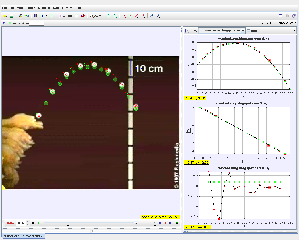

About
projectile motion modelling
For Teachers
- projectileTo_be_modelled.mov
- projectilemotionmodelold.html
Credits
Author: video: douglas brown, model: lookang
Contact: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
Projectile Motion Study Guide
Quiz
Instructions: Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
- What is Tracker software used for in the context of projectile motion?
- Briefly describe one example of a projectile motion simulation available on the Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore website.
- How can Tracker be used to analyze the motion of a basketball in a video recording?
- What types of operating systems is the Tracker software compatible with?
- What is the purpose of using simulations to study projectile motion?
- Can Tracker be used to model projectile motion beyond simple ballistic trajectories? Give an example.
- What are some advantages of using open educational resources for studying physics concepts like projectile motion?
- How can the study of projectile motion be applied to real-world scenarios? Provide an example.
- What other physics concepts, besides kinematics and dynamics, might be relevant to understanding projectile motion?
- Where can you find e-books related to the study of simple harmonic motion and gravity on the provided website?
Quiz Answer Key
- Tracker software is used to analyze video recordings of objects in motion, including projectiles. By tracking the object's position over time, Tracker can calculate its velocity, acceleration, and other kinematic and dynamic quantities.
- One example is the "Tracker Projectile Bouncing Model by RGS Soh Qian Ying." This simulation likely models the motion of a projectile, such as a ball, as it bounces, taking into account factors like energy loss and elasticity.
- By importing a video of a basketball being thrown, users can mark the basketball's position in each frame of the video. Tracker then uses this data to plot the basketball's trajectory, calculate its velocity, and analyze other aspects of its motion.
- The Tracker software is compatible with a wide range of operating systems, including Windows, MacOSX, and Linux. This makes it accessible to users on various platforms, including laptops and desktops.
- Simulations offer a controlled environment to study projectile motion, allowing for manipulation of variables and visualization of trajectories. They can help learners understand the underlying physics principles and explore different scenarios.
- Yes, Tracker can be used to model more complex projectile motion scenarios. For example, the "Tracker Modeling in Light Damping in Shuttle Cock Compared to a Ball" likely analyzes the effects of air resistance on projectile motion, which goes beyond simple ballistic trajectories.
- Open educational resources like the simulations on the website provide free access to high-quality learning materials. This promotes equitable learning opportunities and allows educators to customize their teaching approaches.
- Projectile motion principles are used in various fields. For instance, engineers designing a rocket launch must consider factors like initial velocity, launch angle, and air resistance to ensure the rocket reaches its intended target.
- Concepts like energy conservation, momentum, and forces (including gravity and air resistance) are crucial to understanding the complete picture of projectile motion.
- Direct links to e-books on SHM (Simple Harmonic Motion) and Gravity are provided within the "Credits" section of the website. These resources offer further in-depth study material on related physics topics.
Essay Questions
- Discuss the role of initial velocity and launch angle in determining the range and maximum height of a projectile. Use diagrams and equations to support your explanation.
- Explain how air resistance affects the trajectory of a projectile. How does the shape and mass of the projectile influence the impact of air resistance?
- Compare and contrast the motion of a projectile in a vacuum environment versus in an environment with air resistance.
- Describe how Tracker software can be used to investigate the conservation of energy in projectile motion. What data would you collect, and how would you analyze it?
- Design a simple experiment using readily available materials to demonstrate the principles of projectile motion. Explain the procedure, the data you would collect, and how you would analyze the data to draw conclusions.
Glossary of Key Terms
Projectile Motion: The motion of an object moving through the air, subjected only to the force of gravity.
Trajectory: The curved path that a projectile follows through the air.
Initial Velocity: The velocity of a projectile at the moment it is launched.
Launch Angle: The angle at which a projectile is launched with respect to the horizontal.
Range: The horizontal distance that a projectile travels before landing.
Maximum Height: The highest vertical point that a projectile reaches during its flight.
Air Resistance: A force that opposes the motion of an object through the air.
Tracker Software: A free video analysis and modeling tool used to study the motion of objects, including projectiles.
Simulation: A computer model that mimics the behavior of a real-world system, allowing for the study and manipulation of variables.
Open Educational Resources (OER): Freely accessible educational materials that can be used, modified, and shared.
Kinematics: The study of motion, describing an object's position, velocity, and acceleration without considering the forces causing the motion.
Dynamics: The study of forces and their effects on the motion of objects.
Tracker Projectile Motion FAQ
What is Tracker?
Tracker is a free and open-source video analysis and modeling tool built on the Java platform. It is designed for use in physics education and can be used to analyze the motion of objects in videos. Tracker allows users to:
- Track the motion of objects in videos. You can manually mark the position of an object in each frame of a video, or you can use Tracker's auto-tracking features to track objects automatically.
- Create models of the motion of objects. Tracker can fit a variety of mathematical models to the data you collect, allowing you to make predictions about the future motion of objects.
- Visualize the motion of objects. Tracker provides a variety of ways to visualize the motion of objects, including graphs, charts, and animations.
What are some common uses of Tracker?
Tracker can be used to analyze a wide variety of physical phenomena, including:
- Projectile motion: Analyze the trajectory of a ball thrown in the air, or study the factors that affect the range and height of a projectile.
- Circular motion: Investigate the relationship between the speed, radius, and period of an object moving in a circle.
- Simple harmonic motion: Study the motion of a mass on a spring or a pendulum, and explore the concepts of period, frequency, and amplitude.
- Collisions: Analyze the momentum and energy changes that occur during collisions between objects.
What types of videos can I analyze with Tracker?
You can use Tracker to analyze videos from a variety of sources, including:
- Your own videos: Record videos of physical phenomena using a smartphone, tablet, or digital camera.
- Videos from the internet: Download videos from YouTube, Vimeo, or other video-sharing websites.
- Tracker's built-in video library: Access a library of videos that have been specifically designed for use with Tracker.
What are some tips for getting started with Tracker?
Here are a few tips for getting started with Tracker:
- Watch the tutorial videos: Tracker comes with a series of tutorial videos that can help you learn the basics of the software.
- Start with a simple video: Choose a video of a simple physical phenomenon, such as a ball being dropped or a car driving at a constant speed.
- Use the auto-tracking features: Tracker's auto-tracking features can save you a lot of time and effort.
- Experiment with different models: Tracker can fit a variety of mathematical models to your data. Experiment with different models to see which one best describes the motion of the object in your video.
What operating systems does Tracker run on?
Tracker is a cross-platform application that runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Where can I find more information about Tracker?
The Open Educational Resources / Open Source Physics @ Singapore website is an excellent resource for information about Tracker. It provides links to downloads, documentation, tutorials, and examples.
What are some of the physics concepts that can be explored with Tracker?
Tracker can be used to investigate a wide range of physics concepts, including:
- Kinematics: Displacement, velocity, acceleration, and time.
- Dynamics: Force, mass, momentum, and energy.
- Gravitation: Gravitational force, gravitational potential energy, and escape velocity.
- Electromagnetism: Electric and magnetic fields, electric potential, and circuits.
- Waves: Wave motion, frequency, wavelength, and superposition.
Are there any limitations to using Tracker?
While Tracker is a powerful tool, it does have some limitations:
- Accuracy: The accuracy of your results will depend on the quality of your video and the accuracy of your tracking.
- Complexity: Analyzing complex videos can be time-consuming and challenging.
- Computational resources: Analyzing high-resolution videos or complex models may require a powerful computer.
- Details
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 01 Kinematics
- Hits: 6050
