
About
For Teachers
Credits
Title: "Tracker 5/6 Increasing Accelerating Car: Using Model Builder to Simplify Graphs for Secondary School"
This document examines the motion of a car with increasing acceleration using Tracker software and its Model Builder tool. The goal is to create simplified graphs that illustrate complex kinematic concepts for secondary school students.
Study Guide:
Objective:
- Analyze the motion of a car with increasing acceleration.
- Use Model Builder to construct and simplify graphical representations for educational purposes.
Key Concepts:
-
Non-Uniform Acceleration:
- Acceleration increases over time, resulting in progressively faster changes in velocity.
-
Key Graphs:
- Displacement vs. Time: Exponential curve representing rapidly increasing distance.
- Velocity vs. Time: Upwardly curving line due to increasing acceleration.
- Acceleration vs. Time: A line with a positive slope indicating growing acceleration.
-
Model Builder:
- A Tracker tool that generates theoretical models to compare with experimental data, simplifying complex motion for students.
Experiment Overview:
-
Setup:
Record a video of a car undergoing increasing acceleration on a flat, friction-controlled surface, ensuring steady tracking and consistent lighting. -
Procedure:
- Import the video into Tracker and analyze the car's position over time.
- Extract data for displacement, velocity, and acceleration.
- Use Model Builder to create a theoretical model with increasing acceleration.
- Compare the theoretical model with the experimental data.
- Simplify the graphs for instructional purposes.
-
Observation Points:
- Exponential growth in the displacement graph due to rapidly increasing speed.
- Non-linear velocity graph showing accelerated growth.
- Positive-slope acceleration graph indicating increasing force or power.
Questions to Consider:
-
What factors cause increasing acceleration in the car?
- Answer: Gradually increasing engine power or reducing opposing forces (e.g., friction).
-
Why is the displacement graph exponential?
- Answer: The car covers larger distances in shorter intervals as it speeds up faster over time.
-
How does the velocity graph reflect non-uniform acceleration?
- Answer: Its upward curvature indicates faster velocity changes over time.
-
What does the slope of the acceleration graph represent?
- Answer: The rate of increase in acceleration due to growing force.
-
How does Model Builder assist in understanding increasing acceleration?
- Answer: It provides theoretical trends to clarify experimental observations, making them accessible to students.
Applications:
- Physics Education: Simplifies complex kinematic behaviors for classroom understanding.
- Engineering Insights: Offers foundational knowledge for vehicle performance analysis.
- Graph Interpretation: Builds skills in analyzing and comparing theoretical and experimental data.
ICT Connection Lesson
http://library.opal.moe.edu.sg/ictc&func=view&rid=2094
http://library.opal.moe.edu.sg/ictc&func=view&rid=2094
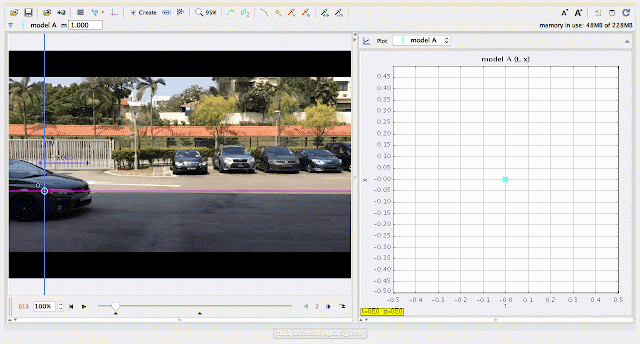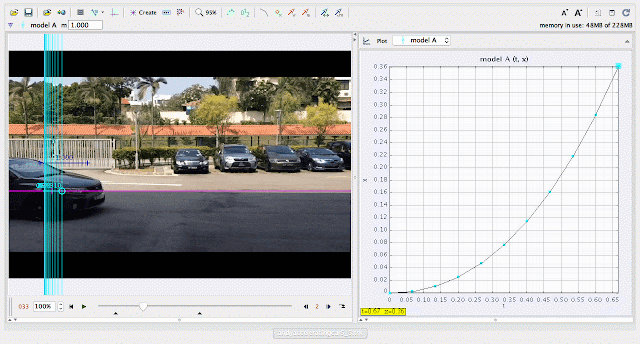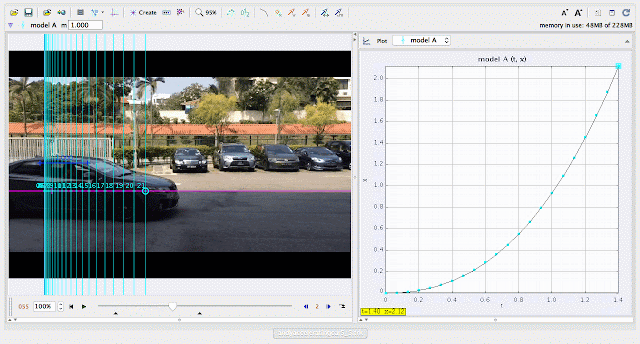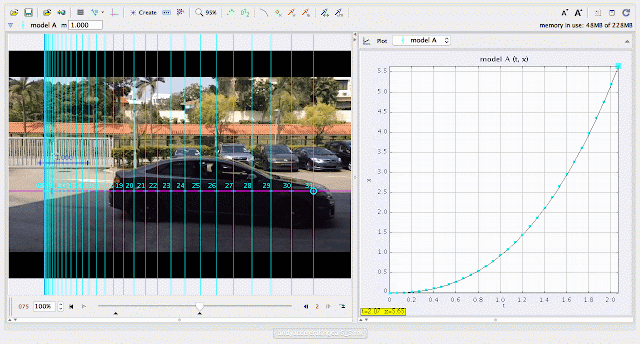 |
| using Tracker Model Builder to create theoretic graphs for simplifying Physics concepts. increasing position x^3 motion is illustrated through position x versus time graph |
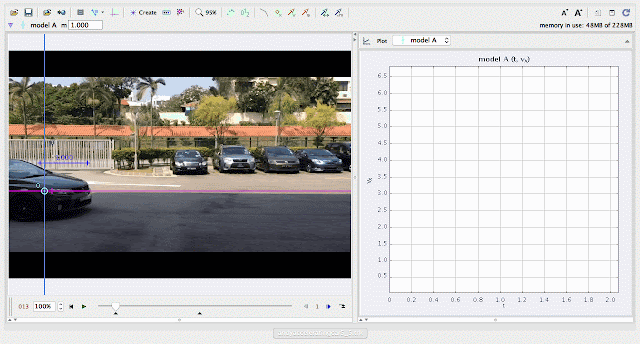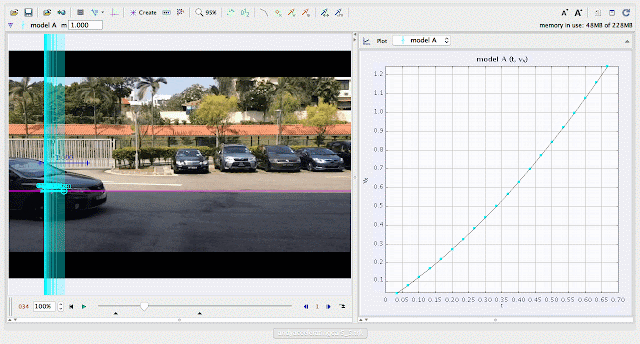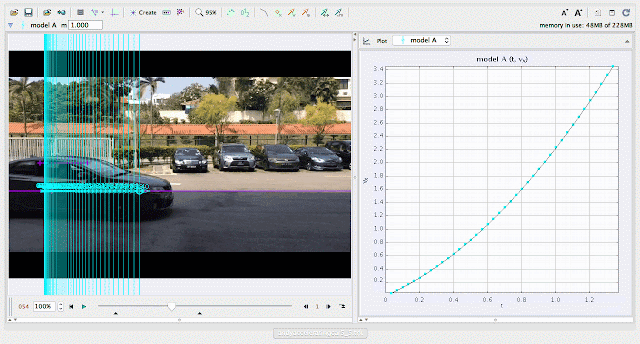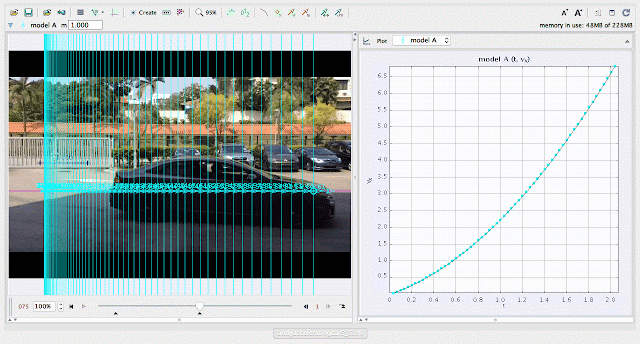 |
| using Tracker Model Builder to create theoretic graphs for simplifying Physics concepts. increasing velocity vx^2 motion is illustrated through position vx versus time graph |
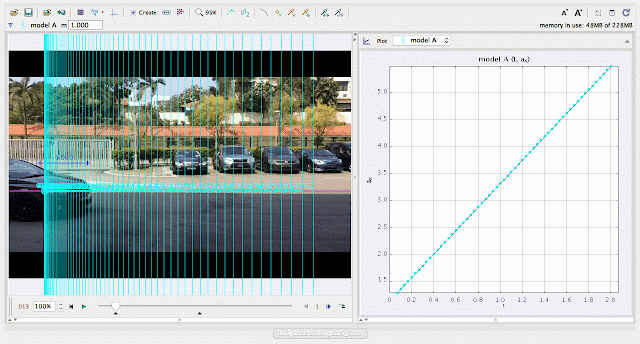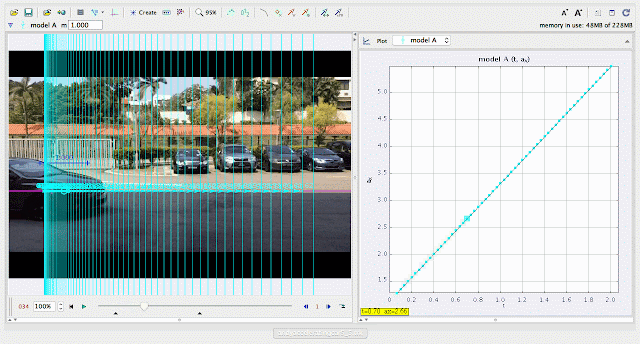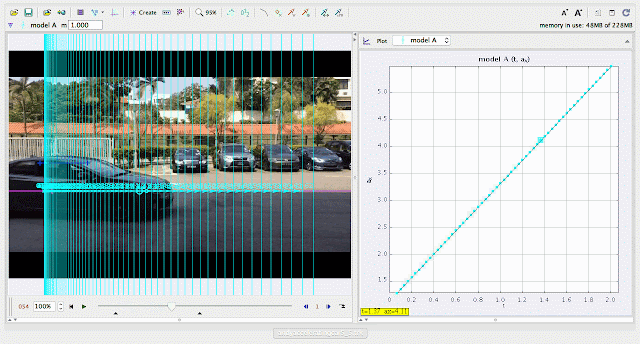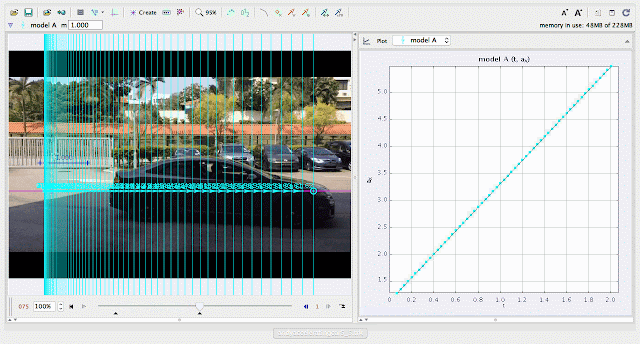 |
| using Tracker Model Builder to create theoretic graphs for simplifying Physics concepts. increasing acceleration ax^1 motion is illustrated through position ax versus time graph |
FAQ:
-
Why does the car accelerate at an increasing rate?
- The increasing force applied to the car overcomes inertia more effectively over time.
-
How can Model Builder accommodate increasing acceleration?
- It allows input of variable forces or equations to simulate realistic motion trends.
-
What real-world examples parallel this experiment?
- Rocket launches, vehicles under turbo boost, or objects on decreasingly resistive surfaces.
-
What challenges might arise in tracking increasing acceleration?
- Maintaining precise measurements at high speeds and accounting for external influences like drag.
-
How can this study be expanded?
- Explore the effects of varying mass, introduce drag forces, or study acceleration limits in different scenarios.
- Details
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 01 Kinematics
- Hits: 6736
