About
Monte Carlo methods are often useful for solving problems in physics and mathematics, which cannot be solved by analytical means.
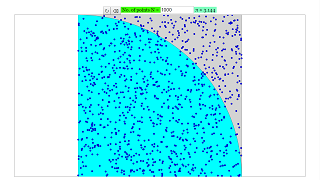
The goal of this virtual-lab is to obtain an approximated value of PI, using a Monte Carlo method. Next, we describe briefly how this method is used to estimate PI.
Imagine that we are throwing a dart over a square surface of side 1 m. There is a circle of radius 1 m. inscribed in the square. Assuming that the probability is uniformly distributed, the probability of hitting inside the circle is equal to PI/4. Dividing the number of hits by the number of throws, it is obtained an estimation of PI. We will obtain a better approximation by increasing the number of throws.
This virtual-lab allows the user to select the number of throws, with a maximum of 10000 throws.
Dpto. de Informática y Automática
E.T.S. de Ingeniería Informática, UNED
Juan del Rosal 16, 28040 Madrid, Spain
Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits

Carla Martn; Tan Wei Chiong; Loo Kang Wee
Executive Summary:
This briefing document reviews the description of a JavaScript simulation applet designed to estimate the value of Pi (π) using the Monte Carlo method. The applet, part of the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore initiative, aims to provide an interactive virtual lab for educational purposes. The core concept involves randomly "throwing darts" at a unit square containing an inscribed quadrant. By calculating the ratio of darts landing within the quadrant to the total number of throws, an approximation of π/4 is obtained, which is then used to estimate π. The simulation allows users to control the number of throws (up to 50,000 in the described version for teachers) to observe how increasing the number of trials improves the accuracy of the Pi estimation. This tool is presented as a valuable resource for teaching probability, the Monte Carlo method, and the concept of approximating mathematical constants through simulation, especially in situations where analytical solutions are difficult.
Main Themes and Important Ideas/Facts:
- Monte Carlo Method for Pi Estimation: The central theme is the application of the Monte Carlo method to approximate the value of Pi. The description clearly explains the underlying principle:
- A unit square (side length 1) is considered.
- A quadrant (a quarter of a circle with radius 1) is inscribed within this square.
- Random points ("darts") are generated within the square.
- The probability of a point landing inside the quadrant is proportional to the ratio of the quadrant's area to the square's area.
- Area of the square = 1 * 1 = 1
- Area of the inscribed quadrant = (1/4) * π * (1)^2 = π/4
- Therefore, the probability of hitting inside the circle is approximately the number of hits inside the quadrant divided by the total number of throws, which is equal to π/4.
- The value of Pi can then be estimated by multiplying this ratio by 4.
- Quote: "Assuming that the probability is uniformly distributed, the probability of hitting inside the circle is equal to PI/4. Dividing the number of hits by the number of throws, it is obtained an estimation of PI."
- Virtual Lab for Learning: The applet is positioned as a "virtual-lab" intended for educational purposes, particularly for solving problems in mathematics and physics that lack analytical solutions.
- Quote: "The goal of this virtual-lab is to obtain an approximated value of PI, using a Monte Carlo method. Next, we describe briefly how this method is used to estimate PI."
- Impact of Number of Throws: The description emphasizes that the accuracy of the Pi estimation improves with an increased number of random throws.
- Quote: "We will obtain a better approximation by increasing the number of throws."
- User Controllability: The applet allows users to "select the number of throws," providing an interactive learning experience where students can experiment with different sample sizes and observe the effect on the Pi approximation. The initial description mentions a maximum of 10,000 throws for the embedded model.
- Quote: "This virtual-lab allows the user to select the number of throws, with a maximum of 10000 throws."
- Pedagogical Value for Teachers: The "For Teachers" section explicitly highlights the educational benefits of the simulation, contrasting it with the analytical approach of Archimedes' algorithm. It emphasizes the broader applicability of the Monte Carlo method.
- Quote: "This simulation shows yet another method that can be used to approximate the value of π. The Monte Carlo method is done by taking a unit square (a square of length 1) and inscribing a quadrant inside. A arbitrary number of points is then randomly scattered in the square... the ratio of the number of points that land in the quadrant to the total number of points becomes an estimate of π/4, which is then multiplied by 4 to estimate π."
- Broader Application of Monte Carlo Methods: The text points out that the Monte Carlo method is not limited to estimating Pi but is a widely used technique in mathematics and physics for problems that are difficult or impossible to solve analytically.
- Quote: "This method is used widely in mathematics and physics when a problem cannot be solved analytically."
- Technical Details and Authorship: The description provides information about the author (Carla Martín) and credits contributions from Tan Wei Chiong and Loo Kang Wee. It also mentions that the applet is a "JavaScript Simulation Applet HTML5," indicating its web-based nature and compatibility.
- Version Information and Related Resources: The source provides links to different versions or related discussions of the applet, offering teachers and learners additional context and resources.
- Integration within a Larger Educational Ecosystem: The presence of the applet on the "Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore" platform, along with its listing among numerous other simulations and learning tools, suggests its role within a broader effort to provide interactive and open-source educational materials. The mention of a "Web EJS beta Workshop" further indicates the technological framework (Easy JavaScript Simulations) behind these resources.
- License Information: The footer notes that the contents are licensed under a "Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License," promoting the sharing and adaptation of the resource.
Key Takeaways:
- The Monte Carlo Pi Calculation JavaScript Simulation Applet is an interactive tool designed to teach the Monte Carlo method for approximating Pi.
- It utilizes a geometric probability approach based on randomly distributed points within a square and an inscribed quadrant.
- The accuracy of the approximation increases with the number of simulated "throws."
- This applet serves as a valuable educational resource for visualizing and understanding a powerful numerical method used in various scientific disciplines.
- It is part of a larger collection of open educational resources focused on physics and mathematics, developed using the Easy JavaScript Simulations (EJS) framework.
This briefing provides a comprehensive overview of the key aspects of the Monte Carlo Pi Calculation JavaScript Simulation Applet as described in the provided source. It highlights its educational purpose, the underlying mathematical principles, and its place within a broader context of open educational resources.
Key Concepts
- Monte Carlo Method: A computational technique that relies on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results. It is particularly useful for problems that are difficult or impossible to solve analytically.
- Estimation of Pi: Approximating the value of π (pi), the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
- Probability and Area: The fundamental principle that the probability of a randomly selected point landing in a specific area is proportional to the size of that area.
- Uniform Distribution: The assumption that each point within the defined space (the square in this case) has an equal chance of being selected or "hit."
- Inscribed Shape: A geometric shape contained within another shape, touching it at certain points. In this context, a circle (or quadrant) inscribed within a square.
- Analytical Solution: Solving a problem using mathematical formulas and exact methods, as opposed to numerical approximations.
- Virtual Lab/Simulation: A computer-based interactive environment that allows users to perform experiments or explore concepts.
- Number of Throws/Points: The total number of random samples taken in the Monte Carlo simulation. Increasing this number generally leads to a more accurate approximation.
- Number of Hits: The number of random points that fall within the inscribed shape (the circle or quadrant).
- Approximation: A value that is close to the exact value but may not be precisely the same.
Quiz
- Explain the basic principle behind using a Monte Carlo method to estimate the value of Pi as described in the source.
- What geometric shapes are central to this Monte Carlo simulation for Pi estimation, and what is the relationship between their dimensions according to the source?
- According to the source, what is the probability of a randomly thrown dart hitting inside the inscribed circle (or quadrant) within the square? How is this probability related to Pi?
- How does the virtual lab described in the source allow users to influence the accuracy of the Pi estimation? What is the maximum number of throws permitted in one version of the simulation?
- In the context of the Monte Carlo Pi calculation, what does the ratio of "number of hits" to "number of throws" represent? How is this ratio used to estimate Pi?
- Why are Monte Carlo methods considered useful in mathematics and physics, as highlighted by the source? Provide an example from the text.
- The "For Teachers" section mentions an alternative method for calculating Pi. What is this method, and how does the Monte Carlo method differ from it in its approach?
- Describe the setup of the Monte Carlo simulation for Pi estimation using a unit square and an inscribed quadrant, as explained in the "For Teachers" section.
- What is the significance of randomly scattering points within the square in this simulation? What assumption about probability distribution is being made?
- According to the source, what happens to the accuracy of the Pi estimation as the number of throws in the Monte Carlo simulation increases? Briefly explain why.
Quiz Answer Key
- The Monte Carlo method estimates Pi by simulating random "dart throws" onto a square with an inscribed circle (or quadrant). The probability of hitting inside the circle is proportional to the ratio of the circle's area to the square's area, which is related to Pi.
- A square and a circle (or a quadrant of a circle) are central to the simulation. The circle (or quadrant) has a radius that is half the side length of the square, effectively being inscribed within it.
- The probability of hitting inside the inscribed circle of radius 1 m within a square of side 1 m is PI/4. This is because the area of the circle is π(1)^2 = π, and the area of the square is (2)^2 = 4 (if considering a full circle). For a unit square and inscribed quadrant, the probability is also related to PI/4.
- Users can select the number of throws in the virtual lab; increasing the number of throws generally leads to a better approximation of Pi. One version of the simulation allows for a maximum of 10000 throws, while another allows up to 50000 points.
- The ratio of the number of hits (points landing inside the circle or quadrant) to the total number of throws approximates the probability of hitting within that area. This ratio is an estimate of PI/4, which is then multiplied by 4 to estimate Pi.
- Monte Carlo methods are useful when problems cannot be solved by analytical means. The source explicitly states they are often used in mathematics and physics for such problems. The Pi estimation itself is an example where a probabilistic approach provides a numerical solution.
- The alternative method mentioned is Archimedes' algorithm. While Archimedes' method uses deterministic geometric constructions and calculations to bound Pi, the Monte Carlo method uses random sampling and probability to approximate it.
- The simulation takes a unit square (side length 1) and inscribes a quadrant (a quarter circle with radius 1) within it. Points are then randomly scattered across the entire square.
- Randomly scattering points ensures that each location within the square has an equal chance of being hit, reflecting the assumption of a uniformly distributed probability. This randomness is fundamental to the Monte Carlo method.
- The accuracy of the Pi estimation generally improves as the number of throws increases. This is because with more random samples, the ratio of hits to throws becomes a better statistical representation of the true ratio of the areas, which is directly related to Pi/4.
Essay Format Questions
- Discuss the advantages and limitations of using the Monte Carlo method for estimating Pi compared to analytical methods. Consider factors such as accuracy, computational cost, and conceptual understanding.
- Explain how the relationship between probability, area, and random sampling forms the foundation of the Monte Carlo method for Pi calculation. Elaborate on the role of uniform distribution in this process.
- The source highlights that Monte Carlo methods are useful for problems that cannot be solved analytically. Analyze why approximating Pi through random simulation can be considered such a problem, and discuss other potential applications of Monte Carlo methods in science or mathematics.
- Describe the virtual lab simulation for Monte Carlo Pi calculation, detailing the user interactions and the underlying mathematical principles that connect the simulation to the estimation of Pi.
- Compare and contrast the Monte Carlo method of Pi estimation with Archimedes' algorithm, considering their historical context, mathematical approaches, and the nature of the results they provide (approximation vs. bounds).
Glossary of Key Terms
- Analytical Method: A way of solving problems using exact mathematical formulas and logical reasoning.
- Approximation: A value or result that is intentionally close to the exact value but not precisely the same.
- Inscribed: A shape drawn inside another shape such that it touches the inner boundaries of the outer shape at certain points.
- Monte Carlo Method: A computational algorithm that relies on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results for complex problems.
- Pi (π): A mathematical constant representing the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159.
- Probability: A measure of the likelihood of an event occurring.
- Quadrant: One of the four equal parts into which a circle is divided by two perpendicular diameters; a quarter of a circle.
- Random Sampling: Selecting a subset of individuals (or in this case, points) from within a statistical population (or a defined area) in such a way that each individual has an equal probability of being chosen.
- Simulation: The use of a model (often a computer program) to imitate the behavior of a real-world system or process.
- Uniform Distribution: A probability distribution where every possible value within a certain range has an equal probability of occurring.
Sample Learning Goals
[text]
For Teachers
Before, we had a simulation on the calculation of π using Archimedes' algorithm. This simulation shows yet another method that can be used to approximate the value of π.
The Monte Carlo method is done by taking a unit square (a square of length 1) and inscribing a quadrant inside. A arbitrary number of points is then randomly scattered in the square. Since the area of the square is 1 and the area of the inscribed quadrant is π/4, the ratio of the number of points that land in the quadrant to the total number of points becomes an estimate of π/4, which is then multiplied by 4 to estimate π.
This method is used widely in mathematics and physics when a problem cannot be solved analytically.
The number of points can be set up to 50000 points. Hit the randomize button to randomize the placement of the points.
Research
[text]
Video
[text]
Version:
- http://weelookang.blogspot.com/2018/05/monte-carlo-pi-calculation-javascript.html
- http://www.euclides.dia.uned.es/simulab-pfp/curso_online/cap7_caseStudies/sec_MonteCarloPI.htm by Alfonso Urquia and Carla Martin-Villalba
Other Resources
[text]
Frequently Asked Questions: Monte Carlo Pi Calculation Simulation
- What is the Monte Carlo method for estimating Pi? The Monte Carlo method estimates Pi by simulating random events. In this simulation, it involves imagining throwing darts at a square containing an inscribed circle. The ratio of darts landing inside the circle to the total number of darts thrown approximates the ratio of the circle's area to the square's area. Since the area of a circle is πr² and the area of a square with side length 2r is (2r)², the ratio is (πr²)/(4r²) = π/4. Therefore, by multiplying the ratio of hits inside the circle to the total throws by 4, we can estimate the value of Pi.
- How does the provided JavaScript simulation applet work? The JavaScript simulation is a virtual lab that allows users to perform the Monte Carlo method to estimate Pi. It simulates randomly scattering points within a unit square (a square with sides of length 1). Inside this square, a quadrant (a quarter of a circle with a radius of 1) is conceptually inscribed. The applet counts the number of points that fall within this quadrant and the total number of points generated. By calculating the ratio of points in the quadrant to the total points and multiplying by 4, the simulation provides an approximation of Pi. Users can typically adjust the number of points ("throws") to see how the accuracy of the Pi estimation changes.
- Why is the Monte Carlo method useful? The Monte Carlo method is particularly useful for solving problems in mathematics and physics that are too complex or impossible to solve using traditional analytical methods. These are often problems involving randomness, high dimensionality, or intricate geometries. By using repeated random sampling, Monte Carlo methods can provide numerical approximations to these problems. In the context of Pi, it offers a different approach to understanding and approximating this fundamental constant compared to geometric series or analytical derivations.
- How does increasing the number of throws/points affect the accuracy of the Pi estimation in this simulation? According to the principle of the Monte Carlo method, increasing the number of random samples (in this case, the number of throws or scattered points) generally leads to a better approximation of the true value. With more points, the ratio of points landing within the inscribed quadrant to the total number of points will more closely reflect the true ratio of their areas (π/4). The simulation allows users to select a higher number of throws (up to 50,000 in some versions mentioned in the text), demonstrating this principle of improved accuracy with larger sample sizes.
- What is the relationship between the areas of the square and the inscribed circle (or quadrant) in this method? In the unit square implementation of the Monte Carlo Pi estimation, the square has an area of 1 x 1 = 1. The inscribed circle (with a radius of 0.5 if inscribed fully within the unit square, or a radius of 1 if a quadrant is considered within a unit square) has an area of πr². If a full circle of radius 0.5 is used, its area is π(0.5)² = π/4. The ratio of the circle's area to the square's area is (π/4)/1 = π/4. If a quadrant of radius 1 is used within a unit square, the quadrant's area is (1/4)π(1)² = π/4, and the ratio to the square's area (1) is still π/4. This ratio is key to the Monte Carlo estimation.
- How does this simulation relate to other methods of calculating Pi, such as Archimedes' algorithm mentioned in the text? The text explicitly mentions that there was a previous simulation based on Archimedes' algorithm. Archimedes' method was a deterministic geometric approach that involved approximating the circumference of a circle by calculating the perimeters of inscribed and circumscribed regular polygons with an increasing number of sides. This method provides rigorous bounds for Pi. In contrast, the Monte Carlo method is a probabilistic approach that relies on random sampling to estimate Pi. While Archimedes' method is deterministic and provides guaranteed bounds with more iterations, the Monte Carlo method is stochastic and its accuracy improves statistically with more trials. This simulation provides a visual and interactive way to understand a fundamentally different approach to approximating Pi.
- Who created this Monte Carlo Pi Calculation JavaScript Simulation Applet? The author of the Monte Carlo Pi Calculation JavaScript Simulation Applet is Carla Martín from the Dpto. de Informática y Automática, E.T.S. de Ingeniería Informática, UNED (Spain). The credits also mention Tan Wei Chiong and Loo Kang Wee.
- Where can this simulation be accessed and potentially embedded? The simulation can be accessed through the provided iframe embed code, which points to the URL: https://iwant2study.org/lookangejss/math/ejss_model_CalculoPI/CalculoPI_Simulation.xhtml. This indicates that the simulation is hosted on the iwant2study.org platform as part of the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore project. The embed code allows users to integrate this interactive model directly into other webpages. Additionally, the text mentions alternative versions accessible via specific URLs in blog posts and UNED websites.
- Details
- Written by Wei Chiong
- Parent Category: Mathematics
- Category: Numbers and Algebra
- Hits: 9425