key Themes and Ideas:
- Blended Learning Definition: The workshop adopts a broad understanding of blended learning as a combination of various instructional elements: "a mixture of instructional modalities, delivery media, instructional methods, and web-based technologies (Graham, 2006)". It emphasizes the integration of online and face-to-face (F2F) learning experiences to create a more engaging and effective learning environment. The document stresses that blended learning is not just about adding technology, but rather thoughtfully combining the best of online and F2F methods.
- Challenges of Blended Learning Implementation: The workshop identified challenges at various levels:
- Policy Level: While Singapore has government initiatives supporting ICT use in education (MP1, MP2, MP3), there's a need to further support "participatory and localized learning" and ensure access and use of ICT.
- School Level: Schools need to support ongoing professional development for teachers and manage ICT resources effectively. The document notes that Singapore has Professional Learning Communities (PLCs) in schools and Learning Management Systems (LMS) in place, but further integration of LMS with F2F activities is needed.
- Training Providers: These providers should model good ICT practices and use blended methods. The document notes Singapore has the Academy of Singapore Teachers as well as a number of sharing platforms from the schools.
- Individual Level (Teachers): A significant cultural shift is required, moving towards "ongoing, situated, participatory, and collaborative approaches". A challenge at the individual level include the lack of time and money, with teachers resorting to using free platforms like Google Blogger, Google Sites and Facebook and Twitter.
- Benefits of Blended Learning: Drawing on the work of Kerrs and De Witt (2003), the workshop highlights:
- "24/7 access anytime, anywhere and anyplace learning (increase access and flexibility)"
- Integration of online resources with existing F2F learning, augmenting what is lacking in traditional instruction.
- Using a "connect, engage, and participate framing", the workshop further highlights
- Connection: connecting teacher learners and expertise beyond time and space constraints
- Engagement: engaging teacher learners in enriched quality dialogues and in-depth reflective practices
- Participation: fostering ownership and participation from different types of teacher learners
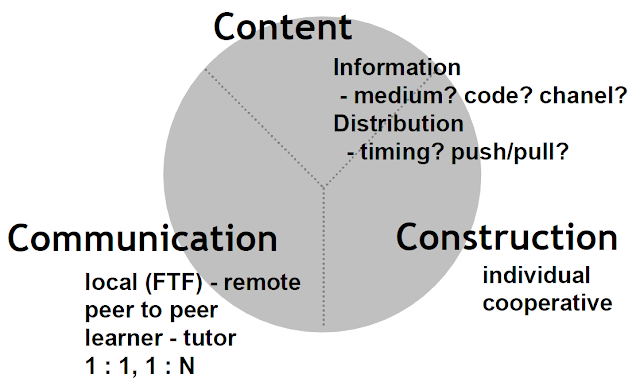
- Components of a Blended Learning Environment: Blended learning can combine three key components:
- Content: Leveraging "WWW links and teacher created" materials.
- Communications: Utilizing platforms like "Facebook, twitter, e-tutoring 1:1 & 1:N".
- Constructions: Encouraging students to engage with simulations, blog about learning, and reflect.
- Active Learning Pedagogy: The document highlights the importance of "HANDS-ON (Active learning pedagogy )INTERACTIVITY EASILY ENABLED" in blended learning. It also mentions that technology can be used to "VISUALIZATION AND SCIENTIFIC VIEW IMPROVED" and that simulations offer a "RISK FREE AND ACCURATE SIMULATION". Blended learning can "AUGMENT WITH REAL EQUIPMENT", and it also is meant to be "SELF DIRECTED AND PACE" and with the capability of "INTEGRATION WITH EXISTING SCHOOL PRACTICE".
- Models of Blended Learning (Penn State): The workshop introduces three models of blended learning from Penn State:
- Supplemental Model: Technology supplements the traditional classroom without reducing F2F time. The workshop presenters suggest that it "could be a beginning phase to start with" when implementing blended learning.
- Replacement Model: Reduces classroom time by replacing some F2F instruction with online activities. It fundamentally changes the in-class experience to more interactive and collaborative work. The presenters express skepticism about the feasibility of this model in Singapore given the need for physical presence in schools, except for students who are homeschooled.
- Emporium Model: Eliminates all F2F meetings, replacing them with a learning resource center and online materials. The presenters see this model as "pretty Future School type of scenario, probably would see it anytime soon."
- Blended Learning Continuum: Drawing from Watson (2008), the workshop participants looked at blended learning models as a continuum ranging from fully face-to-face to fully online and determined that "a possible meaningful blended learning suitable for Singapore physics curriculum" would be a curriculum that blends face-to-face and online components. It was deemed that a "fully online curriculum" was not ideal due to Singapore's well connected nature.
- Tools for Blended Learning:Blogger (Google Blogspot): The workshop recommended Blogger as a preferred blogging platform due to its high searchability on Google, many features, and ability to embed Java applets. The document provides examples of teachers/educators using Blogger for their classes.
- Google Sites: Also highlighted as a platform, several Google Sites used for blended learning initiatives in Singapore are listed as examples.
- Open Educational Resources (OER): The document implicitly promotes OER through the emphasis on free tools like Blogger and Google Sites. The numerous links provided to Java/JavaScript simulations (like those built with Easy Java Simulations) point to the usage of OER for the purpose of creating active learning. It also highlights the use of simulations to enable “learning by inquiry”.
III. Key Quotes:
- "Blended learning is about a mixture of instructional modalities, delivery media, instructional methods, and web-based technologies (Graham, 2006)."
- "change is needed in the culture of teaching and learning so that ongoing, situated, participatory, and collaborative approaches are accepted."
- "24/7 access anytime, anywhere and anyplace learning (increase access and flexibility)"
- "the online resources in a replacement model are fully integrated into the overall instructional effort. The online content acts as a replacement for time that would have been spent in a lecture hall."
- "HANDS-ON (Active learning pedagogy )INTERACTIVITY EASILY ENABLED"
- "VISUALIZATION AND SCIENTIFIC VIEW IMPROVED"
- "RISK FREE AND ACCURATE SIMULATION"
- "AUGMENT WITH REAL EQUIPMENT"
- "SELF DIRECTED AND PACE"
- "INTEGRATION WITH EXISTING SCHOOL PRACTICE"
IV. Implications & Conclusion:
This workshop document provides a snapshot of the early thinking around blended learning in Singapore in 2011, particularly for physics education. It reveals a clear understanding of the potential of technology to enhance learning, while also acknowledging the challenges of implementation. The document advocates for a move toward more participatory and flexible learning models, with a focus on using OER and simulation to create engaging and effective lessons. The preference for the Supplemental model suggests a pragmatic approach to incorporating blended learning into the existing educational structure. The emphasis on both the potential and the challenges of blended learning suggests that the need for teacher training, policy support, and a cultural shift was recognized early on.
This document also acts as an archive of the work being done in Singapore at the time and the Open Educational Resources and Open Source Physics being developed and promoted in the country.
The numerous links to online resources demonstrate a commitment to leveraging these technologies for enhancing science education. The sheer volume of simulations listed also demonstrates the dedication to the creation of such content.
Blended Learning Workshop @NJC 2011 July 07
https://sites.google.com/a/moe.gov.sg/blended-learning-nyc-2011july21/
Activity one: Challenges of BL implementationPolicy
Government should support participatory and localised learning and institutionalise ICT access and use - SG has MP1 , MP2 and MP3Schools
Schools should support on-going teacher learning in the workplace - SG has PLC in schools
Schools should manage ICT resources for use by both teachers and students - SG has LMS
Schools LMS or WWW internet activities integration with F2F classrooms activitiesTraining Providers
Training providers should use blended methods and should model good ICT practices. - SG has Academy of Singapore Teachers. SG has many sharing from the schools. IPSG, National ICT, Zonal COE sharing, ICT mentor, NIE redesign conference etc.Individual level
change is needed in the culture of teaching and learning so that ongoing, situated, participatory, and collaborative approaches are accepted. - SG has MP3 that focus on SDL n CoL with ICT.
Lack of time
Lack of money - SG has some teachers using Free Google Blogger, Google Sites and Google form Facebook, Twitter to blended the learning for students.Benefits: Kerrs and De Witt (2003) Model of Blended Learning taken from http://mediendidaktik.uni-duisburg-essen.de/system/files/Draft-JEM-BL_0.pdf
- 24/7 access anytime, anywhere and anyplace learning (increase access and flexibility)
- integration into existing F2F school experience, augment what is lacking in F2F with online. Using Kerrs and De Witt (2003)
- Content (WWW links and teacher created)
- Communications (Facebook, twitter, e-tutoring 1:1 & 1:N) and
- Constructions (perhaps getting students to do some inquiry on simulations, blog about what they learnt, what was useful etc).
- Connection: connect teacher learners and expertise beyond time/space constraints
- Engagement: engage teacher learners in enriched quality dialogues and in- depth reflective practices
- Participation: foster ownership and participation from different types of teacher learners
- Giving students a voice, Democratizing Knowledge everyone can learn and create, everyone is important.
- allow for opportunity to Self Directed and Self Pace learning.
- if simulations are used, http://ictconnection.edumall.sg/cos/o.x?ptid=711&c=/ictconnection/ictlib&func=view&rid=643 based on student's feedback
- HANDS-ON (Active learning pedagogy )INTERACTIVITY EASILY ENABLED
- VISUALIZATION AND SCIENTIFIC VIEW IMPROVED
- RISK FREE AND ACCURATE SIMULATION
- AUGMENT WITH REAL EQUIPMENT
- SELF DIRECTED AND PACE
- INTEGRATION WITH EXISTING SCHOOL PRACTICE
Activity two: Models of Blended Learning by Penn State
- Supplemental Model
- The supplemental model retains the basic structure of the traditional course and uses technology resources to supplement traditional lectures and textbooks. The supplemental model for blended learning incorporates technology into the instructional approach of the course, but does not alter its basic structure. Students may be required to complete online readings or activities, or participate in lab sessions. However, there is no reduction in course meeting time under the supplemental model; a three-hour course would still meet in-class for three hours per week. My take is implementing BL takes time, perhaps a supplemental model could be a beginning phase to start with.
- Replacement Model
- The replacement model reduces the number of in-class meetings, or classroom "seat-time," and: replaces some in-class time with out-of-class, online, interactive learning activities
-
- makes significant changes in remaining in-class meetings. Under a replacement model, there are fundamental changes to the course. Unlike the supplemental model, the online resources in a replacement model are fully integrated into the overall instructional effort. The online content acts as a replacement for time that would have been spent in a lecture hall. Consequently, the nature of the in-class activities is changed as well. Instead of traditional lectures, in-class time is freed for more interactive, collaborative learning experiences. My take is likely not going to happen in SG, a small place where traveling to school is probably mandatory, except for those learning at home week.
- Emporium Model
- The emporium model eliminates all class meetings and replaces them with a learning resource center. This resource center, typically a large computer lab, offers access to course online materials in addition to live assistance and guidance.
- The emporium model is a radical re-conceptualization of the traditional course. Though attendance at the learning center can be required, there are no longer lectures in a traditional sense. Course content is delivered via online materials, and in-person help is provided in the learning resource center. My take is it seems to be pretty Future School type of scenario, probably would see it anytime soon.
Activity three: Types (Continuum) of Blended Learning
|
Fully Face-to-Face learning Fully Online learning
|
||||||
|
Traditional face-to-face setting with few or no online resources
|
Classroom Instruction integrating online resources, but limited or no requirements for students to be online
|
Classroom Instruction with significant, required online components that extend learning beyond the classroom and beyond the school day
|
Mostly or fully online curriculum in computer lab or classroom where students meet everyday
|
Mostly or fully online curriculum with select days required in computer lab or classroom
|
Fully online curriculum with options for face-to-face instruction, but not required
|
Fully online curriculum with all learning done online and at a distance and no face-to-face
|
|
Many lessons
|
Some lessons
|
A possible meaningful blended learning suitable forSingaporephysics curriculum
|
|
|
|
Not recommended forSingapore lesson due to the fact thatSingapore is well connected country
|
|
Numerous ways of using blended learning that can be incorporated successfully into the classroom
|
||||||
Tools for blended learning
I suggest using Blogger instead of Other Blogs http://weelookang.blogspot.com/ Advantages are
- highly searchable content by Google search engine
- many features
- can embed java applets, critical for experiencing through learning by inquiry through simulations etc.
- http://weelookang.blogspot.com/2010/06/ejs-open-source-micrometer-java-applet.html
- http://weelookang.blogspot.com/2011/05/my-geogebra-portfolio-on-triangle.html
- http://montfortsecprincipal.wordpress.com/
- http://www.banhar.blogspot.com/
- http://tucksoon.wordpress.com/
- http://ashleytan.wordpress.com/
- http://edublog.net/wp/
- http://2010qss304physics.blogspot.com/
My sites in moe.gov.sg
- Blended Approach for PD Shared with everyone in the world
- Blended Learning Shared with everyone in the world
- BLended Learning @NJC 2011July21 Shared with everyone in the world
- Blended Learning Symposium Shared with everyone in the world
- Blended Learning WZ COE Science Shared with everyone in the world
- CrADLe Conference 2011 ETD Shared with everyone in moe.gov.sg
- ePLC Sharing Hands-on Shared with everyone in the world
- ICT Mentor Homecoming 2011 Shared with everyone in the world
- lookang education, technology, high schoolShared with everyone in the worldServing CTHS staff
- PLC Pilot Study Wiki (2010) educationShared with 5 peoplePLC Pilot Study Wiki for year 2010.
- plcpilotstudy educationShared with everyone in the world
- SDL and CoL training and developmentShared with everyone in the worldUnderstanding SDL and CoL in Singapore's Education Context
Reproduced.
Course Description (Background)Schools in Singapore are well equipped with numerous stand-alone ICT tools for teachers in planning ICT-supported lessons. However, not all educators have the knowledge and skills to conduct online learning as well as face to face classroom learning. Many e-learning lessons are either standalone, or not well connected to the face-to-face lessons, with the uploading of lectures notes and video presentations serving only as a repository of lesson archives.
Blended learning is about a mixture of instructional modalities, delivery media, instructional methods, and web-based technologies (Graham, 2006). Combining the best elements of e-learning or online learning and in-person or face-to-face learning, blended learning is likely to emerge as the predominant mode of teaching and learning to engage today’s digital native students who expect their learning environment to include technology.ObjectiveFacilitate a discussion and understanding of:
The use of online platforms / tools for e-learning
The implementation of blended approaches - challenges and benefitsProgramme
2.45-3.45 pm: Sharing by Mr Lak Yak Hui ,Mr Wee Loo Kang and Teh Li Heong , with hands-on sessionInfo
Date: 07 July 2011 (Tuesday)
Time: 2.30 -5.00 pm
Session: 2.45-3.45 pm
Venue: National Junior College NJC Singapore
Location: Computer Lab BYTZ for learning by doing.
View Larger Map
Reference:Kerres, M., & De Witt C. (2003). A didactical framework for the design of blended learning
arrangements. Journal of Educational Media, 28, (2–3).
FAQ on Blended Learning and Open Educational Resources
- What is blended learning and why is it gaining popularity?
- Blended learning is an educational approach that combines online learning with traditional face-to-face instruction. It's gaining popularity because it leverages the benefits of both methods. Online components offer flexibility, 24/7 access, and the ability to personalize learning through various resources and interactions. Face-to-face interactions enable deeper engagement, collaboration and immediate feedback. This combined approach aims to engage today's "digital native" students by integrating technology seamlessly into their learning experience. It aims to go beyond simply archiving content online by actively integrating online resources with classroom teaching.
- What are some common challenges in implementing blended learning, and how can they be addressed?
- Several challenges exist, including the need for a shift in teaching and learning culture to accept ongoing, participatory, and collaborative approaches, a lack of time for teachers to develop and implement new blended approaches, and resource limitations. However, these challenges can be addressed through governmental policies that support localized learning and institutionalize access to ICT, through schools that manage and integrate ICT resources, and through teacher training and professional development. Additionally, the use of free or low-cost online tools (e.g., Google Blogger, Google Sites) can alleviate financial constraints. Schools can start with a "supplemental model" of blended learning and then move to other more substantial models later.
- What are the main models of blended learning and what does implementation of each look like?
- There are primarily three models discussed: the Supplemental Model, the Replacement Model, and the Emporium Model. The Supplemental Model adds online resources to a traditional course without reducing in-class time, like requiring students to complete online readings but still having the standard class time. The Replacement Model reduces in-class time and replaces it with online activities, fundamentally changing the nature of classroom interactions to focus more on active learning. The Emporium Model eliminates traditional class meetings entirely, utilizing a learning resource center (like a computer lab) for access to online materials and in-person assistance. These models exist on a continuum from fully face-to-face to fully online instruction.
- How can blended learning promote student-centered learning experiences?
- Blended learning allows for opportunities for Self-Directed and Self-Paced learning. It promotes student-centered learning by giving students a voice and fostering a democratic approach to knowledge creation and ownership. By using simulations and online platforms, students can actively engage in inquiries, reflect on their learning through blogging or journaling and explore topics at their own pace. The use of simulations allows for visualization and a "risk-free" environment to experiment with.
- What are some examples of online tools and platforms that can be used in blended learning?
- The resource mentions several tools including Google Blogger, Google Sites, Facebook, and Twitter as platforms for content, communication, and student constructions. Specifically, Blogger is highlighted for its searchability and ability to embed interactive elements like Java applets and HTML5 simulations. The Singapore Student Learning Space (SLS) is also cited as a resource, although the focus of the materials leans more heavily on self-made, or open access resources.
- What is the importance of open educational resources (OER) and open-source physics (OSP) in blended learning?
- Open educational resources and open-source physics are critical to making blended learning models scalable and affordable. These resources allow teachers to access and share content, simulations, and activities without financial barriers. By using OER, teachers can customize resources to fit the specific needs of their students and subject matter. Open-source physics also allows for customization. Moreover, using open-source solutions facilitates the sharing of effective blended learning approaches among different educators, fostering a community of practice that drives innovation and improvement. The focus is on ensuring that access to quality learning tools is widely available.
- How can simulations and interactive elements enhance blended learning experiences?
- Simulations and interactive elements can enhance blended learning by providing opportunities for hands-on, active learning that goes beyond traditional lectures. Simulations allow students to visualize abstract concepts, test their ideas in a risk-free environment, and deepen their scientific understanding. Interactivity makes learning more engaging and caters to different learning styles. These tools also offer data for analysis and modeling, moving learners from passive observation to active inquiry, which allows them to explore complex processes or phenomena.
- What role do teachers play in a blended learning environment, and how does this change from traditional teaching roles?
- Teachers in a blended learning environment shift from being primarily lecturers to facilitators of learning. They design and curate learning experiences, support students in navigating online resources, foster collaboration, and guide students' inquiries. They become leaders in building and participating in learning communities, both online and offline. The resource also points to the need for teacher professional development and ongoing support to adapt to new modes of instruction, to model effective use of technology, and to use the data provided to refine teaching practice and learning experiences.