
About
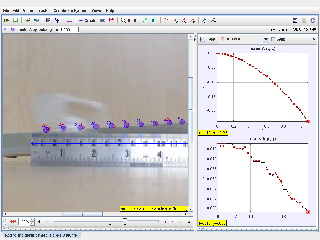
Tracker Modeling in Plastic Rod rolling down a metal slope
For Teachers
- Rod rolling down a metal slope HD480.mov
Credits
Author: lookang
Contact: weelookang@gmail.com
Tracker Modeling Study Guide
Quiz
- What is Tracker used for in the context of physics education?
- Provide three examples of physics concepts that can be modeled using Tracker.
- What types of files can be analyzed using Tracker?
- What is the significance of Open Educational Resources (OER) in relation to Tracker?
- Describe two ways Tracker can enhance the learning experience for physics students.
- How does Tracker utilize video analysis for physics modeling?
- Explain the role of "breadcrumbs" in the organization of the provided website.
- What is the purpose of the "Credits" section on the webpage?
- Name three different models or simulations available on the webpage besides those related to Tracker.
- What is the primary function of the Open Source Physics @ Singapore website?
Quiz Answer Key
- Tracker is used to model and analyze various physics phenomena by tracking the motion of objects in videos. This allows students to visualize and quantify real-world physics concepts.
- Examples of physics concepts that can be modeled using Tracker include projectile motion, collisions, oscillations, and gravitational forces. (Many other valid examples exist).
- Tracker can analyze video files in common formats such as .avi, .mov, and .mp4.
- Tracker is often distributed as an Open Educational Resource (OER), making it freely accessible to educators and students, promoting wider adoption and reducing educational costs.
- Tracker enhances learning by: a) providing a visual and interactive way to study physics, b) allowing students to collect and analyze their own data, fostering a deeper understanding of experimental methods.
- Tracker analyzes videos frame-by-frame, allowing users to mark the position of an object in each frame. This data is then used to calculate the object's velocity, acceleration, and other relevant physical quantities.
- "Breadcrumbs" on the webpage act as a navigational trail, showing the user their current location within the site's hierarchy.
- The "Credits" section acknowledges the individuals and organizations who contributed to the creation and development of the Tracker software and related resources.
- Besides Tracker models, the webpage offers simulations related to topics like Simple Harmonic Motion, gravity, wave-particle duality, and electric circuits.
- The Open Source Physics @ Singapore website aims to provide a platform for open educational resources and interactive simulations in physics, facilitating physics learning and teaching.
Essay Questions
- Discuss the advantages and limitations of using video analysis software like Tracker for physics education.
- Compare and contrast Tracker with other physics simulation tools or software you may be familiar with.
- Explain how Tracker can be integrated into a physics curriculum to enhance student understanding of specific physics principles. Choose one principle and elaborate.
- Critically analyze the role of open-source software and open educational resources in promoting access to quality education in physics and STEM fields.
- Imagine you are tasked with creating a new Tracker model to demonstrate a particular physics concept. Describe your chosen concept, the experimental setup you would use, and the steps involved in creating the Tracker model.
Glossary of Key Terms
- Tracker: A free, open-source video analysis and modeling tool used in physics education to track the motion of objects in videos.
- Open Educational Resources (OER): Freely accessible educational materials that can be used, adapted, and shared by anyone.
- Simulation: A computer program or model that mimics a real-world phenomenon, allowing users to experiment and observe the system's behavior under different conditions.
- Model: A simplified representation of a system or process, used to understand, explain, or predict its behavior.
- Video Analysis: The process of extracting quantitative data from videos, such as object position, velocity, and acceleration.
- Physics Phenomena: Observable events or occurrences in the physical world that can be explained by scientific principles.
- Dynamics: The branch of physics that studies the motion of objects and the forces that cause motion.
- Junior College: A pre-university educational institution, typically for students aged 16-19, that prepares them for higher education.
- HTML5: A markup language used for structuring and presenting content on the World Wide Web.
- JavaScript: A programming language commonly used for creating interactive elements within web pages.
- Applet: A small, self-contained program that can be embedded within a web page and run within a web browser.
Tracker Modeling FAQ
What is Tracker?
Tracker is a free and open-source video analysis and modeling tool. It is used to analyze the motion of objects in videos. Tracker allows you to track the position, velocity, and acceleration of objects over time. It can be used to analyze a wide variety of motions, including projectile motion, simple harmonic motion, and collisions.
What are the benefits of using Tracker?
Tracker is a powerful tool that can be used to enhance physics education in several ways:
- Visualize motion: Tracker allows students to see how objects move in real-time, which can help them to understand concepts such as velocity and acceleration.
- Collect real-world data: Students can use Tracker to analyze videos of real-world events, such as a ball rolling down a slope. This can help them to connect physics concepts to the real world.
- Develop modeling skills: Tracker requires students to create models of physical systems, which can help them to develop their problem-solving skills.
- Free and accessible: Tracker is a free and open-source software, making it accessible to all students.
How does Tracker work?
Tracker uses a technique called video tracking to analyze the motion of objects in videos. To use Tracker, you first need to import a video of the motion you want to analyze. Then, you need to define a coordinate system and calibrate the video. Once the video is calibrated, you can track the motion of objects in the video by marking their position in each frame.
What types of motion can be analyzed with Tracker?
Tracker can be used to analyze a wide variety of motions, including:
- Linear motion: Motion in a straight line.
- Projectile motion: Motion of an object that is projected into the air.
- Circular motion: Motion of an object in a circle.
- Simple harmonic motion: Oscillatory motion where the restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium.
- Collisions: Interactions between two or more objects.
Can Tracker be used on different operating systems?
Yes, Tracker is a cross-platform software that can be used on Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems. This makes it a versatile tool that can be used in a variety of educational settings.
Are there resources available to help me learn how to use Tracker?
Yes, there are many resources available to help you learn how to use Tracker.
- The Open Source Physics @ Singapore website has a variety of resources on Tracker, including tutorials and example projects.
- The Tracker website has documentation and a user forum where you can ask questions and get help from other users.
- There are also many YouTube videos that demonstrate how to use Tracker.
What are some examples of how Tracker is used in education?
Tracker can be used for a wide range of physics experiments and demonstrations. Here are a few examples:
- Analyzing the motion of a ball rolling down a slope: Students can use Tracker to measure the ball's position, velocity, and acceleration as it rolls down the slope. This data can be used to verify the laws of motion and to calculate the ball's kinetic and potential energy.
- Investigating projectile motion: Students can use Tracker to analyze videos of projectiles, such as a ball thrown in the air or a rocket launched. They can measure the projectile's range, maximum height, and time of flight. This data can be used to verify the equations of motion for projectile motion.
- Studying collisions: Students can use Tracker to analyze videos of collisions, such as a ball bouncing off a wall or two cars crashing. They can measure the objects' velocities before and after the collision. This data can be used to verify the law of conservation of momentum.
How can I contribute to the Tracker project?
Tracker is an open-source project, which means that anyone can contribute to its development. If you are interested in contributing to Tracker, you can visit the project's website to learn more about how to get involved. Contributions can include reporting bugs, writing documentation, or developing new features.
- Details
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 02 Dynamics
- Hits: 5312
