
About
For Teachers
Credits
Author: Andy Video, Lawrence Model
Contact: yeo_wei_yong_andy@moe.edu.sg
Title: "Tracker 4/6 Accelerating Car: Using Model Builder to Simplify Graphs for Secondary School"
This document focuses on analyzing the motion of an accelerating car using Tracker software and its Model Builder tool. The aim is to create simplified graphs that help secondary school students understand fundamental concepts in kinematics, such as acceleration and velocity.
Study Guide:
Objective:
- Observe and analyze the motion of an accelerating car.
- Use Model Builder to generate simplified graphical representations for educational purposes.
Key Concepts:
-
Uniform Acceleration:
- Motion where the car's velocity increases linearly over time due to a constant force.
-
Key Graphs:
- Displacement vs. Time: Represents the increasing distance traveled by the car.
- Velocity vs. Time: A straight line indicating constant acceleration.
- Acceleration vs. Time: A horizontal line representing constant acceleration.
-
Model Builder:
- A Tracker feature that helps visualize theoretical motion alongside experimental data.
Experiment Overview:
-
Setup:
Record a video of a car accelerating on a straight path, ensuring clear visibility of motion and consistent frame rate. -
Procedure:
- Import the video into Tracker and mark the car's position frame by frame.
- Extract data for displacement, velocity, and acceleration over time.
- Use Model Builder to create a theoretical motion model based on uniform acceleration.
- Compare experimental data with the theoretical model.
- Generate simplified graphs for secondary school instruction.
-
Observation Points:
- Linear increase in velocity over time due to constant acceleration.
- Parabolic displacement graph characteristic of uniform acceleration.
- Horizontal acceleration graph showing constant value.
Questions to Consider:
-
What causes the car to accelerate uniformly?
- Answer: A constant net force, such as the engine force overcoming resistance.
-
Why is the displacement-time graph parabolic?
- Answer: The car covers increasingly larger distances as it gains speed.
-
How does the slope of the velocity-time graph relate to acceleration?
- Answer: The slope represents the magnitude of constant acceleration.
-
How does Model Builder assist in understanding motion?
- Answer: It generates theoretical trends, providing a benchmark to compare experimental data.
-
What can we learn from deviations between experimental and theoretical graphs?
- Answer: Deviations can indicate factors like friction, air resistance, or measurement errors.
Applications:
- Physics Education: Demonstrates kinematics principles in real-world contexts.
- Graphical Analysis: Develops skills in interpreting motion graphs.
- Engineering Insights: Provides foundational understanding for vehicle dynamics and design.
ICT Connection Lesson
http://library.opal.moe.edu.sg/ictc&func=view&rid=2094
http://library.opal.moe.edu.sg/ictc&func=view&rid=2094
 |
| using Tracker Model Builder to create theoretic graphs for simplifying Physics concepts. uniform acceleration motion is illustrated through position x versus time graph |
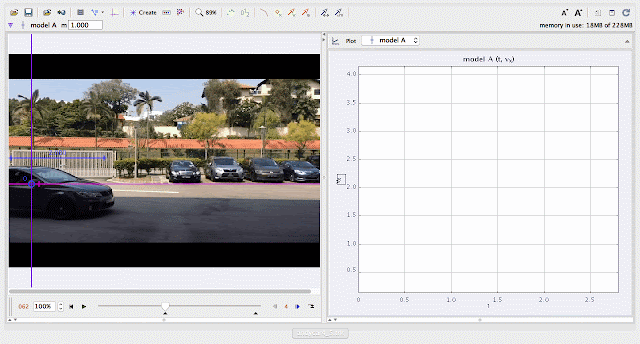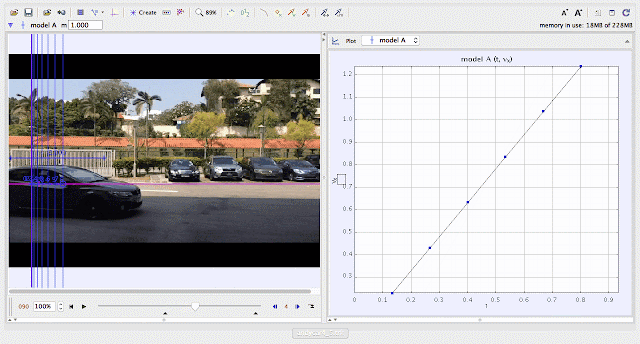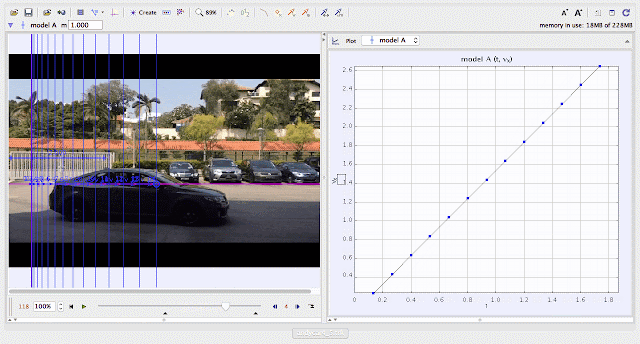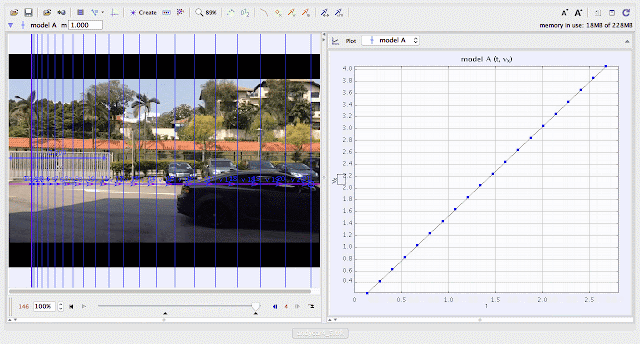 |
| using Tracker Model Builder to create theoretic graphs for simplifying Physics concepts. uniformly increasing velocity motion is illustrated through position vx versus time graph |
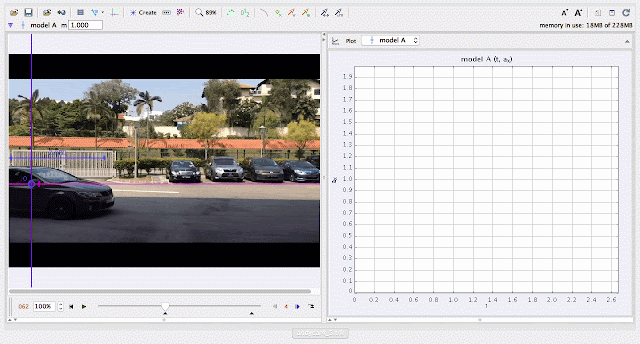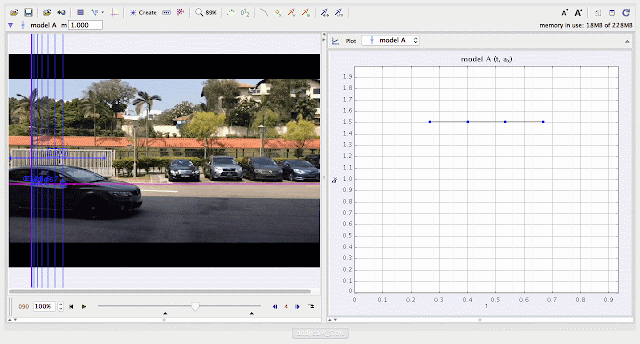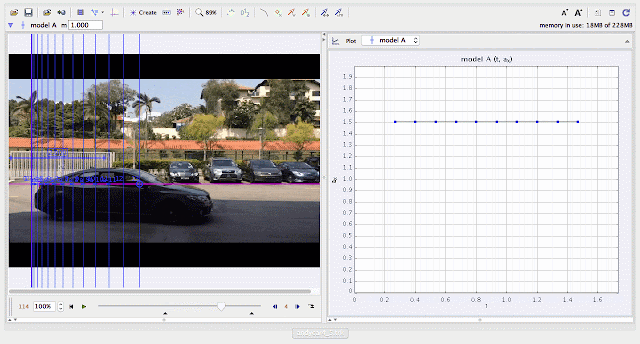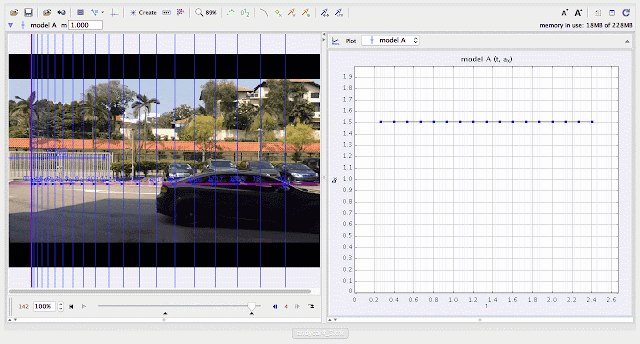 |
| using Tracker Model Builder to create theoretic graphs for simplifying Physics concepts. uniform acceleration motion is illustrated through position ax versus time graph |
FAQ:
-
Why use Model Builder for this experiment?
- To create clear and simplified visualizations of motion, aiding student comprehension.
-
What factors might affect the accuracy of experimental data?
- Air resistance, uneven terrain, or errors in video tracking can cause discrepancies.
-
Can this model include non-uniform acceleration?
- Yes, Model Builder allows for adjustments to reflect changing acceleration.
-
How does this study apply to real-world scenarios?
- It mirrors real-life applications, such as understanding vehicle performance and safety.
-
What additional experiments can follow this study?
- Investigating the effects of friction, varying forces, or drag on the car’s motion.
- Details
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 01 Kinematics
- Hits: 7071

