
About
For Teachers
Credits
Author: samuel ooi video, analysis lookang
Contact: ooi_junwei_samuel@moe.edu.sg, weelookang@gmail.com
This document provides an overview of the website "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore".
Main Themes
The website is dedicated to providing open educational resources and promoting the use of open-source physics simulations.
Key Features
- Interactive Resources: The website features a vast collection of interactive physics simulations created using Easy JavaScript Simulations (EJS). These simulations cover a wide range of physics topics, from basic kinematics to more advanced concepts like oscillations and gravitational fields.
- Focus on Accessibility: The simulations are designed to be accessible on multiple platforms, including Windows, MacOS, and Linux, and can run on various devices like laptops and desktops.
- Breadcrumbs Navigation: The site utilizes a breadcrumbs navigation system, allowing users to easily understand their current location within the site's structure and navigate back to previous levels.
- Teacher Resources: While not detailed in the excerpt, the website indicates a section specifically for teachers, suggesting that it provides resources and support for educators looking to incorporate these simulations into their teaching.
- Community Contributions: The website showcases a long list of simulations created by individuals and institutions across Singapore, highlighting the collaborative nature of the project.
Examples of Simulations
The excerpt provides a long list of simulation titles. Here are a few examples that illustrate the diversity of topics covered:
- Tracker Toy Car on High Acceleration Slope: This simulation likely allows students to analyze the motion of a toy car on an inclined plane, exploring concepts like acceleration and forces.
- 🏀Tracker Basketball Model Throw: This simulation likely models the trajectory of a basketball throw, allowing students to investigate projectile motion.
- ⚛️Hydrogen, Bromine, Hydrogen Bromide equilibrium: This simulation delves into chemical equilibrium, allowing students to visualize and manipulate the concentrations of reactants and products.
Most Important Ideas/Facts
- Open Education and Open Source: The website emphasizes the importance of open educational resources and open-source software in physics education.
- Interactive Learning: The site promotes the use of interactive simulations as a valuable tool for enhancing students' understanding of physics concepts.
- Collaboration and Community: The website highlights the contributions of numerous individuals and institutions, showcasing a strong community focused on developing and sharing educational resources.
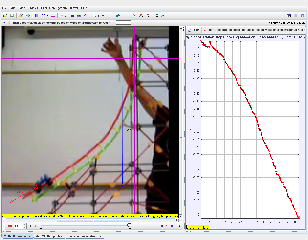
Tracker Toy Car on a High Acceleration Slope Study Guide
Short-Answer Questions
- What is the purpose of using Tracker software in physics experiments?
- Describe the basic setup of the "Tracker Toy Car on High Acceleration Slope" experiment.
- What are the key kinematic variables involved in analyzing the motion of the toy car? Explain each variable briefly.
- How can Tracker be used to determine the acceleration of the toy car?
- What is the difference between average velocity and instantaneous velocity? How are these concepts relevant to the experiment?
- Explain how the slope of the track affects the acceleration of the toy car.
- What are some potential sources of error in this experiment and how might they affect the results?
- How can you use Tracker to create a position-time graph for the toy car's motion? What does the shape of this graph tell you about the car's motion?
- How can you use Tracker to create a velocity-time graph for the toy car's motion? What does the slope of this graph represent?
- Discuss how the concepts of force and gravity are related to the motion of the toy car down the slope.
Answer Key
- Tracker software is used to analyze videos of physical phenomena. It allows users to track the motion of objects in the video and extract data about their position, velocity, and acceleration over time. This data can be used to make quantitative measurements and test physics principles.
- The experiment involves a toy car rolling down a sloped track. A video of the car's motion is recorded, and Tracker software is used to analyze the video. The setup includes a camera, the sloped track, the toy car, and a meter stick or other reference object for scale.
- The key kinematic variables are position (the car's location on the track), displacement (the change in position), velocity (the rate of change of position), and acceleration (the rate of change of velocity). Time is also a crucial variable.
- Tracker can be used to determine the acceleration by plotting the car's velocity versus time. The slope of the resulting graph represents the acceleration of the car.
- Average velocity is the total displacement divided by the total time, while instantaneous velocity is the velocity at a particular instant. In this experiment, the average velocity can be calculated over the entire motion, while Tracker allows for the calculation of instantaneous velocities at different points in time.
- The steeper the slope of the track, the greater the component of gravitational force acting parallel to the track, leading to a larger acceleration of the car.
- Sources of error include friction between the car and the track, air resistance, inaccuracies in the video tracking process, and the resolution of the camera. These errors can affect the accuracy of the measured values for position, velocity, and acceleration.
- In Tracker, you mark the position of the car in each frame of the video. Tracker then generates a position-time graph. A curved position-time graph indicates that the car is accelerating.
- By calculating the car's velocity between each frame, Tracker can create a velocity-time graph. The slope of the velocity-time graph represents the car's acceleration.
- Gravity provides the force that pulls the car down the slope. The component of the gravitational force parallel to the slope determines the acceleration of the car. The steeper the slope, the larger this component, and the faster the car accelerates.
Essay Questions
- Discuss the relationship between position, velocity, and acceleration, and explain how these concepts are applied in the analysis of the "Tracker Toy Car on High Acceleration Slope" experiment.
- Explain how Tracker software can be used to determine the experimental values for the toy car's position, velocity, and acceleration. Discuss the advantages of using video analysis software in physics experiments.
- Analyze the potential sources of error in the "Tracker Toy Car on High Acceleration Slope" experiment. Discuss how each source of error could affect the measured values and suggest ways to minimize their impact.
- Compare and contrast the concepts of average velocity and instantaneous velocity. Explain how these concepts are relevant to the analysis of motion in the toy car experiment. Provide examples from the experiment to illustrate your points.
- Explain how the slope of the track and the force of gravity influence the motion of the toy car. Discuss how changing the angle of the slope would affect the car's acceleration and overall motion.
Glossary of Key Terms
Acceleration: The rate of change of velocity over time. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
Average velocity: The total displacement of an object divided by the total time taken. It represents the overall rate of change of position.
Displacement: The change in position of an object. It is a vector quantity, measured in meters (m).
Dynamics: The branch of physics concerned with the study of forces and their effects on motion.
Force: An interaction that can cause an object to accelerate. It is a vector quantity, measured in Newtons (N).
Gravity: The force of attraction between any two objects with mass.
Instantaneous velocity: The velocity of an object at a specific point in time.
Kinematics: The branch of physics concerned with the description of motion, without considering the forces that cause it.
Position: The location of an object in space, relative to a chosen reference point.
Slope: The incline or steepness of a surface.
Tracker: Video analysis software used to track the motion of objects in videos and extract data about their position, velocity, and acceleration.
Velocity: The rate of change of position over time. It is a vector quantity, measured in meters per second (m/s).
Tracker Toy Car on High Acceleration Slope FAQ
What is "Tracker Toy Car on High Acceleration Slope"?
This is an educational resource hosted on the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore website. It is a physics simulation created using the Tracker software, designed for Junior College level students. The simulation focuses on the kinematics and dynamics of a toy car moving down a steep slope.
What physics concepts does the simulation cover?
The simulation primarily covers:
- Kinematics: The study of motion, including concepts like displacement, velocity, and acceleration.
- Dynamics: The study of forces and their effects on motion, including Newton's laws of motion.
What is Tracker software?
Tracker is a free video analysis and modeling tool used in physics education. It allows users to analyze the motion of objects in videos by tracking their position over time. This data can then be used to create graphs and models of the object's motion.
What operating systems is the Tracker simulation compatible with?
The simulation is compatible with Windows, MacOSX, and Linux operating systems, including both laptops and desktops.
How can I use this simulation in my teaching?
This simulation can be used for various educational purposes, including:
- Demonstrating the concepts of kinematics and dynamics in a visual and interactive way.
- Allowing students to collect and analyze real-world data on motion.
- Engaging students in problem-solving activities related to motion and forces.
Are there instructions or guides available for using the simulation?
The website doesn't provide specific instructions for this particular simulation, but it likely utilizes the standard features of the Tracker software. You can find general tutorials and documentation for Tracker on the website and elsewhere online.
Are there other similar Tracker simulations available on the website?
Yes, the website hosts a wide variety of Tracker simulations covering different physics topics and levels. These include simulations on projectile motion, collisions, simple harmonic motion, and many more. You can find a list of these simulations on the website's "Interactive Resources" page.
How can I access the simulation?
You can access the simulation by visiting the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore website and navigating to the "Interactive Resources" section. You can then find the simulation by searching for "Tracker Toy Car on High Acceleration Slope." You may need to download the Tracker software to run the simulation.
- Details
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 01 Kinematics
- Hits: 5304
