
About
For Teachers
- KoayTzeMinrollerbladingmodel.mp4
Credits
Author: author of video: KoayTzeMin, author of model: lookang
Contact: weelookang@gmail.com
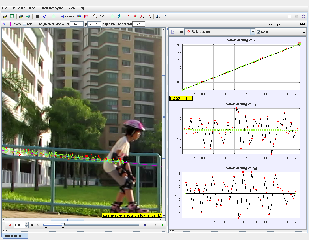
Roller Blading Down a Slope: A Tracker Physics Study Guide
I. Short Answer Questions
Instructions: Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
- What is the purpose of using Tracker software in physics experiments?
- Describe a real-world scenario where analyzing the motion of an object rolling down a slope would be relevant.
- How can Tracker help determine the acceleration of a rollerblader going down a slope?
- What are some potential sources of error when using Tracker to analyze motion?
- Explain the concept of a reference frame in the context of Tracker analysis.
- Why is it important to calibrate the video footage in Tracker before analyzing the motion?
- What types of data can be extracted from a Tracker analysis of a rollerblading video?
- How can you use Tracker to compare the motion of a rollerblader on slopes with different angles?
- What are the limitations of using Tracker to analyze motion in real-world scenarios?
- How can understanding the physics of rollerblading down a slope inform the design of rollerblades or skateparks?
II. Short Answer Key
- Tracker software allows for the analysis of video footage to track the motion of objects over time. This enables the calculation of physical quantities like velocity, acceleration, and position.
- Analyzing the motion of a car rolling down a hill during a safety test is a relevant scenario. Tracker could be used to determine the car's acceleration and velocity, helping engineers assess the effectiveness of braking systems.
- By tracking the position of the rollerblader in each frame of the video, Tracker can calculate the change in velocity over time, which provides the acceleration.
- Sources of error in Tracker analysis include blurry video footage, inaccurate calibration, and difficulty identifying the object's center of mass in each frame.
- The reference frame is the viewpoint from which the motion is observed. In Tracker, you define a coordinate system that acts as the reference frame for your analysis.
- Calibration involves establishing a known distance within the video footage. This allows Tracker to accurately convert pixel measurements into real-world units, ensuring accurate data analysis.
- Tracker analysis can provide data on the object's position, velocity, and acceleration over time. Additionally, you can derive information about the object's trajectory and energy.
- By analyzing separate videos of the rollerblader on different slopes, Tracker can calculate and compare the accelerations, velocities, and trajectories for each scenario.
- Tracker's reliance on clear video footage and precise calibration can be limitations in real-world scenarios where environmental factors may interfere with data collection.
- Understanding how slope angle and friction affect a rollerblader's motion can inform the design of rollerblades with specific wheel configurations for different terrains or the construction of skateparks with varying ramp angles for diverse skill levels.
III. Essay Questions
- Discuss the relationship between the angle of a slope and the acceleration of a rollerblader traveling down it. How do factors like friction and air resistance come into play?
- Compare and contrast the motion of a rollerblader going down a straight slope versus a curved slope. How would the analysis in Tracker differ between these scenarios?
- Explain how the concepts of potential and kinetic energy apply to a rollerblader descending a slope. Use Tracker data to support your explanation.
- Imagine you are designing a skatepark. How could you use Tracker to test and refine the design of ramps and other features to ensure safe and exciting experiences for skaters?
- Critically evaluate the strengths and limitations of Tracker as a tool for physics education. Discuss how it can enhance student understanding of motion but also acknowledge potential drawbacks or challenges.
IV. Glossary of Key Terms
- Tracker: Open-source video analysis and modeling software used in physics education to track the motion of objects.
- Acceleration: The rate of change of velocity over time.
- Velocity: The rate of change of position over time, including both speed and direction.
- Reference Frame: The viewpoint from which motion is observed and measured.
- Calibration: Establishing a known distance within video footage to ensure accurate measurements in Tracker.
- Trajectory: The path an object takes as it moves through space.
- Potential Energy: Stored energy due to an object's position or configuration.
- Kinetic Energy: Energy possessed by an object due to its motion.
- Friction: A force that opposes motion between surfaces in contact.
- Air Resistance: A force that opposes the motion of objects through the air.
Rollerblading Down a Slope: FAQ
1. What is Tracker?
Tracker is a free and open-source video analysis and modeling tool that can be used to study the motion of objects. It is commonly used in physics education to analyze videos of experiments and create models of physical phenomena.
2. How can I use Tracker to study rollerblading down a slope?
To use Tracker to study rollerblading, you would first need to record a video of someone rollerblading down a slope. Then, you would import the video into Tracker and use the software to track the motion of the rollerblader. Tracker can be used to measure the rollerblader's position, velocity, and acceleration. This data can then be used to create a model of the rollerblader's motion, which can be used to predict the rollerblader's future motion.
3. What are some of the physics concepts involved in rollerblading down a slope?
Some of the physics concepts involved in rollerblading down a slope include gravity, friction, and energy. Gravity is the force that pulls the rollerblader down the slope. Friction is the force that opposes the rollerblader's motion. Energy is the ability to do work.
4. How does gravity affect rollerblading down a slope?
Gravity causes the rollerblader to accelerate down the slope. The steeper the slope, the greater the acceleration.
5. How does friction affect rollerblading down a slope?
Friction slows the rollerblader down. The amount of friction depends on the surface of the slope and the rollerblader's wheels.
6. How does energy play a role in rollerblading down a slope?
As the rollerblader goes down the slope, their potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. Potential energy is the energy that an object has due to its position. Kinetic energy is the energy that an object has due to its motion.
7. What are some of the safety considerations for rollerblading down a slope?
Some of the safety considerations for rollerblading down a slope include wearing a helmet and pads, choosing a safe slope, and being aware of your surroundings.
8. Where can I find more resources on Tracker and physics education?
The Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore website provides a variety of resources on Tracker and physics education. These resources include tutorials, simulations, and sample projects. You can also find many other resources online, including videos, articles, and forums.
- Details
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 02 Dynamics
- Hits: 5620
