
About
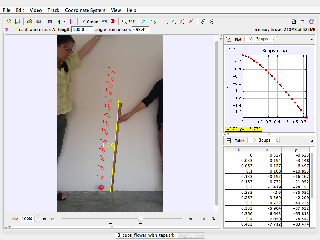
Free fall with air resistance, using 3 cupcake cups stacked arrangement
For Teachers
- 3CupStackedFreeFall22.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall21.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall20.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall19.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall18.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall17.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall16.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall15.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall14.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall13.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall12.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall11.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall10.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall09.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall08.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall07.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall06.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall05.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall04.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall03.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall02.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall01.jpg
- 3CupStackedFreeFall00.jpg
Credits
Author: Thomas Yeu
Contact: yeu_chee_wee_thomas@moe.edu.sg
Document Brief: Title: "Three Stacked Paper Cups Falling: A Study by MJC Thomas Yeu"
This document explores the dynamics of three stacked paper cups in free fall, as analyzed by MJC Thomas Yeu. The study investigates how stacking influences factors like stability, air resistance, and motion, drawing connections to fundamental principles of physics.
Study Guide:
Objective: Analyze the behavior of three stacked paper cups during free fall and understand the effects of stacking on descent dynamics.
Key Concepts:
-
Stability in Free Fall:
-
Stacked objects may have a different center of mass and structural integrity, influencing their fall.
-
-
Air Resistance and Surface Area:
-
Increased surface area due to stacking can lead to greater drag force, altering the fall rate.
-
-
Gravitational Force:
-
Gravity acts uniformly on all objects, but variations in descent arise from differences in air resistance and stability.
-
Experiment Overview:
-
Setup: Three identical paper cups stacked together and dropped from a height.
-
Procedure: Observe their descent, recording any wobbling, separation, or other behaviors.
-
Observation Points:
-
Compare with the fall of single or two stacked cups.
-
Monitor stability and alignment during descent.
-
Questions to Consider:
-
How does stacking three cups impact their stability compared to two stacked cups?
-
What role does air resistance play in the descent of three stacked cups?
-
How might altering the stacking method or adding weight change the results?
Applications:
-
Investigating the stability of stacked configurations in various free-fall contexts.
-
Gaining insights into the aerodynamics of multi-body systems in motion.
FAQ:
-
Why study three stacked cups in free fall? Studying three stacked cups provides a model for understanding how complex stacking arrangements behave under gravity and air resistance, with practical implications in physics and engineering.
-
What is the difference between two and three stacked cups? Adding an extra cup increases both the height and surface area of the stack, potentially altering stability and air resistance.
-
How does air resistance affect the fall? Increased surface area from stacking can create more drag, slowing the descent and potentially causing instability.
-
Would the results differ with heavier or differently shaped cups? Yes, heavier or differently shaped cups would change the center of mass, inertia, and drag, influencing their falling behavior.
-
What are real-world applications of this study? Applications include designing stacked configurations in transport systems, understanding aerodynamic drag in multi-body systems, and ensuring stability in free-falling structures like satellites.
- Details
- Written by leongster
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 02 Dynamics
- Hits: 5446
