
About
For Teachers
- 1a RAW Straight Ramp.mp4
- toycarsLesson Guide .docx
Credits
Author: Ooi Junwei, Samuel
Contact: ooi_junwei_samuel@moe.edu.sg, weelookang@gmail.com
This briefing document analyzes content from the "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore" website, focusing on its use of the Tracker software for physics education.
Key Themes:
- Tracker for Physics Education: The website showcases a vast repository of interactive physics resources created using the Tracker video analysis and modeling tool. These resources span a wide range of physics topics, from fundamental concepts like kinematics and dynamics to more advanced subjects like oscillations, waves, and gravitational fields.
- Open Educational Resources (OER): The website embodies the principles of OER, providing freely accessible, adaptable, and shareable educational materials. This aligns with the website's mission to democratize physics education and empower teachers and students globally.
Important Ideas/Facts:
- Tracker's Versatility: The website demonstrates Tracker's ability to analyze real-world videos, allowing students to investigate physics principles in action. Examples include:
- "Tracker toy car rolling down a slope": This resource lets students analyze the motion of a toy car, exploring concepts like velocity, acceleration, and forces.
- "🏀Tracker Basketball Model Throw by RGS Chen XiMin": Students can study projectile motion by analyzing the trajectory of a basketball throw.
- Breadth of Topics: The website's resources cover diverse physics topics, including:
- Foundational Physics: Kinematics, Dynamics, Forces, Motion.
- Waves and Oscillations: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), wave interference, standing waves.
- Gravitational Fields: Earth's gravitational field, escape velocity, satellite motion.
- Thermodynamics: Ideal gas model, Brownian motion.
- Electromagnetism: Electric fields, magnetic fields.
Quotes:
No direct quotes are included in the provided source excerpt. However, the resource titles themselves provide insights into the content.
Overall Significance:
The "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore" website serves as a valuable hub for physics educators and learners. By leveraging the power of Tracker and adhering to OER principles, it offers a rich and accessible platform for exploring physics concepts in an engaging and interactive manner.
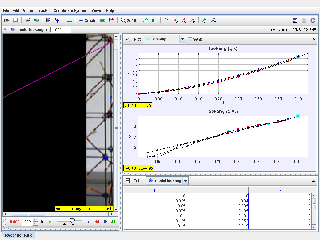
Tracker Toy Car Rolling Down a Slope Study Guide
Short Answer Questions
- What is the purpose of using Tracker software in a physics experiment?
- Explain how Tracker can be used to analyze the motion of a toy car rolling down a slope.
- What are some of the key kinematic variables that can be measured using Tracker?
- Describe the difference between a position-time graph and a velocity-time graph in the context of Tracker.
- How can Tracker be used to determine the acceleration of a toy car?
- What are some potential sources of error when using Tracker to analyze motion?
- How can you mitigate the errors mentioned in question 6?
- What information can be derived from analyzing the slope of a velocity-time graph generated in Tracker?
- Explain how Tracker could be used to investigate the relationship between the angle of a slope and the acceleration of a toy car.
- Beyond simple kinematics, how could Tracker be used to explore more complex concepts like energy conservation or forces?
Short Answer Key
- Tracker software is used to analyze video footage of an experiment and extract quantitative data about the motion of objects. This allows for precise measurements and visualization of movement, aiding in the understanding and verification of physics principles.
- Tracker allows you to mark the position of the car in each frame of the video. This data is then used to calculate the car's position, velocity, and acceleration over time. By plotting these variables, you can analyze the car's motion down the slope.
- Tracker can measure position, time, velocity, and acceleration. These variables are fundamental to understanding the motion of any object, including a toy car rolling down a slope.
- A position-time graph in Tracker shows how the position of the car changes over time, while a velocity-time graph shows how the velocity of the car changes over time. The slope of the position-time graph represents the car's velocity, while the slope of the velocity-time graph represents the car's acceleration.
- Tracker can determine the acceleration of the car by analyzing the slope of the velocity-time graph. A steeper slope indicates a greater acceleration.
- Potential sources of error include camera angle, parallax, frame rate limitations, and the accuracy of marking the car's position in each frame. These factors can introduce inaccuracies in the measured variables.
- Errors can be mitigated by using a high frame rate camera, ensuring a perpendicular camera angle to the motion, using a clear marker on the car for tracking, and carefully marking the car's position in each frame.
- The slope of a velocity-time graph represents the acceleration of the object. A positive slope indicates increasing velocity (acceleration), a negative slope indicates decreasing velocity (deceleration), and a zero slope indicates constant velocity (no acceleration).
- By recording videos of the car rolling down slopes with different angles, you can analyze the resulting velocity-time graphs in Tracker. Comparing the slopes of these graphs will reveal how the acceleration changes with the angle of the incline.
- Tracker can be used to calculate the kinetic and potential energy of the car at different points along the slope, allowing for an investigation of energy conservation. Additionally, by incorporating the mass of the car, Tracker data can be used to calculate forces acting on the car, like gravity or friction.
Essay Questions
- Discuss the advantages and limitations of using video analysis software like Tracker for studying motion in physics.
- Explain how the concepts of displacement, velocity, and acceleration are interconnected and can be visualized using Tracker.
- Design an experiment using Tracker to investigate the factors affecting the acceleration of a toy car rolling down a slope. Describe the procedure, data collection, and analysis techniques.
- Analyze the potential sources of error in a Tracker experiment involving a toy car rolling down a slope and discuss methods for minimizing these errors.
- Compare and contrast the motion of a toy car rolling down a slope with and without friction. How would Tracker be used to analyze these differences?
Tracker Toy Car FAQ
What is Tracker?
Tracker is a free video analysis and modeling tool built on the Open Source Physics (OSP) Java framework. It is a cross-platform application that runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux, including laptops and desktops.
What can Tracker be used for?
Tracker can be used for a wide range of physics experiments and demonstrations, particularly in the areas of kinematics and dynamics. It allows you to analyze the motion of objects in videos, create models to simulate that motion, and compare the two.
How is Tracker used in education?
Tracker is a valuable tool for physics education at both the secondary and tertiary levels. It allows students to:
- Visualize and analyze real-world motion.
- Explore concepts like velocity, acceleration, and force.
- Develop scientific inquiry skills through experimentation and data analysis.
- Create and test models to understand physical phenomena.
What are some examples of Tracker activities?
There are numerous examples of Tracker activities available online, including:
- Projectile Motion: Analyze the trajectory of a ball thrown in the air.
- Constant Acceleration: Investigate the motion of a cart rolling down a slope.
- Collisions: Examine the momentum and energy transfer during collisions.
- Simple Harmonic Motion: Study the oscillations of a pendulum or spring-mass system.
What file formats does Tracker support?
Tracker supports a variety of video file formats, including AVI, MOV, MP4, and WMV. It also allows you to import image sequences.
Are there any resources available to learn how to use Tracker?
Yes, there are many resources available to help you learn how to use Tracker. The OSP website has a comprehensive user manual, tutorials, and a forum where you can ask questions and get support. Many educational institutions also provide training materials and workshops on using Tracker.
What are some of the benefits of using Tracker?
- Free and open source: Tracker is freely available for anyone to use and modify.
- Cross-platform compatibility: It can be used on a variety of operating systems.
- User-friendly interface: The software is designed to be intuitive and easy to use.
- Powerful analysis tools: Tracker provides a range of tools for analyzing motion data.
- Educational value: It is an excellent tool for teaching and learning physics.
Where can I download Tracker?
Tracker can be downloaded for free from the Open Source Physics website: https://www.compadre.org/osp/
- Details
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 01 Kinematics
- Hits: 7103
