
About
For Teachers
Credits
Author: Leong Tze Kwang
Document Brief: Title: "Tracker Gymnast: Center of Gravity Analysis by RGS Leong Tze Kwang"
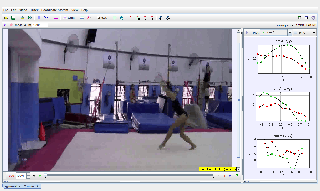
This document explores the concept of center of gravity (CG) using a gymnast’s movements as a practical example. RGS Leong Tze Kwang’s analysis demonstrates how a gymnast’s CG shifts during various poses and movements, providing insights into balance, stability, and body dynamics.
Study Guide:
Objective: Understand the principles of center of gravity by analyzing a gymnast’s body positions and their impact on balance and motion.
Key Concepts:
-
Center of Gravity (CG):
-
The point where the mass of an object or body is concentrated and balanced in all directions.
-
-
Stability and Balance:
-
A lower CG generally improves stability, while a higher CG increases the risk of toppling.
-
-
Body Dynamics:
-
Movements and poses that shift the CG affect a gymnast’s ability to maintain balance and perform controlled motions.
-
Experiment Overview:
-
Setup: Analyze various poses of a gymnast, noting CG positions relative to their base of support.
-
Procedure:
-
Observe static and dynamic poses.
-
Identify the CG location and its movement during transitions.
-
-
Observation Points:
-
How the CG shifts in different poses.
-
The relationship between CG and the gymnast’s stability.
-
Questions to Consider:
-
How does the gymnast’s CG change with different body positions?
-
What strategies do gymnasts use to control their CG and maintain balance?
-
How does the placement of limbs affect the overall CG?
Applications:
-
Enhancing performance and safety in sports involving balance and agility.
-
Applying CG principles to robotics, engineering, and ergonomics.
FAQ:
-
Why study a gymnast’s center of gravity? A gymnast’s movements provide a clear example of how CG influences stability and motion, which is fundamental in physics and biomechanics.
-
How does the CG affect balance? The closer the CG is to the base of support, the more stable the gymnast. When the CG moves outside the base, balance is harder to maintain.
-
What role do limb movements play in CG shifts? Extending or retracting limbs shifts the CG, which gymnasts use to control their movements and poses.
-
How does this study apply to real-world scenarios? Understanding CG is crucial in designing stable structures, improving athletic performance, and developing balanced robotic systems.
-
Would the CG principles change in microgravity? In microgravity, the concept of a fixed CG becomes less relevant, as there is no weight to create balance constraints.
- Details
- Written by leongster
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 02 Dynamics
- Hits: 5635
