
About
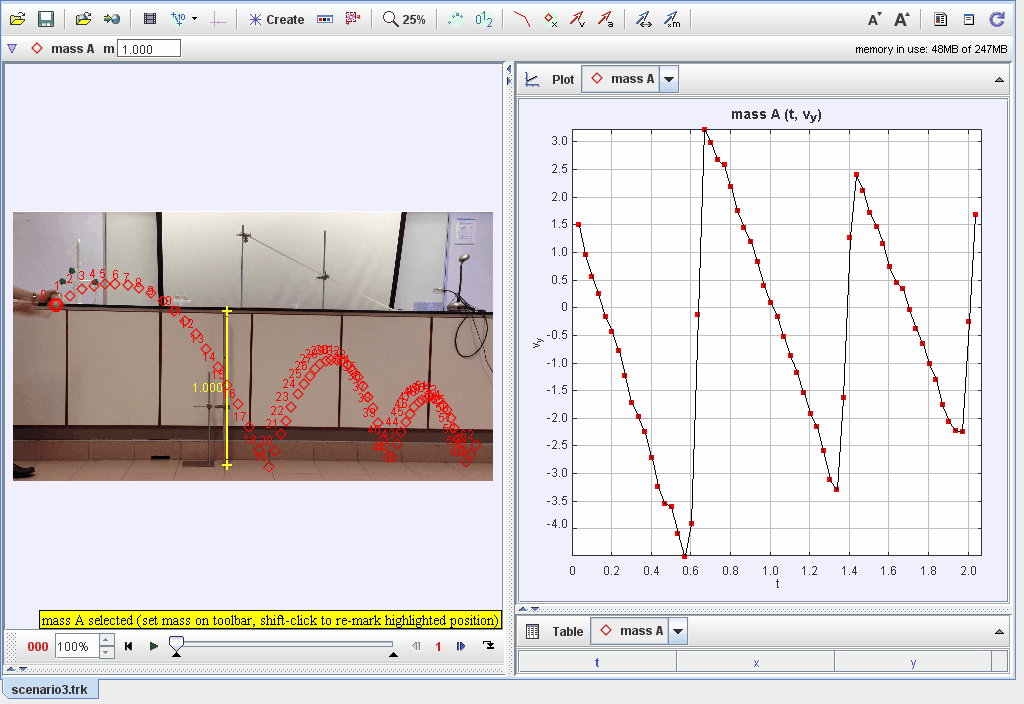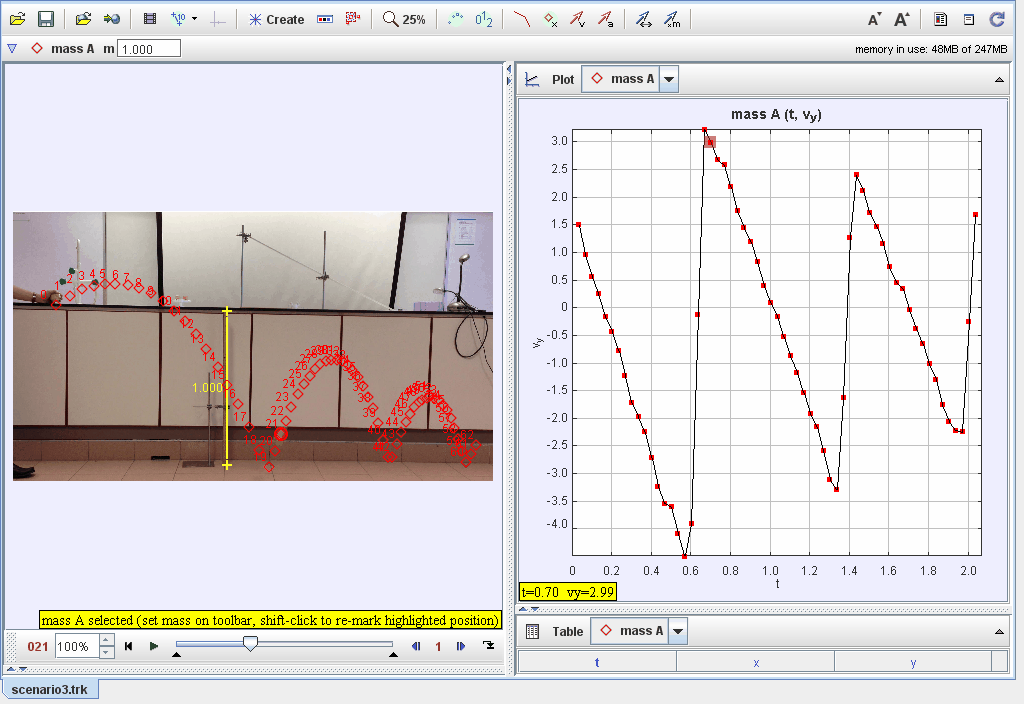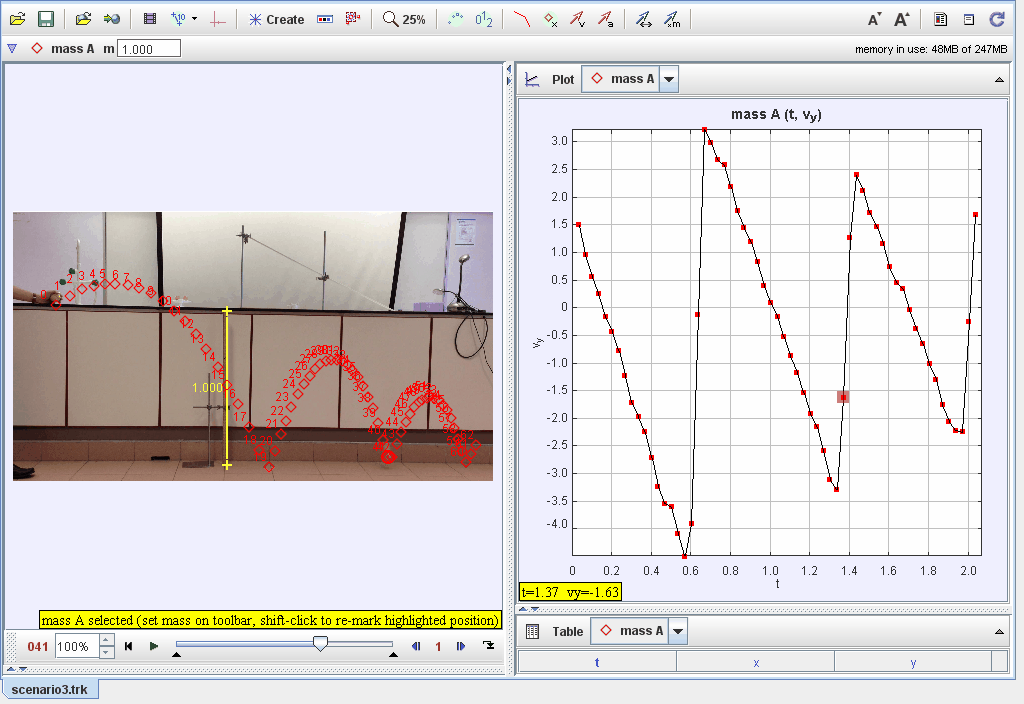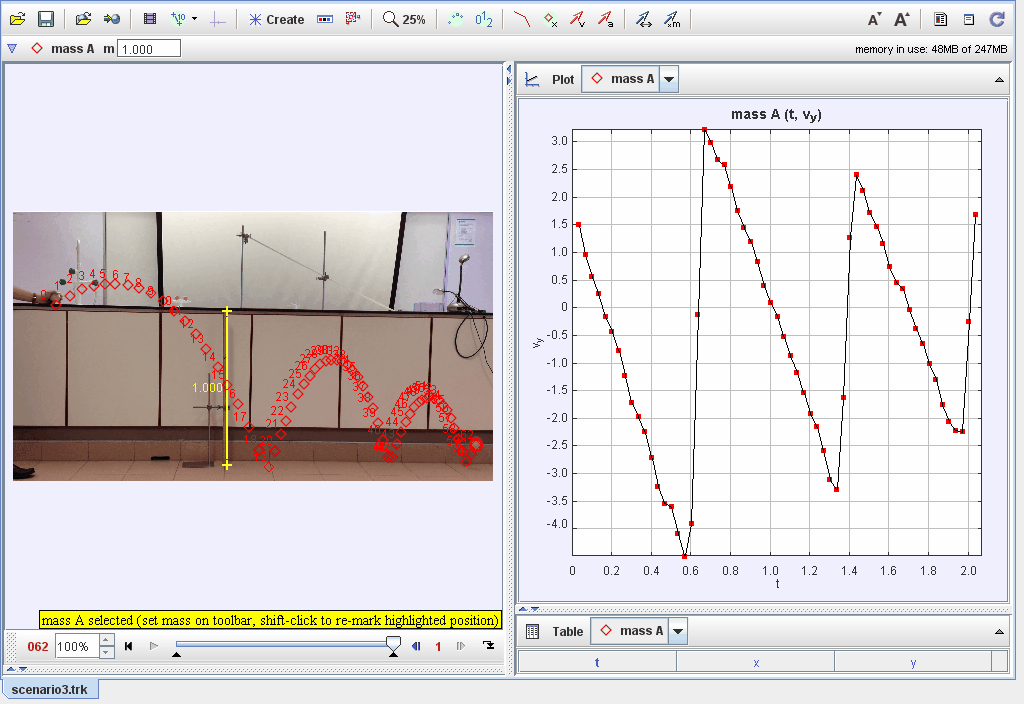
Video analysis of tennis ball bouncing forward in projectile motion (Scenario 3).
For Teachers
- scenario65.jpg
- scenario64.jpg
- scenario63.jpg
- scenario62.jpg
- scenario61.jpg
- scenario60.jpg
- scenario59.jpg
- scenario58.jpg
- scenario57.jpg
- scenario56.jpg
- scenario55.jpg
- scenario54.jpg
- scenario53.jpg
- scenario52.jpg
- scenario51.jpg
- scenario50.jpg
- scenario49.jpg
- scenario48.jpg
- scenario47.jpg
- scenario46.jpg
- scenario45.jpg
- scenario44.jpg
- scenario43.jpg
- scenario42.jpg
- scenario41.jpg
- scenario40.jpg
- scenario39.jpg
- scenario38.jpg
- scenario37.jpg
- scenario36.jpg
- scenario35.jpg
- scenario34.jpg
- scenario33.jpg
- scenario32.jpg
- scenario31.jpg
- scenario30.jpg
- scenario29.jpg
- scenario28.jpg
- scenario27.jpg
- scenario26.jpg
- scenario25.jpg
- scenario24.jpg
- scenario23.jpg
- scenario22.jpg
- scenario21.jpg
- scenario20.jpg
- scenario19.jpg
- scenario18.jpg
- scenario17.jpg
- scenario16.jpg
- scenario15.jpg
- scenario14.jpg
- scenario13.jpg
- scenario12.jpg
- scenario11.jpg
- scenario10.jpg
- scenario09.jpg
- scenario08.jpg
- scenario07.jpg
- scenario06.jpg
- scenario05.jpg
- scenario04.jpg
- scenario03.jpg
- Kinematics Video Analysis using Tracker (tutor).pdf
- Kinematics Video Analysis using Tracker (student).pdf
Credits
Author: Thomas Yeu, MJC Physics
Contact: yeu_chee_wee_thomas@moe.edu.sg
Document Brief: Title: "Tracker Scenario 3 Object Bouncing by MJC Thomas Yeu"
This document explores the dynamics of an object bouncing after being dropped from a height, focusing on energy transformations, restitution, and damping effects. Observations and models are used to investigate the factors affecting the motion and behavior of the bouncing object.
Study Guide:
Objective: Analyze the bouncing motion of an object, examining energy conversion, the coefficient of restitution, and how external factors influence its behavior.
Key Concepts:
-
Energy Transformation:
-
Conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy during free fall and vice versa during the bounce.
-
-
Coefficient of Restitution (e):
-
A measure of elasticity, indicating how much kinetic energy is retained after a collision.
-
-
Damping:
-
The reduction in bounce height over time due to energy loss through heat, sound, and deformation.
-
-
Motion Analysis:
-
Using kinematic equations to describe position, velocity, and acceleration during successive bounces.
-
Experiment Overview:
-
Setup: An object is dropped onto a hard surface, and its motion is recorded using video analysis tools or sensors.
-
Procedure:
-
Drop the object from a known height and record its bounces.
-
Measure the height of each bounce and calculate the coefficient of restitution.
-
Analyze how material properties and surface type affect the motion.
-
-
Observation Points:
-
Energy loss between bounces.
-
Patterns in velocity and acceleration.
-
Effects of object and surface material properties.
-
Questions to Consider:
-
How does the coefficient of restitution vary with different materials?
-
What factors contribute to energy loss in the system?
-
How does damping affect the motion of the bouncing object?
Applications:
-
Understanding energy dissipation in mechanical systems.
-
Designing sports equipment and safety materials.
-
Exploring collision dynamics in physics and engineering.
FAQ:
-
Why study bouncing objects? Bouncing dynamics illustrate fundamental principles of energy conservation, collision physics, and material behavior.
-
What is the coefficient of restitution? It is a dimensionless value that quantifies the elasticity of a collision, ranging from 0 (perfectly inelastic) to 1 (perfectly elastic).
-
What causes damping in a bouncing object? Damping arises from energy loss due to heat, sound production, and material deformation.
-
How do surface properties affect bouncing? Harder, more elastic surfaces typically result in higher bounce heights, while softer surfaces absorb more energy.
-
What are practical applications of this study? Insights are used in designing sports balls, vehicle suspensions, shock absorbers, and materials for energy efficiency and impact safety.
- Details
- Written by leongster
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 01 Kinematics
- Hits: 5336
