
About
For Teachers
- cartsteepslope.mp4
- cart steep slop.mp4
- cart steep slop_thumbnail.png
- cart steep slop.trk
Credits
Author: Leong Tze Kwang
Document Brief: Title: "Tracker Free Body Diagram: Cart Rolling Down a Gentle 4-Degree Slope by RGS Leong Tze Kwang"
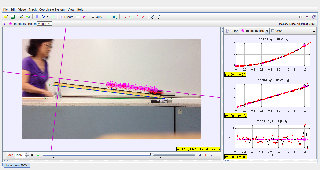
This document explores the dynamics of a cart rolling down a 4-degree inclined slope. Using Tracker software, the free-body diagram (FBD) of the cart is analyzed to visualize and quantify the forces involved in the motion. The study provides a practical understanding of kinematics and dynamics principles, focusing on incline motion.
Study Guide:
Objective:
-
Analyze the motion of a cart rolling down a gentle slope using Tracker software.
-
Construct and interpret a free-body diagram to understand the forces at play.
Key Concepts:
-
Inclined Plane Dynamics:
-
Decomposition of gravitational force into parallel and perpendicular components.
-
-
Free Body Diagram (FBD):
-
Representation of forces including gravity, normal force, and friction.
-
-
Kinematics and Acceleration:
-
Relationship between slope angle, net force, and acceleration.
-
Experiment Setup:
-
Materials:
-
A cart, a smooth 4-degree inclined plane, and Tracker software.
-
-
Procedure:
-
Place the cart at the top of the incline and release it without an initial push.
-
Record the motion using a high-speed camera.
-
Analyze the video in Tracker, marking the cart's position over time.
-
Construct the FBD for the cart and calculate forces using the measured data.
-
Expected Observations:
-
The cart accelerates down the slope due to the component of gravitational force along the incline.
-
Friction and air resistance slightly reduce acceleration from the theoretical value.
-
The normal force counteracts the perpendicular component of gravity.
Questions to Consider:
-
What forces act on the cart?
-
Answer: Gravitational force, normal force, and friction.
-
-
How does the incline angle affect acceleration?
-
Answer: A steeper angle increases the parallel component of gravitational force, leading to higher acceleration.
-
-
Why is friction included in the FBD?
-
Answer: Friction opposes motion and influences net force and acceleration.
-
-
What assumptions are made in this analysis?
-
Answer: Negligible air resistance and constant friction coefficient.
-
-
How can energy conservation be applied here?
-
Answer: Potential energy converts into kinetic energy, with some energy dissipated due to friction.
-
FAQ:
-
Why use Tracker for this analysis?
-
Tracker enables precise measurement of the cart's position, velocity, and acceleration over time.
-
-
How is the FBD useful?
-
It visually represents all forces acting on the cart, helping to understand the motion dynamics.
-
-
What is the significance of the slope angle?
-
The slope angle determines the magnitude of the gravitational force component driving the motion.
-
-
How does friction affect the results?
-
Friction reduces the net force and actual acceleration compared to the theoretical value.
-
-
Can this setup be extended?
-
Yes, experiments with varying slope angles, cart masses, or surface materials can provide deeper insights.
-
Would you like to include additional scenarios or visualizations for this analysis?
