About
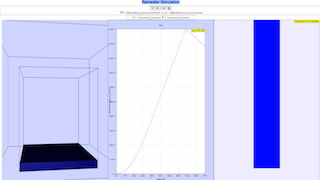
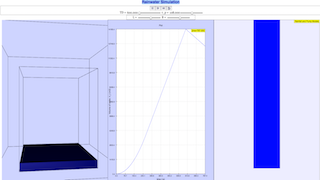
We model a simple steady state catchment and drainage system with stormwater pit and pumps
A catchment is the plan area in which rain falls upon, and flows to drains that serve this catchment.
A particular township may be divided into more than one catchment, and the drains for each catchment may be connected to form a drainage system.
The rainwater collected goes to a stormwater pit and the water is pumped out either to a larger network that eventually discharges into the sea and prevents
localized flooding.
This simulation of the rain water flow is to assist in the design of storm water pit dimensions and water pump sizes
About this Simulation
This interactive rainwater simulation models how water flows into and through stormwater management systems. Students can observe real-time fluid dynamics, drainage rates, and pit capacity as they adjust variables affecting water movement, precipitation intensity, and system design parameters to understand effective stormwater management.
Learning objectives: Understand how stormwater systems manage water flow and prevent flooding | Explore the relationship between rainfall intensity, drainage capacity, and water accumulation | Apply mathematical and physics principles to optimize water management solutions
Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits
Vincent Lew
Briefing Document: Storm Water Pit Simulator
1. Introduction
This document provides a summary and analysis of the "Storm Water Pit Simulator JavaScript HTML5 Applet Simulation Model" by Vincent Lew, as presented on the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore website. This simulation is an educational tool designed to help understand and design stormwater management systems. The document will analyze the purpose, functionality, and context of the simulator within the larger ecosystem of open educational resources provided by the site.
2. Key Themes and Ideas
- Simulation for Design: The core purpose of this simulation is to aid in the design of stormwater pit dimensions and water pump sizes. It allows users to visualize and manipulate variables related to rainwater flow in a catchment area.
- "This simulation of the rain water flow is to assist in the design of storm water pit dimensions and water pump sizes"
- Catchment and Drainage Systems: The simulation models a simplified steady-state catchment and drainage system. This includes a catchment area where rain falls, drains that collect the rainwater, a stormwater pit for storage, and pumps that move the water out. This highlights the basic components of urban drainage infrastructure.
- "We model a simple steady state catchment and drainage system with stormwater pit and pumps" "A catchment is the plan area in which rain falls upon, and flows to drains that serve this catchment." "The rainwater collected goes to a stormwater pit and the water is pumped out either to a larger network that eventually discharges into the sea and prevents localized flooding."
- Preventing Localized Flooding: The simulation highlights the critical role of stormwater pits and pumps in preventing localized flooding. This emphasizes the practical importance of understanding and optimizing these systems in urban environments.
- "The rainwater collected goes to a stormwater pit and the water is pumped out either to a larger network that eventually discharges into the sea and prevents localized flooding."
- Open Educational Resource: The simulator is part of a larger collection of open educational resources. The simulation is explicitly identified as being released under a specific license, which encourages re-use and adaptation of the simulation:
- "© 2017, Vincent Lew. Released under a license."
- Technology and Accessibility: The simulator is a JavaScript HTML5 applet, making it accessible via web browsers without needing specialized software. This is aligned with the goals of Open Educational Resources of reaching wide audiences.
- "Embed this model in a webpage:" ... "iframe"
- Context within Open Source Physics: The simulator is one of many simulations available on the Open Educational Resources/ Open Source Physics @ Singapore platform. This indicates an ongoing effort to leverage simulations as learning tools. The very extensive listing of other simulations shows the breadth of topics this group is covering.
3. Important Facts and Details
- Author: The simulator was created by Vincent Lew.
- Date: The simulator was released in 2017, and the blog post for it in October 2017.
- Technology: It uses JavaScript and HTML5, indicating that it is designed to run in web browsers.
- Licensing: It is released under a Creative Commons license, allowing for sharing and remixing.
- Function: The simulation focuses on steady-state flow, indicating that it does not model the dynamics of changing rainfall rates. This implies a focus on understanding general principles and less on the simulation of specific, unique events.
- Intended Use: The simulation is specifically designed to aid in the design process of storm water pit dimensions and water pump sizes, with a practical focus on the built environment and how engineering design prevents flooding.
4. Other Resources and Context
The listed resources within the source are extensive, showcasing a variety of simulations on topics ranging from physics and mathematics to chemistry, along with many additional resources and workshops and conferences where the resources were shared. The site is a valuable repository of interactive learning tools, particularly within the STEM fields. The diversity of content emphasizes the commitment of the team towards a comprehensive approach to using simulations for educational purposes. Some common themes seen in the larger context are:
- Use of open source tools and frameworks like Easy JavaScript Simulations (EJS)
- A focus on STEM subjects including physics, mathematics, and chemistry
- Use of simulations to improve teaching and learning
- Emphasis on the use of interactive tools and methods
- Training and workshops for teachers to use the simulation tools
- An active community using and contributing to open source physics resources
- A combination of original simulations and those converted to HTML5 from older Java-based versions.
5. Conclusion
The "Storm Water Pit Simulator" is a practical tool designed to help in understanding the principles of stormwater management. Its open licensing and browser-based technology make it widely accessible. This applet, situated within a larger body of open source educational tools, demonstrates the commitment of its creators to providing simulations as a means to improve teaching and learning, particularly in the STEM fields. This simulator can help users visualize and understand the relationships between rain fall, catchment areas, drainage systems, stormwater pits and water pumps, ultimately helping to mitigate flooding.
Storm Water Pit Simulation Study Guide
Quiz
- What is a catchment, and how might a township be divided into multiple catchments?
- Describe the basic flow of rainwater in the modeled system from where it falls to where it is discharged.
- What is the purpose of the stormwater pit in this model, and why is it important?
- What role do pumps play in the stormwater management system being modeled?
- What is the purpose of the simulation model according to the text?
- Who is the author of this simulation, and when was it created?
- Under what license is this simulation released?
- What type of software was used to create the simulation?
- What does the list of other resources suggest about the scope of the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore project?
- What information can be gained by simulating a storm water pit?
Quiz Answer Key
- A catchment is the area where rain falls and flows to a drainage system. A township can be divided into multiple catchments, each with its own drainage system that may connect to form a larger network.
- Rain falls on the catchment area and flows into drains. The collected rainwater is then directed to a stormwater pit where it is pumped out to a larger network, ultimately discharging into the sea.
- The stormwater pit serves as a temporary holding area for collected rainwater. It is essential for preventing localized flooding by managing the water before it is pumped out.
- Pumps are crucial for moving water out of the stormwater pit and into a larger drainage network. This process prevents the pit from overflowing and causing localized flooding.
- The simulation is to assist in the design of stormwater pit dimensions and water pump sizes.
- The simulation was created by Vincent Lew in 2017.
- The simulation is released under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License.
- The simulation was created using Javascript and HTML5.
- The list suggests the project encompasses a wide range of educational simulations across various subjects, particularly in science and mathematics.
- Simulating a storm water pit can help engineers understand how to correctly size storm water pits and pumps for efficient management of rainwater.
Essay Questions
- Discuss the importance of modeling and simulation in the design of civil engineering systems like stormwater management. How does this specific model by Vincent Lew contribute to the field?
- Explain the hydrological cycle and how the simulation of a catchment area, drainage system, stormwater pit, and pumps relates to it.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the simulation as a tool for education. What are the advantages and potential limitations of using a simulation model like this one in teaching about storm water management?
- Describe the purpose of open-source educational resources. How does the Creative Commons license impact the accessibility and usage of this simulation?
- Based on the various resources linked within the article, discuss how technology is used in education. What kind of impact does the use of technology seem to have on teaching?
Glossary
Catchment: An area of land where water from rain or snow collects and flows into a common outlet, such as a river, lake, or drain.
Drainage System: A network of natural and man-made channels, pipes, and structures designed to collect and carry away surface water and stormwater runoff.
Stormwater Pit: A structure, often a basin or underground reservoir, designed to temporarily store excess stormwater runoff before it can be discharged, preventing flooding and allowing some settling of pollutants.
Pumps: Mechanical devices used to move liquids from one place to another, in this context, from the stormwater pit to a larger drainage network or outfall.
Simulation Model: A computer-based tool that represents a real-world system or process, allowing users to experiment and observe the effects of different variables without affecting the actual system.
Steady State: A condition in which the input and output of a system are equal, resulting in no net change of the system over time. In this context, it refers to the state of water flow in the catchment and drainage system where the inflow rate is equal to the outflow rate.
Open Educational Resources (OER): Freely available educational materials that can be used, adapted, and shared without restrictions or licensing fees.
JavaScript: A programming language commonly used for creating interactive elements and dynamic content on websites, often used for simulations and interactive models.
HTML5: The latest version of Hypertext Markup Language, the standard language used for creating web pages and web applications.
Creative Commons License: A type of copyright license that allows for the free distribution and use of a work, subject to certain conditions specified by the author. The Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 license requires users to give credit to the creator and to share adaptations under the same license.
Version:
Other Resources
[text]
FAQ
- What is the purpose of the Storm Water Pit Simulator? The Storm Water Pit Simulator is a JavaScript HTML5 applet designed to model a simple steady-state catchment and drainage system. Its primary goal is to assist in the design of storm water pit dimensions and water pump sizes. By simulating rainwater flow within a defined catchment area, it helps users understand how to effectively manage rainwater to prevent localized flooding.
- How does the simulator model a catchment area? The simulator models a catchment area as the plan area upon which rain falls and flows to drains. It represents a simplified system where rainwater collected within the catchment flows into a stormwater pit. The simulator considers the dimensions of this area when simulating water collection. A particular township may have multiple catchments, and their drains can be connected.
- What is the role of a stormwater pit in the simulation? The stormwater pit in the simulation acts as a collection point for rainwater. Water flows into this pit from the catchment area. The pit's dimensions (likely volume) are a key design parameter that users can explore using the simulation. The simulator will pump water out of the pit to prevent overflow, thus simulating the draining of excess water from a typical system.
- What parameters can be adjusted in the simulation? While the provided information doesn't specify the adjustable parameters directly, we can infer from the description that users would likely be able to adjust parameters related to the stormwater pit dimensions, water pump sizes, and possibly parameters that influence the rate of rainfall. The simulation is designed to allow users to examine the effect of changing these parameters on the overall system.
- What are the practical applications of this simulation model? This simulation model is designed to be a tool for the practical design of stormwater management systems. It can be used to determine appropriate storm water pit dimensions and the required pump capacities to prevent flooding. The simulation can be applied to any catchment area where there is a need to manage rainwater effectively.
- Who created the Storm Water Pit Simulator? The Storm Water Pit Simulator was created by Vincent Lew in 2017. It is part of the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore initiative.
- Is the simulation freely available for educational use? Yes, the simulation is released under a Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License, meaning that it can be used and shared freely for educational purposes. However, commercial use of the underlying EasyJavaScriptSimulations library requires contacting the developers directly for licensing information.
- Where can the Storm Water Pit Simulator be accessed? The simulator is embedded in the webpage using an iframe, with the source URL being https://iwant2study.org/lookangejss/00workshop/2017FelixPaco/day4/ejss_model_stormwaterpit/stormwaterpit_Simulation.xhtml. The embedding indicates it can be accessed and used on other webpages as well.
- Details
- Written by Fremont
- Parent Category: Measurement and Geometry
- Category: Area and Volume
- Hits: 8333