
About
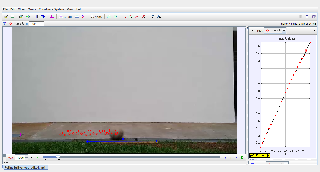
Uniform displacement of a rolling ball in horizontal direction.
For Teachers
- Rolling ball various_edited.mp4
- RateofchangeTanKimKiaRateofchange-lessonplan.doc
- RateofchangeGraphmotions-RateofChange.pptx
- Rateofchange-guidedlessonnotes-studentscopy.doc
- Rateofchange-guidedlessonnotes-studentscopy-answer.doc
Credits
Author: Tan Kim Kia
Contact: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
![]()
Document Brief: Title: "Tracker Rate of Change Constant Speed Rolling by Evergreen Sec Tan Kim Kia"
This document examines the motion of an object rolling at a constant speed, focusing on the rate of change of displacement (velocity) and analyzing factors contributing to maintaining uniform motion. Observations are made to understand the dynamics of constant speed rolling and the absence of acceleration in such scenarios.
Study Guide:
Objective: Investigate the motion of an object rolling at a constant speed and understand the relationship between displacement, time, and velocity.
Key Concepts:
-
Uniform Motion:
-
An object moving at constant speed covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
-
-
Velocity:
-
The rate of change of displacement with respect to time, calculated as .
-
-
Balanced Forces:
-
For constant speed, net force acting on the object is zero, implying forces like friction and applied force are balanced.
-
Experiment Overview:
-
Setup: A rolling object (e.g., a wheel or ball) is tracked using a video tracker or motion sensor on a flat, friction-managed surface.
-
Procedure:
-
Record the motion over a set distance.
-
Plot displacement-time and velocity-time graphs.
-
Verify uniformity in speed by analyzing the slope of displacement-time graphs.
-
-
Observation Points:
-
Linearity of displacement-time graph.
-
Consistency in velocity values over time.
-
Questions to Consider:
-
What conditions ensure the object rolls at a constant speed?
-
Answer: A flat surface with balanced forces, minimal resistance, and no external unbalanced forces.
-
-
How is velocity determined from the displacement-time graph?
-
Answer: The slope of the displacement-time graph represents velocity. A constant slope indicates constant speed.
-
-
What factors might cause deviations from constant speed?
-
Answer: Friction, surface irregularities, and changes in applied force can introduce acceleration or deceleration.
-
Applications:
-
Understanding principles of uniform motion in physics.
-
Designing systems with minimal resistance for steady operation.
-
Analyzing real-world applications like conveyor belts or wheeled transport.
FAQ:
-
What is constant speed? Constant speed refers to motion where an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time without changing velocity.
-
How do we verify uniform motion? By plotting a displacement-time graph and ensuring it is a straight line with a constant slope.
-
Why is there no acceleration in constant speed motion? Acceleration measures the rate of change of velocity. In constant speed motion, velocity remains unchanged, so acceleration is zero.
-
What practical examples use constant speed motion? Systems like conveyor belts, escalators, and vehicles in cruise control rely on principles of constant speed motion.
-
How does friction affect constant speed? Friction opposes motion, so to maintain constant speed, an equal and opposite force must counteract it, ensuring net force remains zero.
- Details
- Written by Kimkia
- Parent Category: 03 Motion & Forces
- Category: 01 Kinematics
- Hits: 7853
