
About
For Teachers
- 130.mp4
- 130-frame.mp4
- 130-frame.gif
Credits
"2/6 Paper Square Drag to Terminal Velocity SYPT2016 by Tze Kwang Leong"
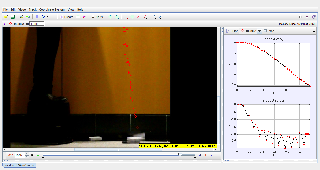
This study examines the drag forces and terminal velocity of a 2/6 paper square as it falls through the air. Utilizing Tracker software, the research investigates how increased surface area influences air resistance, stabilization, and descent behavior, offering insights into aerodynamic principles.
Study Guide:
Objective:
- Analyze the effects of surface area on drag and terminal velocity.
- Investigate stabilization and descent patterns of a 2/6 paper square.
Key Concepts:
-
Drag Force and Surface Area:
- Larger surfaces encounter more air resistance, affecting terminal velocity.
-
Terminal Velocity Dynamics:
- A balance point where gravitational force equals air resistance, resulting in constant speed.
-
Stability in Free Fall:
- Wider objects may exhibit fluttering or oscillatory motion due to uneven drag forces.
-
Material Density and Fall Dynamics:
- Low-density materials interact strongly with air resistance.
Experiment Overview:
-
Setup:
A 2/6 paper square is dropped from a fixed height, recorded using high-speed video, and analyzed with Tracker software. -
Procedure:
- Release the paper square under controlled conditions.
- Record the motion focusing on velocity and acceleration profiles.
- Analyze the data using Tracker to calculate terminal velocity and observe stabilization.
- Introduce slight disturbances to test response and stability.
-
Observation Points:
- Time to achieve terminal velocity.
- Stabilization of the square during descent.
- Velocity and acceleration profiles.
Questions to Consider:
-
How does doubling the surface area impact terminal velocity?
- Answer: Doubling the surface area increases drag, reducing terminal velocity and prolonging descent time.
-
What factors contribute to fluttering or oscillation?
- Answer: Uneven drag forces, initial disturbances, and air currents can induce instability.
-
How can the descent pattern be stabilized?
- Answer: Uniform release and reducing external disturbances help achieve smoother motion.
-
What are the benefits of using Tracker software?
- Answer: It allows for precise measurement of displacement, velocity, and acceleration to analyze complex motion patterns.
-
How does the paper square's material affect its fall?
- Answer: The lightweight nature amplifies air resistance effects, highlighting drag and stability dynamics.
Applications:
- Physics Education: Illustrating aerodynamic principles and the effects of drag.
- Design Optimization: Applying findings to lightweight material applications like parachutes.
- Aerodynamics Research: Understanding stabilization techniques for flat, lightweight surfaces.
Version
http://weelookang.blogspot.sg/2016/08/sypt2016-workshop-materials.html
FAQ:
-
What is unique about the 2/6 paper square compared to 1/6?
- A larger surface area increases drag force, reducing terminal velocity and making stabilization more complex.
-
Why study paper squares of different sizes?
- Exploring variations highlights how surface area impacts motion dynamics and terminal velocity.
-
How does fluttering occur in this experiment?
- Fluttering results from uneven drag distribution and can be visualized effectively using Tracker software.
-
What are potential challenges?
- Controlling environmental factors like air currents and ensuring consistent release conditions.
-
Can the findings be applied to real-world systems?
- Yes, especially in the design of drag-based devices like parachutes or sails.
- Details
- Written by leongster
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 02 Dynamics
- Hits: 5207
