v2: fixed the sliders of Mass to dynamically show at t =0
Credits
['mhchang', 'Jonathan', 'Loo Kang']
Translations
| Code | Language | Translator | Run | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
Credits
mhchang; Jonathan; Loo Kang
Sample Learning Goals
[text]
For Teachers
In this blog post, we explore a hands-on learning experience using the Archimedes Weight of Cube JavaScript Simulation Applet (HTML5). This simulation demonstrates fundamental concepts in fluid mechanics, specifically Archimedes' Principle and the forces acting on an object submerged in water.
Overview of the Simulation
 |
| https://sg.iwant2study.org/ospsg/index.php/951-archimedes-weight-of-cube link |
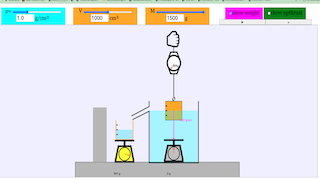
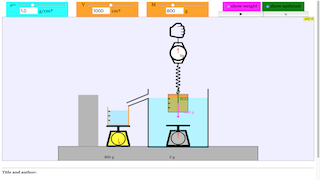
The interface includes key adjustable parameters:
- Density (ρ): This slider allows you to set the density of the fluid (in g/cm³).
- Volume (V): This controls the volume of the submerged object (in cm³).
- Mass (M): This is the mass of the cube (in grams).
In the visual setup, the simulation models a cube submerged in water with various forces acting upon it. It illustrates:
- Weight (shown in pink when selected): The gravitational force acting on the cube due to its mass.
- Upthrust (shown in green when selected): The buoyant force acting upward due to the fluid displaced by the submerged object.
The scales below display the net forces acting on the object when it is partially or fully submerged in water. The simulation emphasizes the buoyancy force and how it changes depending on the density and volume of the cube and the fluid in which it is submerged.
Key Learning Points
This applet serves as a visual tool to grasp Archimedes' Principle, which states:
Any object submerged in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
By adjusting the parameters in the simulation, students can investigate how:
- Density of the fluid: Affects the buoyant force. For example, increasing the fluid's density increases the upthrust acting on the cube.
- Volume of the object: Affects the amount of fluid displaced and therefore the magnitude of the upthrust.
- Mass of the object: Affects the weight of the cube, impacting whether the object sinks or floats, depending on the balance between weight and upthrust.
Educational Benefits
-
Interactive Learning: The ability to manipulate density, volume, and mass fosters an inquiry-based learning approach where students can experiment and directly observe the outcome of changing variables.
-
Visualizing Forces: The dynamic display of forces allows students to conceptualize the invisible forces at work in buoyancy and fluid displacement, which are often challenging to imagine without a practical demonstration.
-
Reinforcement of Theoretical Concepts: The simulation helps solidify students' understanding of fluid mechanics, buoyancy, and Archimedes' Principle, providing a bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical observation.
Classroom Use Cases
This simulation is ideal for use in lessons focused on:
- Physics: Particularly in units involving forces and fluids, density, and buoyancy.
- Real-World Applications: Understanding the science behind ships floating, submarines submerging, and the behavior of objects in different fluid mediums.
Conclusion
The Archimedes Weight of Cube Simulation provides an interactive, visual representation of buoyancy and Archimedes' Principle. It serves as an engaging tool for learners to explore fundamental physics concepts and enhance their conceptual understanding through experimentation. Teachers can incorporate this applet into lessons to support students' learning journeys in fluid mechanics.
Research
[text]
Video
[text]
Version
- https://weelookang.blogspot.com/2020/03/archimedes-weight-of-cube-javascript.html
- https://weelookang.blogspot.com/2024/10/archimedes-weight-of-cube-javascript.html
Other Resources
[text]
end faq
{accordionfaq faqid=accordion4 faqclass="lightnessfaq defaulticon headerbackground headerborder contentbackground contentborder round5"}
- Details
- Written by Jonathan
- Parent Category: 02 Newtonian Mechanics
- Category: 03 Mass Weight Density
- Hits: 7039