
About
For Teachers
- Rachelongapplicationsmodel.mp4
Credits
Author: author of video: rachelong, author of model: lookang
Contact: weelookang@gmail.com
Physics Tracker Models Study Guide
Short Answer Questions
- What is the purpose of Tracker software in physics education?
- Describe how Tracker can be used to analyze the motion of a tennis ball dropped in water.
- Explain the concept of a "reference frame" in the context of Tracker video analysis.
- List three examples of physics concepts that can be explored using Tracker, besides projectile motion.
- How does Tracker facilitate the creation of computational models to represent physical phenomena?
- What are the advantages of using open educational resources (OER) like the ones featured on the Open Source Physics @ Singapore website?
- What types of operating systems and devices are compatible with Tracker software?
- Explain the difference between a "model" and a "simulation" in the context of physics simulations.
- How can Tracker be used to investigate the concept of forces and their effects on motion?
- Describe how Tracker can be used to determine the acceleration due to gravity.
Short Answer Key
- Tracker software is used to analyze videos of physical phenomena, allowing students to make quantitative measurements of motion and other variables, leading to a deeper understanding of physics concepts.
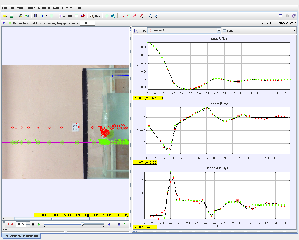
- Tracker can track the position of the tennis ball frame-by-frame as it falls through the water. This data can be used to calculate the ball's velocity and acceleration and to study the effects of drag forces.
- A reference frame is a coordinate system used to describe motion. In Tracker, you define a reference frame on the video, which serves as the origin and orientation for measuring the object's position.
- Examples include oscillations (pendulums, springs), collisions (elastic and inelastic), and rotational motion.
- Tracker allows you to extract data from videos and fit that data to mathematical models. These models can then be used to predict the behavior of the system under different conditions.
- OERs like those on the website are free to use, adapt, and share, making them accessible to a wider audience and promoting collaboration among educators.
- Tracker is compatible with Windows, MacOS, and Linux operating systems, including laptops and desktops.
- A model is a simplified representation of a physical system, often expressed mathematically. A simulation uses a model to generate data and visualize the behavior of the system over time.
- You can use Tracker to analyze videos of objects under the influence of forces. By tracking position and calculating acceleration, you can infer the forces acting on the object.
- By tracking the motion of a freely falling object and analyzing its position-time data, Tracker can be used to calculate the object's acceleration, which approximates the acceleration due to gravity.
Essay Questions
- Discuss the role of technology, specifically video analysis tools like Tracker, in modern physics education. How do these tools enhance the learning experience compared to traditional methods?
- Choose one of the Tracker models listed on the Open Source Physics @ Singapore website. Describe the physical phenomenon being modeled and explain how Tracker is used to investigate it.
- Explain the concept of "modeling" in physics. What are the benefits and limitations of using models to represent real-world phenomena? How does Tracker assist in the process of creating and testing physical models?
- Critically evaluate the importance of open educational resources (OER) in promoting access to quality science education. How do initiatives like the Open Source Physics @ Singapore project contribute to this goal?
- Imagine you are designing a physics lesson using Tracker to explore the motion of a projectile launched at an angle. Describe the experimental setup, the data you would collect with Tracker, and the analysis you would perform to investigate the key concepts of projectile motion.
Glossary of Key Terms
Tracker: Free, open-source video analysis and modeling software used in physics education to analyze the motion of objects in videos.
Open Educational Resources (OER): Freely accessible and reusable teaching and learning materials, often licensed under Creative Commons, which allow for adaptation and sharing.
Computational Model: A mathematical or computational representation of a physical system used to predict its behavior.
Reference Frame: A coordinate system used to describe the position and motion of objects.
Simulation: The process of using a computational model to generate data and visualize the behavior of a system over time.
Dynamics: The branch of mechanics that deals with the motion of objects under the influence of forces.
Kinematics: The study of motion without considering the forces that cause it.
Projectile Motion: The motion of an object projected into the air and subject only to the force of gravity.
Velocity: The rate of change of an object's position with respect to time, including both speed and direction.
Acceleration: The rate of change of an object's velocity with respect to time.
Force: An interaction that can cause a change in an object's motion (acceleration) or shape.
Drag Force: A resistive force that opposes the motion of an object through a fluid (like air or water).
Gravity: The fundamental force of attraction between any two objects with mass.
Tennis Ball Drop in Water: FAQ
1. What is the purpose of the "Tracker tennis ball drop in water motion" simulation?
This simulation, created by Rachel Ong from Raffles Girls' School (RGS), aims to help students understand the dynamics of a tennis ball dropped in water. It utilizes the Tracker software, which allows users to analyze video footage and collect data on the motion of objects. The simulation focuses on concepts such as buoyancy, drag force, and terminal velocity.
2. What is Tracker software, and how is it used in this simulation?
Tracker is a free, open-source video analysis and modeling tool. It allows users to track the movement of an object in a video, frame by frame, and extract data such as position, velocity, and acceleration. In this simulation, Tracker is used to analyze a video of a tennis ball being dropped in water. By tracking the ball's position over time, users can observe the effects of forces like buoyancy and drag, and calculate values for these forces.
3. What physics concepts are explored in this simulation?
The simulation explores several key physics concepts, including:
- Buoyancy: The upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object.
- Drag Force: The resistive force acting on an object moving through a fluid, opposing the direction of motion.
- Terminal Velocity: The constant speed that a freely falling object eventually reaches when the force of gravity is balanced by the drag force.
4. What operating systems are compatible with the simulation?
The simulation is compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, MacOSX, and Linux. It can be run on both desktop computers and laptops.
5. What type of educational level is this simulation targeted towards?
This simulation is primarily targeted towards students at the Junior College (JC) level, which is equivalent to the final years of high school or the first years of university in other educational systems.
- Details
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 02 Dynamics
- Hits: 6216
