Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits


 This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.; Francisco Esquembre; Felix J. Garcia Clemente
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.; Francisco Esquembre; Felix J. Garcia Clemente
Briefing Document: Primary School Numbers Applet
1. Overview
This document analyzes an educational resource: a JavaScript HTML5 applet designed for primary school students to learn about number properties (odd, even, multiples, and factors) within the range of 1 to 100. The applet is part of the Open Educational Resources/Open Source Physics @ Singapore initiative. The resource emphasizes interactive learning through a simulation model, making use of visual and hands-on approaches. The tool is designed for use across various platforms such as Android/iOS devices, Windows/MacOSX/Linux systems and ChromeBook laptops.
2. Main Themes
- Number Properties: The core focus is on understanding fundamental number properties:
- Odd and Even Numbers: The resource explicitly addresses these concepts, which are part of the Primary 3 syllabus. The teaching tips also highlight the use of real-world examples (lining up in pairs) to make the concepts tangible.
- Multiples: The applet aims to help students identify multiples of 1-digit numbers, listing up to the first 12 multiples, a core concept in Primary 4 and 5 math. The document also suggests associating this concept with "skip counting" which is a helpful technique.
- Factors: The applet covers finding factors of numbers up to 100 and the relationship between factors and multiples, which is also part of the Primary 4 and 5 syllabus. This is noted as the most difficult of the concepts but the applet uses a 'pairing' technique to aid in understanding.
- Interactive Learning: The applet leverages JavaScript and HTML5 to create an interactive simulation model. This approach aims to make learning more engaging and effective, compared to traditional methods. The applet can be embedded into webpages.
- Curriculum Alignment: The content is explicitly aligned with the Singaporean Primary School Mathematics curriculum for grades 3, 4 and 5. This is evident from the stated learning goals.
- Accessibility and Multi-Platform Support: The resource is designed to be accessible across different devices and operating systems (Android/iOS, Windows/MacOSX/Linux, Chromebooks), indicating a focus on broad reach.
- Open Educational Resource: As part of the Open Educational Resources/Open Source Physics @ Singapore initiative, the resource is freely available for use, adaptation and sharing, aligning with the principles of open education.
3. Key Ideas & Facts
- Target Audience: The applet is specifically designed for primary school students, primarily those in grades 3, 4, and 5 in Singapore, as aligned with the syllabus topics.
- Learning Goals (as mentioned in the document):Primary 3: "WHOLE NUMBERS Numbers up to 10 000 Include: • number notation and place values (thousands, hundreds, tens, ones), • reading and writing numbers in numerals and in words, • comparing and ordering numbers, • odd and even numbers, • number patterns".
- Primary 4 & 5: "Factors and multiples Include: • determining if a 1-digit number is a factor of a given number, • listing all factors of a given number up to 100, • finding the common factors of two given numbers, • recognising the relationship between factor and multiple, • determining if a number is a multiple of a given 1-digit number, • listing the first 12 multiples of a given 1-digit number, • finding the common multiples of two given 1-digit numbers. Exclude 'highest common factor' (H.C.F.) and 'lowest common multiple’ (L.C.M.)".
- Visual Aids: The resource uses visual aids and color-coding to help students identify patterns and relationships.
- "multiples of three, skip count three, color coded for ease of pattern recognition"
- "factors of a numbers colour coded for ease of pattern recognition 1x48 = 2x24 = 3x16 = 4x12 = 6x8 = 48".
- Concrete Examples: The document recommends using real-world examples (lining up in pairs) to explain even and odd numbers. "even numbers are easier to understand, ask pupils to line up in pairs, so if it is possible to pair up, the number of pupils is even." and "odd numbers is the opposite of even, again, ask pupils to line up in pairs, so if it is not possible to pair up, meaning one pupil has no partner, the number of pupils is odd."
- Teaching Tip: The teaching tip on pairing numbers for factors, which is color coded, highlights a potential method for helping students with what is seen as the most challenging concept, with an example of factors for number 48.
- App Availability: Links are provided for the app on Google Play Store (Android) and the Apple App Store (iOS).
- Versions: This is not the first iteration of the tool as the resource points to 3 separate versioning of it.
- Associated Concepts: The document highlights concepts to help in the teaching of this topic including: "multiples is easier if it is associated to skip count".
- Poem: A poem on even and odd numbers is used as an additional learning resource. "If you are an even number You always have a pair So if you look around Your buddy will always be there But ... If you are an odd number There's always a lonely one He looks around to find his buddy But he's the only one."
- Credits: The applet is credited to email address being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it., Francisco Esquembre and Felix J. Garcia Clemente.
- Licensing: The resource is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 Singapore License, with conditions for commercial use of the EasyJavaScriptSimulations Library.
- Related Resources: The document points to other educational resources (links) both for this topic specifically and other resources in different topic areas. There are over 100 links to other resources included in this document.
4. Implications
- The resource provides a valuable tool for educators teaching number properties to primary school students.
- The interactive and visual nature of the applet can enhance student engagement and learning.
- The open nature of the resource enables educators to adapt and use it in various educational settings.
- The many links to other resources contained in this document means there is a wealth of material from this source.
5. Conclusion
The "Primary School Numbers from 1 to 100" applet is a well-designed educational tool that uses an interactive approach to help students understand important mathematical concepts. Its alignment with the Singaporean curriculum, multi-platform accessibility, and open license make it a significant contribution to educational resources. The additional material provided (teaching tips, poem, links) greatly add to the utility of this resource.
Math Concepts Study Guide: Numbers 1-100
Quiz
Instructions: Answer the following questions in 2-3 complete sentences.
- What are the four main mathematical concepts explored using the applet for numbers 1-100?
- Explain the difference between an even and odd number.
- How can the "lining up in pairs" activity help students understand even and odd numbers?
- What are multiples of a number? Give an example.
- What are factors of a number? Give an example.
- How does the applet visually represent multiples and factors?
- What is the relationship between factors and multiples?
- Why is it helpful to use color-coding when learning about factors?
- According to the source, what mathematical concept is often considered the most difficult for students? Why?
- How can skip counting be used to teach multiples?
Quiz Answer Key
- The four main mathematical concepts explored are odd numbers, even numbers, multiples, and factors. The applet visually demonstrates these concepts using numbers from 1 to 100.
- An even number can be divided by two without a remainder, meaning it can be paired up evenly; an odd number leaves a remainder of one when divided by two, which means one is always left without a pair.
- The "lining up in pairs" activity allows students to physically visualize the concept of pairing in even numbers and the leftover single in odd numbers, making abstract concepts more concrete.
- Multiples of a number are the result of multiplying that number by any whole number; for example, the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, and so on.
- Factors of a number are whole numbers that divide evenly into that number; for example, the factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3, and 6.
- The applet uses color coding to show both multiples and factors, which helps with pattern recognition; in the case of factors, the pairings are also visually linked to make the combinations more concrete.
- Factors are numbers that divide into a given number, while multiples are the result of multiplying a number by another; they are related because factors can be multiplied to give a multiple, and they can also both be viewed as ways to represent a single number.
- Color-coding factors can help pupils notice the pairs that multiply to get the desired number, and it also can assist with remembering that you need to find all possible combinations.
- According to the source, factors are the most difficult for students to grasp, perhaps due to the more complex inverse relationship to multiples, and it can be tricky to learn all the combinations that give the desired product.
- Skip counting is a helpful tool for learning multiples because it represents multiples in an easy to understand sequence. For example, skip counting by 4 (4, 8, 12, 16...) demonstrates multiples of 4.
Essay Questions
Instructions: Answer the following questions in essay format, citing specific examples from the source to support your claims.
- Discuss the importance of using visual aids and concrete examples, like the applet and the "lining up in pairs" activity, in teaching abstract mathematical concepts such as factors and multiples.
- Analyze the different learning goals for students in Primary 3, 4, and 5 regarding whole numbers, factors, and multiples, as outlined in the source. What progression is evident in the curriculum?
- Explain how the strategies listed in the source – skip counting, color-coding, and pairing factors – contribute to the effectiveness of teaching factors and multiples.
- Based on the source, how do teaching strategies for even and odd numbers differ from those for factors and multiples? Why might these differences exist?
- Explore the potential benefits of using an interactive tool like the mentioned JavaScript applet in a classroom setting for teaching these mathematical concepts, and how does it compare to more traditional methods?
Glossary
Applet: A small application, often written in Java or HTML5, that runs within a web page. In this context, the applet is a tool for visualizing number concepts.
Even Number: A whole number that can be divided by 2 with no remainder.
Factor: A whole number that divides evenly into another whole number, with no remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
HTML5: The latest version of Hypertext Markup Language, used for structuring and presenting content on the World Wide Web, which can also include interactive elements such as the applet.
JavaScript: A programming language often used to create interactive effects within web browsers, used to power the number applet in this resource.
Multiple: The result of multiplying a whole number by another whole number. For example, the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, etc.
Odd Number: A whole number that leaves a remainder of 1 when divided by 2.
Open Educational Resources (OER): Teaching and learning materials that are free to use, adapt, and share. This source is an example of OER.
Skip Counting: A method of counting by intervals other than one. For example, skip counting by 5s would be: 5, 10, 15, 20, etc.
Apps
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ionicframework.numbers100app321231

https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ionicframework.numbersapp974975 older version
https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/even-odd-multiples-factors/id1196575475?ls=1&mt=8 iOS version
Sample Learning Goals
Topics
Primary 3
1 WHOLE NUMBERS
Numbers up to 10 000
Include:
• number notation and place values (thousands, hundreds, tens, ones),
• reading and writing numbers in numerals and in words,
• comparing and ordering numbers,
• odd and even numbers,
• number patterns
Primary 4
1 Whole Numbers
Factors and multiples
Include:
• determining if a 1-digit number is a factor of a given number,
• listing all factors of a given number up to 100,
• finding the common factors of two given numbers,
• recognising the relationship between factor and multiple,
• determining if a number is a multiple of a given 1-digit number,
• listing the first 12 multiples of a given 1-digit number,
• finding the common multiples of two given 1-digit numbers.
Exclude 'highest common factor' (H.C.F.) and 'lowest common multiple’ (L.C.M.).
Primary 5 Foundation Mathematics (Calculator is allowed unless otherwise stated)
1 Whole Numbers
Factors and multiples
Include:
• determining if a 1-digit number is a factor of a given number,
• listing all factors of a given number up to 100,
• finding the common factors of two given numbers,
• recognising the relationship between factor and multiple,
• determining if a number is a multiple of a given 1-digit number,
• listing the first 12 multiples of a given 1-digit number,
• finding the common multiples of two given numbers up to 12.
Exclude 'highest common factor' (H.C.F.) and 'lowest common multiple’ (L.C.M.).
Research
SSTRF_2017_ETD_3 Explore-Useful Learning Math Apps
Teaching Tips
even numbers are easier to understand, ask pupils to line up in pairs, so if it is possible to pair up, the number of pupils is even.
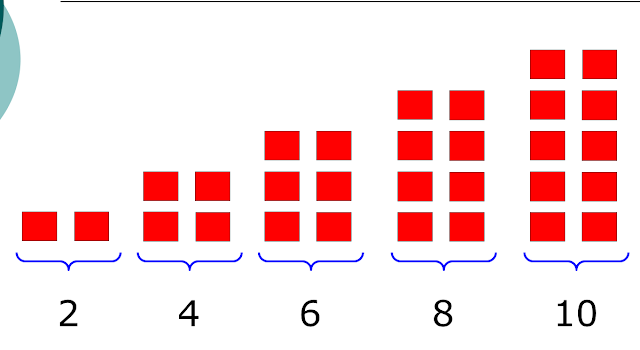 |
| taken from http://library.opal.moe.edu.sg/cos/o.x?ptid=84&c=/library/reslib&func=prop2&id=148606 by Abdul Hakim Bin Mohd Udori |
odd numbers is the opposite of even, again, ask pupils to line up in pairs, so if it is not possible to pair up, meaning one pupil has no partner, the number of pupils is odd.
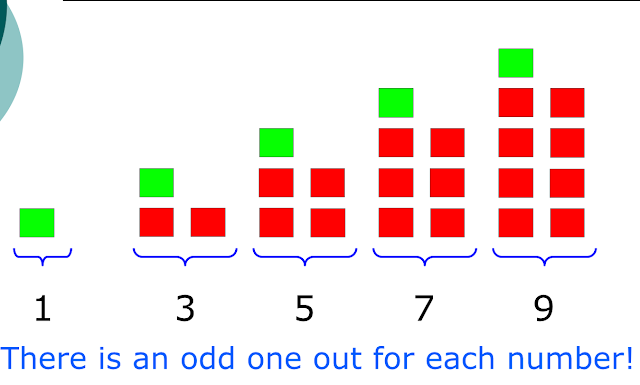 |
| taken from http://library.opal.moe.edu.sg/cos/o.x?ptid=84&c=/library/reslib&func=prop2&id=148606 by Abdul Hakim Bin Mohd Udori |
A Poem on Even & Odd Numbers by Marg Wadsworth
If you are an even number
You always have a pair
So if you look around
Your buddy will always be there
But ...
If you are an odd number
There's always a lonely one
He looks around to find his buddy
But he's the only one.
YouTube
10 Odd Todd and Even Steven swerdy45
multiples is easier if it is associated to skip count, so mulitples of three is skip count three, for example, 3 ,6, 9, 12, ....
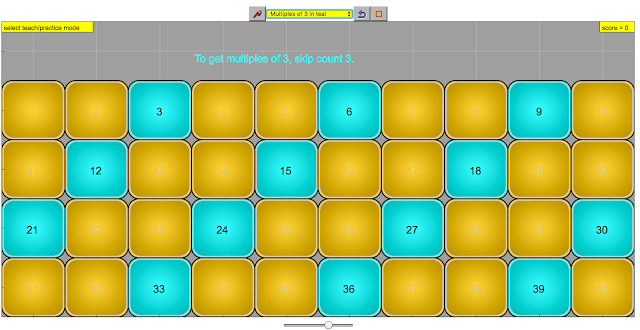 |
| multiples of three, skip count three, color coded for ease of pattern recognition |
factors is the hardest, pairing the first and the last numbers of the factors could help pupils realise
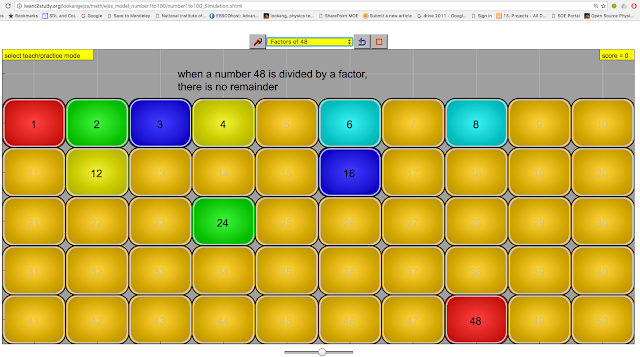 |
| factors of a numbers colour coded for ease of pattern recognition 1x48 = 2x24 = 3x16 = 4x12 = 6x8 = 48 |
Video
[text]
Version:
- http://weelookang.blogspot.sg/2016/06/numbers-1-to-100-properties.html JavaScript version
- based on an earlier swf file from Thong , Thong's files
- http://library.opal.moe.edu.sg/cos/o.x?c=/library/reslib&uid=0&ptid=84&func=view&id=266009&fext=.zip (login required)
Other Resources
Frequently Asked Questions: Numbers 1-100, Factors, and Multiples
- What are the main mathematical concepts covered in the "Primary School Numbers from 1 to 100" interactive resource?
- This resource focuses on foundational number concepts for primary school students, specifically working with whole numbers up to 100. It covers identifying odd and even numbers, understanding number notation and place values, reading and writing numbers, comparing and ordering them. It also delves into the concepts of factors and multiples, including listing factors of numbers up to 100, finding common factors, and understanding the relationship between factors and multiples. The resource also supports learning of multiples of 1-digit numbers.
- How does the resource help students understand even and odd numbers?
- The resource uses a visual and interactive approach to help students grasp the concept of even and odd numbers. The teaching tips in the resource suggest using real-world examples like lining students up in pairs to demonstrate that even numbers can be paired with no remainders, while odd numbers will always leave one unpaired. A poem is included reinforcing the idea of even numbers having a pair, while odd numbers are the "lonely ones."
- What is the relationship between factors and multiples, and how does the resource explain it?
- The resource emphasizes the connection between factors and multiples. A factor of a number divides into it evenly, while a multiple of a number is the result of multiplying that number by an integer. For example, it suggests that pairing the first and last numbers of a factor set could help students realise the relationship between factors. The resource also covers methods for determining if a number is a factor of another, and listing the first 12 multiples of a 1-digit number. It also provides a way to visually represent factors and multiples.
- How does the interactive simulation model aid in learning these concepts?
- The JavaScript HTML5 applet simulation model provides a hands-on way for students to explore numbers and their properties. The interactive format allows them to actively engage with the concepts, rather than passively receiving information. By interacting with the model, students can visually see how numbers are categorized, what their factors and multiples are, and gain a more intuitive understanding of the relationships between numbers.
- How is the concept of multiples explained in the resources, and what teaching aids are suggested?
- Multiples are introduced as related to skip counting. For example, multiples of three are taught by counting in threes: 3, 6, 9, 12, etc. Color coding is used in the resource to make it easier for pattern recognition with multiples. This emphasis on skip counting helps students to visually and kinesthetically connect with the concept of multiples.
- The resource mentions 'highest common factor' and 'lowest common multiple' are excluded. Why?
- The resource is designed for primary school students. 'Highest Common Factor' (HCF) and 'Lowest Common Multiple' (LCM) are more advanced topics that are usually introduced in later grades. By focusing on the fundamental concepts of factors and multiples, students build a solid base for later math concepts without overwhelming them with more complex processes at this stage.
- What are some additional resources that can support learning with the interactive model?
- The main resource is a JavaScript applet simulation model, but additional materials include a GeoGebra file for exploration. There are also multiple apps for iOS and Android, and earlier versions of the software. The inclusion of external websites and multiple formats makes the learning process accessible on a variety of devices and platforms.
- What technology is used to deliver this resource and why?
- The resource is built as a JavaScript HTML5 applet. This allows it to run directly in web browsers on a range of devices including laptops, desktops, tablets, and smartphones, without the need for additional software. This choice of technology makes the resource widely accessible and easily integrated into a variety of teaching and learning environments.
- Details
- Written by Loo Kang Wee
- Parent Category: Whole Numbers
- Category: 1. Numbers up to 100
- Hits: 12082


.png
)




